at TA = 25°C, VIN = 1.4 V or
VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.4 V (whichever is greater),
VBIAS = open, VOUT(NOM) = 0.8 V, VEN = 1.1 V,
COUT = 47 μF, CNR/SS = 0 nF, CFF = 0 nF, and PG
pin pulled up to VIN with 100 kΩ (unless otherwise noted)
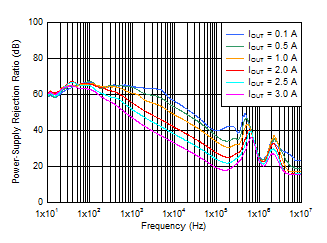
VIN = 1.1 V, VBIAS = 5 V,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10 nF |
Figure 6-1 PSRR
vs Frequency and IOUT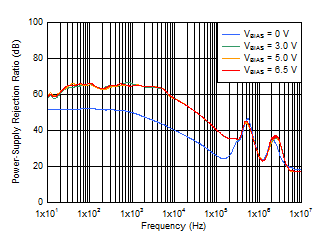
VIN = 1.4 V, IOUT = 1 A,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10 nF |
Figure 6-3 PSRR
vs Frequency and VBIAS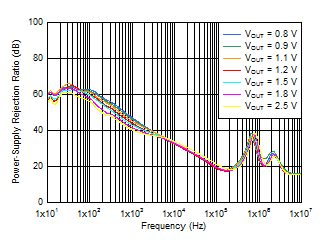
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V,
VBIAS = 5.0 V, IOUT = 3 A,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10
nF |
Figure 6-5 PSRR
vs Frequency and VOUT With Bias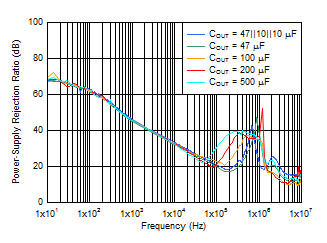
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V,
VOUT = 1 V, IOUT = 3 A,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10
nF |
Figure 6-7 PSRR
vs Frequency and COUT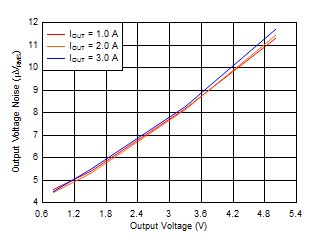
VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V and
VBIAS = 5 V for VOUT ≤ 2.2 V,
COUT = 47
μF || 10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10 nF, RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100
kHz |
Figure 6-9 Output Voltage Noise vs Output Voltage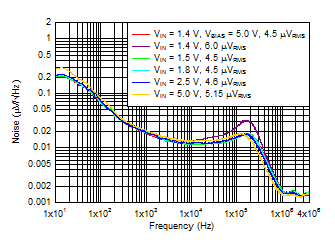
IOUT = 3 A, COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10 nF,
RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
| |
Figure 6-11 Output Noise vs Frequency and Input Voltage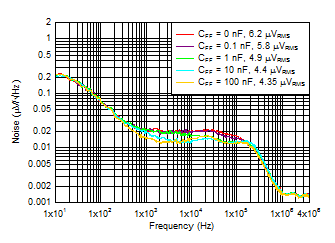
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V,
VBIAS = 5 V, IOUT = 3 A,
sequencing with a dc/dc converter and PG,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to
100 kHz |
Figure 6-13 Output Noise vs Frequency and CFF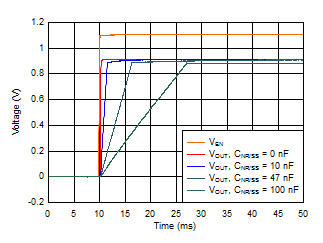
