SWCS059I March 2011 – November 2014 TPS80032
PRODUCT PREVIEW Information. Product in design phase of development. Subject to change or discontinuance without notice.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 Handling Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Thermal Characteristics for YFF Package
- 4.5
Electrical Characteristics
- 4.5.1 Switched-Mode Regulators
- 4.5.2 LDO Regulators
- 4.5.3 Reference Generator
- 4.5.4 Crystal Oscillator
- 4.5.5 RC Oscillators
- 4.5.6 CLK32KAUDIO Buffer
- 4.5.7 Backup Battery Charger
- 4.5.8 Switched-Mode System Supply Regulator
- 4.5.9 Battery Charger
- 4.5.10 Indicator LED Driver
- 4.5.11 USB OTG
- 4.5.12 Gas Gauge
- 4.5.13 GPADC
- 4.5.14 Thermal Monitoring
- 4.5.15 System Control Thresholds
- 4.5.16 Current Consumption
- 4.5.17 Digital Input Signal Electrical Parameters
- 4.5.18 Digital Output Signal Electrical Parameters
- 4.5.19 Digital Output Signal Timing Characteristics
- 4.6 Typical Characteristics
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Real-Time Clock
- 5.2 Clocks
- 5.3 Power Management
- 5.4 Reset System
- 5.5 System Control
- 5.6 System Voltage/Battery Comparator Thresholds
- 5.7 Power Resources
- 5.8 Backup Battery Charger
- 5.9
Battery Charging
- 5.9.1 Charger and System Supply Regulator Controller Operation
- 5.9.2 System Supply Regulator
- 5.9.3 Battery Charging
- 5.9.4 Anticollapse Loop and Supplement Mode
- 5.9.5 Battery Temperature Monitoring
- 5.9.6 Safety Timer and Charging Watchdog
- 5.9.7 Limit Registers
- 5.9.8 Battery Presence Detector
- 5.9.9 Indicator LED Driver
- 5.9.10 Supported Charging Sources
- 5.9.11 USB Suspend
- 5.9.12 Support for External Charging IC
- 5.9.13 Battery Charger Interrupts
- 5.10 USB OTG
- 5.11 Gas Gauge
- 5.12 General-Purpose ADC
- 5.13 Vibrator Driver and PWM Signals
- 5.14 Detection Features
- 5.15 Thermal Monitoring
- 5.16 I2C Interface
- 5.17 Secure Registers
- 5.18 Access Protocol
- 5.19 Interrupts
- 6Recommended External Components
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|155
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
4 Specifications
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All battery and system supply related input balls (LDOs and SMPSs) and supply voltage: _IN, VDD, VSYS_BB, CHRG_VSYS, CHRG_VBAT | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| All SMPS-related input balls _FDBK | –0.3 | SMPSmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Backup battery supply voltage VBACKUP | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| I/O digital supply voltage VIO | –0.3 | VIOmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Battery charger supply voltage VBUS | –0.3 | 20.0 | V | |
| Battery charger supply voltage VAC | –0.3 | 20.0 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_PMID | –0.3 | 20.0 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_SW, CHRG_BOOT | –0.7 | 20.0 | V | |
| Voltage difference between CHRG_CSIN and CHRG_CSOUT inputs | –7.0 | 7.0 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_VREF | –0.3 | 6.5 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_DET_N | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| All other charger analog-related input balls, such as CHRG_CSIN, CHRG_CSOUT, and CHRG_LED_IN | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| Voltage on the USB OTG ID ball | –0.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| Voltage on the VRTC GPADC balls: GPADC_IN0, GPADC_IN1, and GPADC_IN4 | –0.3 | VRTCmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Voltage on the VANA GPADC balls: GPADC_IN2, GPADC_IN3, GPADC_IN5, and GPADC_IN6 | –0.3 | VANAmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Voltage on the crystal oscillator OSC32KIN ball | –0.3 | VRTCmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Voltage on all other analog input balls such as GGAUGE_RESN and GGAUGE_RESP | –0.3 | VANAmax + 0.3 | V | |
