SNVSBL0A November 2020 – December 2021 TPS7H4010-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Synchronous Step-Down Regulator
- 7.3.2 Auto Mode and FPWM Mode
- 7.3.3 Fixed-Frequency Peak Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.4 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.5 Enable and UVLO
- 7.3.6 Internal LDO, VCC_UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 7.3.7 Soft Start and Voltage Tracking
- 7.3.8 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 7.3.9 Frequency Synchronization and Mode Setting
- 7.3.10 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 7.3.11 Bootstrap Capacitor and VBOOT-UVLO
- 7.3.12 Power-Good and Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitors
- 8.2.2.8 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.2.9 BIAS
- 8.2.2.10 Soft Start
- 8.2.2.11 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.12 PGOOD
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RNP|30
- KGD|0
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RNP|30
Orderable Information
7.3.1 Synchronous Step-Down Regulator
The TPS7H4010-SEP is a synchronous buck converter with both power MOSFETs integrated in the device. Figure 7-1 shows a simplified schematic for synchronous and non-synchronous buck converters. The synchronous buck integrates both high-side (HS) and low-side (LS) power MOSFETs. The non-synchronous buck integrates HS MOSFET and works with a discrete power diode as LS rectifier.
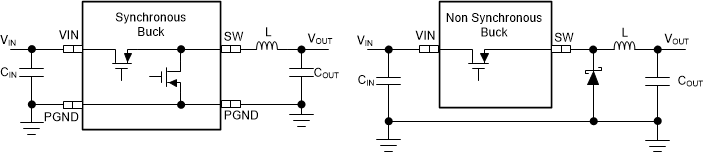 Figure 7-1 Simplified Synchronous vs Non-synchronous Buck Converters
Figure 7-1 Simplified Synchronous vs Non-synchronous Buck ConvertersA synchronous converter with integrated HS and LS MOSFETs offers benefits such as less design effort, lower external components count, reduced total solution size, higher efficiency at heavier load, easier PCB design, and more control flexibility.
The main advantage of a synchronous converter is that the voltage drop across the LS MOSFET is lower than the voltage drop across the power diode of a non-synchronous converter. Lower voltage drop translates into less power dissipation and higher efficiency. The TPS7H4010-SEP integrates HS and LS MOSFETs with very low on-time resistance to improve efficiency. It is especially beneficial when the output voltage is low. Because the LS MOSFET is integrated into the device, at light loads a synchronous converter has the flexibility to operate in either discontinuous or continuous conduction mode.
An integrated LS MOSFET also allows the controller to obtain inductor current information when the LS switch is on. It allows the control loop to make more complex decisions based on HS and LS currents. It allows the TPS7H4010-SEP to have peak and valley cycle-by-cycle current limiting for more robust protection.