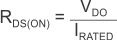SBVS372C December 2018 – December 2022 TPS7A25
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Orderable Information
8.3.2 Dropout Voltage
Dropout voltage (VDO) is defined as the input voltage minus the output voltage (VIN – VOUT) at the rated output current (IRATED), where the pass transistor is fully on. IRATED is the maximum IOUT listed in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. The pass transistor is in the ohmic or triode region of operation, and acts as a switch. The dropout voltage indirectly specifies a minimum input voltage greater than the nominal programmed output voltage at which the output voltage is expected to stay in regulation. If the input voltage falls to less than the nominal output regulation, then the output voltage falls as well.
For a CMOS regulator, the dropout voltage is determined by the drain-source on-state resistance (RDS(ON)) of the pass transistor. Therefore, if the linear regulator operates at less than the rated current, the dropout voltage for that current scales accordingly. Use Equation 1 to calculate the RDS(ON) of the device.