| OTP memory supply voltage VPROG | –0.3 | 20.0 | V | |
| Voltage on VRTC digital input balls | –0.3 | VRTCmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Voltage on VIO digital input balls | –0.3 | VIOmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Voltage on VBAT digital input balls | –0.3 | VBATmax + 0.3 | V | |
| Junction temperature range | –45 | 150.0 | °C | |
| Peak output current on all terminals other than power resources | –5.0 | 5.0 | mA | |
4.2 Handling Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge (ESD) performance: | Human Body Model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS001(1) | All pins | –1 | 1 | kV |
| Charged Device Model (CDM), per JESD22-C101(2) | –250 | 250 | V | |||
4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All battery and system supply related input balls (LDOs and SMPSs) and supply voltage: _IN, VDD, VSYS_BB, CHRG_VSYS, CHRG_VBAT | 2.5 | 3.8 | 4.8 | V | |
| All SMPS-related input balls _FDBK | VOUTmin | VOUTmax | V | ||
| Backup battery supply voltage VBACKUP | 1.9 | 3.2 | 4.8 | V | |
| I/O digital supply voltage VIO | VIOmin | VIO | VIOmax | V | |
| Battery charger supply voltage VBUS | 0 | 5.0 | 6.7 | V | |
| Battery charger supply voltage VAC | 0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_PMID | 0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_SW and CHRG_BOOT | 0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_VREF | 0 | 5.0 | 6.5 | V | |
| Battery charger CHRG_DET_N | 0 | LDOUSB | 4.8 | V | |
| All other charger analog-related input balls such as CHRG_CSIN, CHRG_CSOUT, and CHRG_LED_IN | 0 | 3.8 | 4.8 | V | |
| Voltage on the USB OTG ID ball | 0 | LDOUSB | LDOUSBmax | V | |
| Voltage on the VRTC GPADC balls GPADC_IN0, GPADC_IN1, and GPADC_IN4 | VRTC | VRTCmax | V | ||
| Voltage on the VANA GPADC balls GPADC_IN2, GPADC_IN3, GPADC_IN5, and GPADC_IN6 | VANA | VANAmax | V | ||
| Voltage on the crystal oscillator OSC32KIN ball | VRTC | VRTCmax | V | ||
| Voltage on all other analog input balls such as GGAUGE_RESN and GGAUGE_RESP | VANA | VANAmax | V | ||
| OTP memory supply voltage VPROG | 8.0 | 10.0 | V | ||
| Voltage on VRTC digital input balls | VRTC | VRTCmax | V | ||
| Voltage on VIO digital input balls | VIO | VIOmax | V | ||
| Voltage on VBAT digital input balls | 0 | 3.8 | 4.8 | V | |
| Ambient temperature range | –40 | 27 | 85 | °C | |
| Junction temperature (TJ) | –40 | 27 | 125 | °C | |
| Storage temperature range | –65 | 27 | 150 | °C | |
| Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds) | 260 | °C | |||
4.4 Thermal Characteristics for YFF Package
| NAME | DESCRIPTION | (°C/W)(1) | AIR FLOW (m/s)(2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RΘJC | Junction-to-case (top) | 0.1 | 0.00 |
| RΘJB | Junction-to-board | 19.0 | 0.00 |
| RΘJA | Junction-to-free air | 37.7 | 0.00 |
| PsiJT | Junction-to-package top | 0.7 | 0.00 |
| PsiJB | Junction-to-board | 18.6 | 0.00 |
- JESD51-2, Integrated Circuits Thermal Test Method Environmental Conditions - Natural Convection (Still Air)
- JESD51-3, Low Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages
- JESD51-7, High Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages
- JESD51-9, Test Boards for Area Array Surface Mount Package Thermal Measurements
4.5 Electrical Characteristics
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
4.5.1 Switched-Mode Regulators
Table 4-1 through Table 4-3 lists the SMPS electrical characteristics.