VIN = 1.2 V, VOUT = 0.9 V,
VBIAS = 5.0 V, IOUT = 3 A,
COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CFF = 10 nF |
Figure 6-15 Start-Up Waveform vs Time and CNR/SS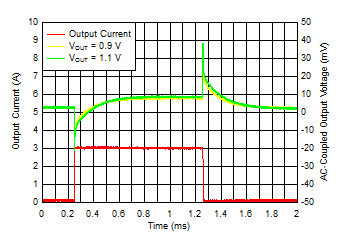
IOUT, DC = 100 mA,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS =
CFF = 10 nF, slew rate = 1 A/μs |
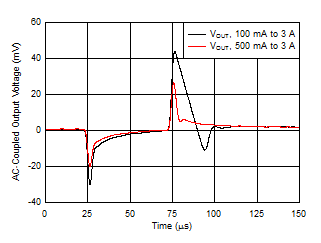
| VIN = 1.2 V, VBIAS = 5.0 V, COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = CFF = 10 nF, slew rate = 1 A/μs |
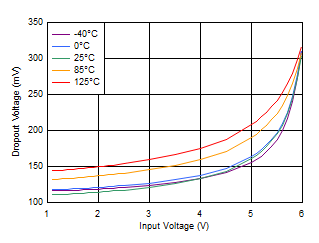
| IOUT = 3 A, VBIAS = 6.5 V |
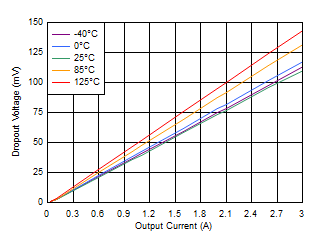 Figure 6-23 Dropout Voltage vs Output
Current With Bias
Figure 6-23 Dropout Voltage vs Output
Current With Bias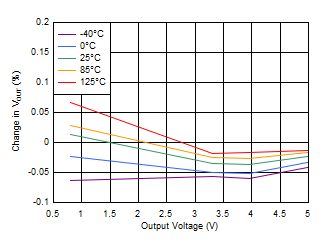 Figure 6-25 Load Regulation vs Output Voltage
Figure 6-25 Load Regulation vs Output Voltage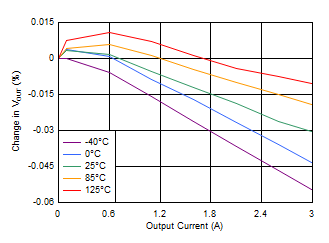 Figure 6-27 Load Regulation (3.3-V Output)
Figure 6-27 Load Regulation (3.3-V Output)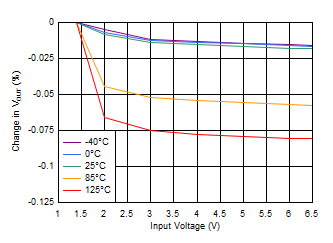
| VOUT = 0.8 V, VBIAS = 0 V, IOUT = 5 mA |
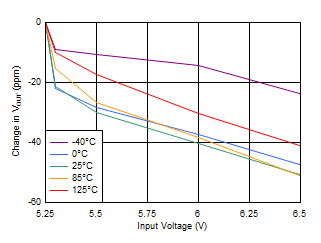 Figure 6-31 Line Regulation (5-V Output)
Figure 6-31 Line Regulation (5-V Output)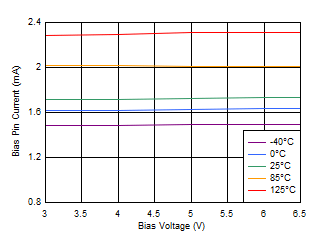 Figure 6-33 Quiescent Current vs Bias Voltage
Figure 6-33 Quiescent Current vs Bias Voltage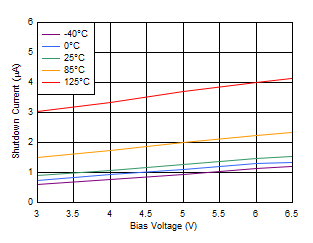 Figure 6-35 Shutdown Current vs Bias Voltage
Figure 6-35 Shutdown Current vs Bias Voltage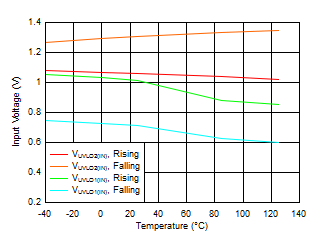 Figure 6-37 VIN UVLO vs Temperature
Figure 6-37 VIN UVLO vs Temperature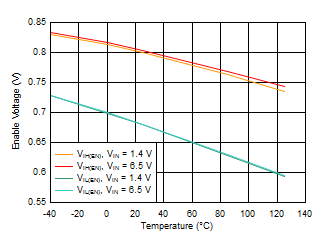 Figure 6-39 Enable Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 6-39 Enable Threshold vs Temperature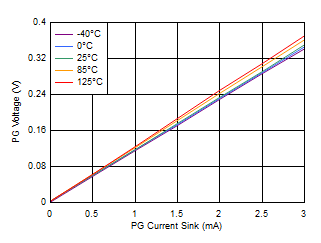 Figure 6-41 PG Voltage vs PG Current Sink
Figure 6-41 PG Voltage vs PG Current Sink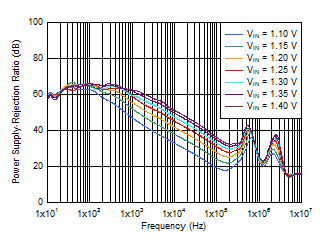
