SLVSAB1G June 2011 – March 2020 TPS7A63-Q1 , TPS7A6401-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|14
Orderable Information
10.1.1.1 Example
If IOUT = 100 mA, VOUT = 5 V, VIN = 14 V, IQUIESCENT = 250 µA, and RθJA= 50°C/W, the continuous power dissipated in the device is 0.9 W. The rise in junction temperature due to power dissipation is 45°C. For a maximum junction temperature of 150°C, the maximum ambient air temperature at which the device can operate is 105°C.
For adequate heat dissipation, TI recommends soldering the thermal pad (exposed heat sink) to the thermal land pad on the PCB. Doing this provides a heat conduction path from the die to the PCB and reduces overall package thermal resistance. Power derating curves for the TPS7A63-Q1 and TPS7A6401-Q1 PWP package and TPS7A6333-Q1 DRK are comparable; see Figure 35.
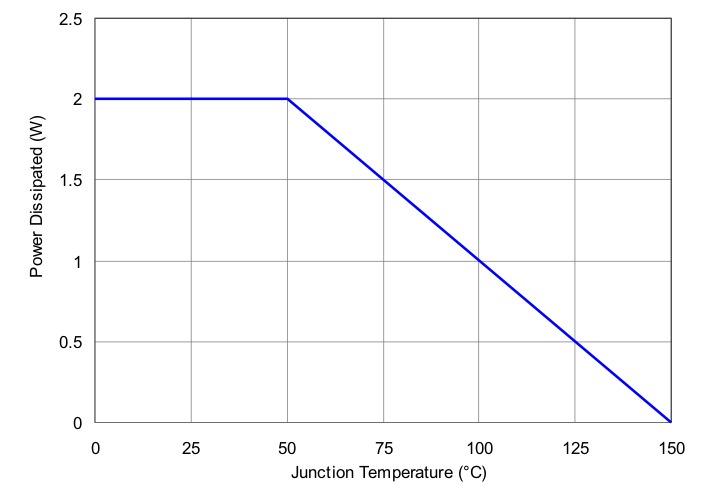 Figure 35. Power Derating Curve
Figure 35. Power Derating Curve For optimum thermal performance, TI recommends using a high-K PCB with thermal vias between the ground plane and solder pad or thermal land pad; see Figure 36 (a) and (b). Further, use a thicker ground plane and a thermal land pad with a larger surface area to inprove considerably the heat-spreading capabilities of a PCB. For a two-layer PCB, a bat wing layout can enhance the heat-spreading capabilities.
 Figure 36. Using Multilayer PCB and Thermal Vias for Adequate Heat Dissipation
Figure 36. Using Multilayer PCB and Thermal Vias for Adequate Heat Dissipation Keeping other factors constant, surface area of the thermal land pad contributes to heat dissipation only to a certain extent.