SLVSEN7D april 2019 – may 2023 TPS7H4001-SP
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics - All Devices
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: CDFP and KGD Options
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: HTSSOP (SHP) Option
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics: HTSSOP (QMLP) Option
- 7.9 Quality Conformance Inspection
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 VIN and Power VIN Pins (VIN and PVIN)
- 8.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.3 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Safe Start-Up Into Prebiased Outputs
- 8.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.6 Enable and Adjust UVLO
- 8.3.7 Adjustable Switching Frequency and Synchronization (SYNC)
- 8.3.8 Soft-Start (SS/TR)
- 8.3.9 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 8.3.10 Sequencing
- 8.3.11 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.12 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.14 Turn-On Behavior
- 8.3.15 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Operating Frequency
- 9.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Set Point
- 9.2.2.7 Output Voltage Feedback Resistor Selection
- 9.2.2.8 Compensation Component Selection
- 9.2.3 Parallel Operation
- 9.2.4 Application Curve
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDW|44
- KGD|0
- HKY|34
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDW|44
Orderable Information
8.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
The device uses a transconductance amplifier for the error amplifier and readily supports two of the commonly used frequency compensation circuits shown in Figure 8-10. In Type 2A, one additional high-frequency pole is added to attenuate high-frequency noise.
The following design guidelines are provided for advanced users who prefer to compensate using the general method.
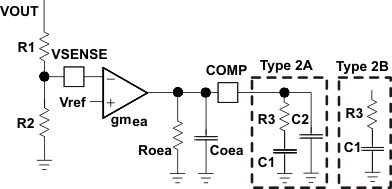 Figure 8-10 Types of
Frequency Compensation
Figure 8-10 Types of
Frequency CompensationThe general design guidelines for device loop compensation are as follows:
- Determine the crossover frequency fco. A good starting point is one-tenth of the switching frequency, ƒSW.
- R3 can be determined
by: Equation 19.

where gmea is the transconductance of the error amplifier (1800 μS), gmps is the transconductance of the power stage (40 S) and VREF is the reference voltage (0.604 V).
- Place a compensation zero at the
dominant pole calculated in Equation 20 using C1 and R3.
C1 can be determined by Equation 21.Equation 20. Equation 21.
Equation 21.
- C2 is optional. It can
be used to cancel the zero from the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of the
output capacitor COUT. Equation 22.