IOUT = 3 A, VBIAS = 5 V,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10 nF |
Figure 6-2 PSRR
vs Frequency and VIN With Bias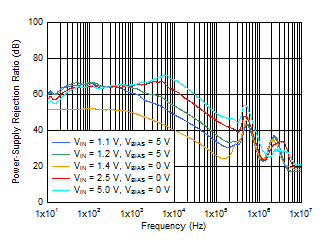
IOUT = 1 A, COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10
nF |
Figure 6-4 PSRR
vs Frequency and VIN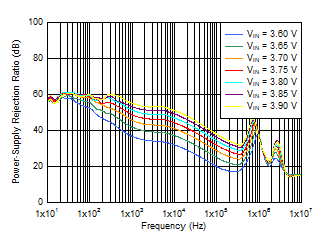
IOUT = 3 A, COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10
nF |
Figure 6-6 PSRR
vs Frequency and VIN for VOUT = 3.3 V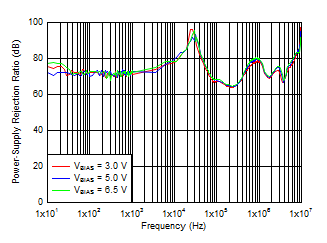
VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V,
VOUT = 1 V, IOUT = 3 A,
COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF,
CFF = 10 nF |
Figure 6-8 VBIAS PSRR vs Frequency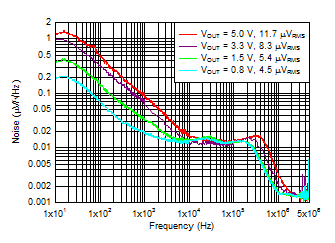
VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V and
VBIAS = 5 V for VOUT ≤ 2.2 V,
IOUT = 3 A,
COUT = 47 μF || 10 μF || 10 μF,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF,
RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
Figure 6-10 Output Noise vs Frequency and Output Voltage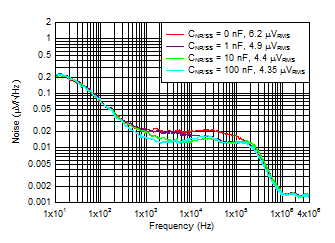
VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V,
VBIAS = 5 V, IOUT = 3 A,
COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF,
CFF = 10 nF, RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to
100 kHz |
Figure 6-12 Output Noise vs Frequency and CNR/SS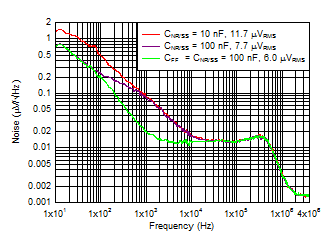
IOUT = 3 A, COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CFF = 10 nF,
RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to
100 kHz |
| |
Figure 6-14 Output Noise at 5.0-V Output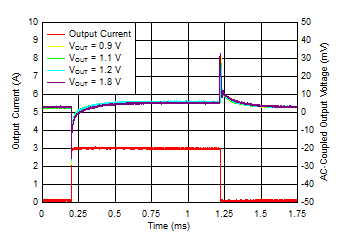
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V,
VBIAS = 5 V, IOUT, DC = 100
mA, slew rate = 1 A/μs, CNR/SS =
CFF = 10 nF, COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF |
Figure 6-16 Load
Transient vs Time and VOUT With Bias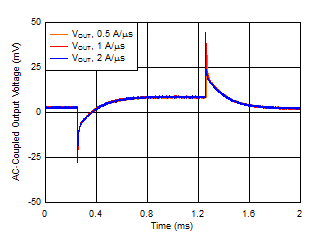
VOUT = 5 V, IOUT, DC = 100
mA, IOUT = 100 mA to 3 A,
COUT = 47 μF ||
10 μF || 10 μF, CNR/SS = CFF = 10
nF |
Figure 6-18 Load
Transient vs Time and Slew Rate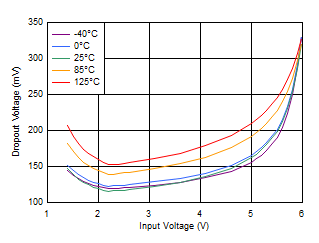 Figure 6-20 Dropout Voltage vs Input
Voltage Without Bias
Figure 6-20 Dropout Voltage vs Input
Voltage Without Bias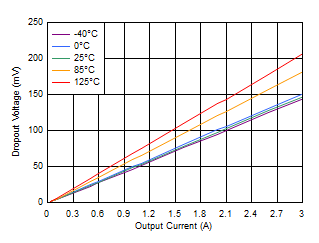 Figure 6-22 Dropout Voltage vs Output
Current Without Bias
Figure 6-22 Dropout Voltage vs Output
Current Without Bias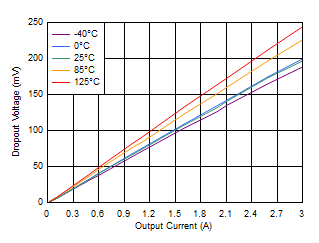 Figure 6-24 Dropout Voltage vs Output Current (High VIN)
Figure 6-24 Dropout Voltage vs Output Current (High VIN)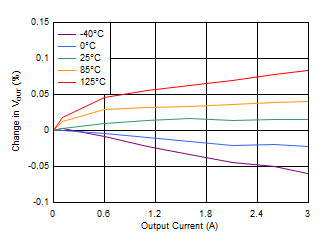 Figure 6-26 Load Regulation With
Bias
Figure 6-26 Load Regulation With
Bias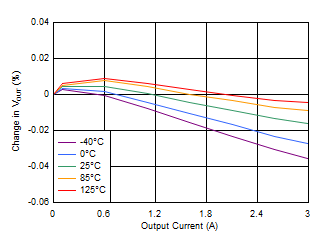 Figure 6-28 Load Regulation (5-V Output)
Figure 6-28 Load Regulation (5-V Output)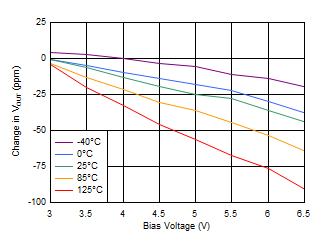
| VOUT = 0.8 V, VIN = 1.1 V, IOUT = 5 mA |
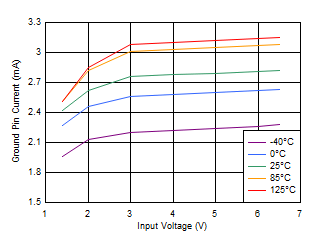 Figure 6-32 Quiescent Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 6-32 Quiescent Current vs Input Voltage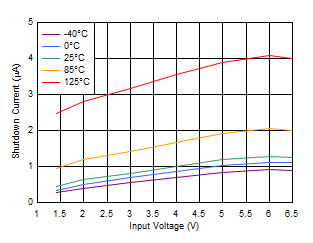 Figure 6-34 Shutdown Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 6-34 Shutdown Current vs Input Voltage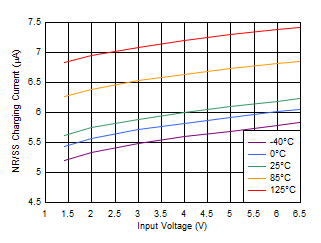 Figure 6-36 INR/SS Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 6-36 INR/SS Current vs Input Voltage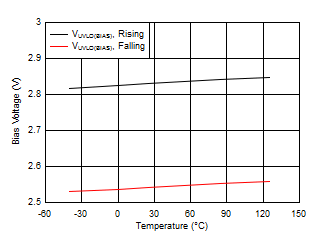 Figure 6-38 VBIAS UVLO vs Temperature
Figure 6-38 VBIAS UVLO vs Temperature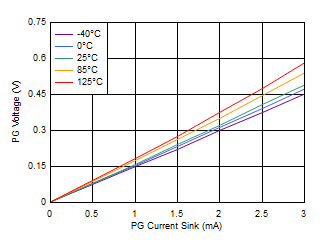 Figure 6-40 PG Voltage vs PG Current Sink
Figure 6-40 PG Voltage vs PG Current Sink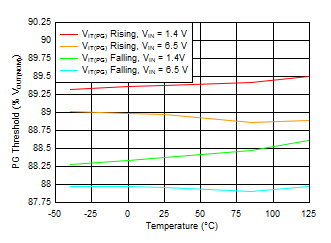 Figure 6-42 PG Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 6-42 PG Threshold vs Temperature








