Table 4-1 SMPS1 Switched-Mode Regulator Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | Input capacitor | 1.5 | 4.7 | µF | ||
| CO | Output filter capacitor: (3-A mode) | 11 | 22 | 29 | µF | |
| Output filter capacitor: (5-A mode) | 22 | 44 | 58 | |||
| Filter capacitor ESR | f = [1 to 10] MHz | 1 | 10 | 20 | ||
| mΩ | ||||||
| LO | Filter inductor: (3-A mode) | Single inductor | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.3 | µH |
| Filter inductor: (5-A mode) | Single inductor | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.3 | ||
| Filter inductor: (5-A mode) | Single inductor | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.65 | ||
| Filter inductor: (5-A mode) | Two inductors in parallel, total inductance (value of single inductor) | 0.2 (0.4) | 0.5 (1.0) | 0.65 (1.3) | ||
| DCRL | Filter inductor DC resistance | 50 | 100 | mΩ | ||
| Filter inductor Q factor | > 6 MHz | 20 | ||||
| NMOS current limit (high side) (3.0-A mode) |
ILIMIT[1:0] = 00 (No current limitation) | – | – | – | mA | |
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 01 (2.0 A) | 2800 | 3500 | 4200 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 10 (2.5 A) | 3500 | 4350 | 5150 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 11 (3.0 A) | 4100 | 5150 | 6200 | |||
| NMOS current limit (high side) (5-A mode) |
ILIMIT[1:0] = 00 (No current limitation) | – | – | – | mA | |
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 01 (3.3 A) | 3900 | 4800 | 5800 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 10 (4.2 A) | 4750 | 5900 | 7000 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 11 (5.0 A) | 5600 | 6900 | 8200 | |||
| Input current limit under short-circuit conditions | SW = 0 V | 10 | 20 | 30 | mA | |
| VINF | Input voltage (functional) | VSYS | max (VOUT + 0.4, 2.3) | 5.5 | V | |
| VINP | Input voltage (performance) | VSYS | max (VOUT + MinDOV, 2.5) | 3.8 | 4.8 | V |
| MinDOV | Dropout voltage (performance) (DOV = VIN – VOUT) |
IOUT = 2.0 A | 0.55 | V | ||
| IOUT = 2.5 A | 0.7 | |||||
| IOUT = 3.0 A | 0.85 | |||||
| IOUT = 3.3 A | 0.91 | |||||
| IOUT = 4.2 A | 1.15 | |||||
| IOUT = 5.0 A | 1.38 | |||||
| TDCOV | Total DC output voltage accuracy
(3-A mode) Includes voltage references, DC load/line regulations, process, and temperature (–1.8%/+3.2%) VOUT > 0.75 V (–2.8%/+4.2%) VOUT < 0.75 V |
0.6 V 1.0 V 1.2 V 1.3 V 1.8 V |
0.591 0.995 1.194 1.293 1.791 |
0.608 1.013 1.216 1.317 1.824 |
0.634 1.045 1.255 1.359 1.882 |
V |
| Total DC output voltage accuracy (5-A mode) Includes voltage references, DC load/line regulations, process, and temperature (–2.4%/+3.2%) VOUT > 0.75 V (–3.4%/+4.2%) VOUT < 0.75 V |
0.6 V 1.0 V 1.2 V 1.35 V 1.5 V |
0.587 0.989 1.187 1.334 1.483 |
0.608 1.013 1.216 1.367 1.519 |
0.634 1.045 1.255 1.411 1.568 |
V | |
| IOUT | Rated output current | PWM mode: SMPS1 (3-A mode) | 3000 | mA | ||
| PWM mode: SMPS1 (5-A mode)(1) | 5000 | |||||
| PFM mode | 200 | |||||
| VOUT | Output voltage, programmable | Low range | 0.6 | 1.3 | V | |
| High range | 0.7 | 1.4 | ||||
| Step size | 12.5 | mV | ||||
| Other selectable voltages | 1.35 1.5 1.8 1.9 2.1 |
V | ||||
| Extended voltage range, multiplier for nominal levels (enabled by OTP bit) | 3.0476 | |||||
| RV | Ripple voltage Measured with 20-MHz LPF |
PWM mode (3-A mode), ILOAD = 0 to IOUTmax | 10 | 20 | mVpp | |
| PWM mode (5-A mode), ILOAD = 0 to IOUTmax | 15 | 30 | ||||
| PFM mode, ∆VOUT/VOUT | 1.9 % | 3.8 % | p-p | |||
| DCLDR | DC load regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | PWM mode, (3-A mode): IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 0.25 % | 0.6 % | ||
| PWM mode, (5-A mode): IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 0.6 % | 1.2 % | ||||
| DCLNR | DC line regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | PWM mode, (3-A mode): VIN = VINPmin to VINPmax, IOUT = IOUTmax | 0.8 % | 1.6 % | ||
| PWM mode, (5-A mode): VIN = VINPmin to VINPmax, IOUT = IOUTmax | 1.4 % | 2.5 % | ||||
| TLDR | Transient load regulation (3-A mode) |
1.0 V IOUT = 10 to 500 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
12 | 20 | mV | |
| Transient load regulation (5-A mode) |
1.2 V IOUT = 1.5 to 5.0 A, tR/tF = 1 µs |
67 | 101 | mV | ||
| TLNR | Transient line regulation, (3-A mode), TLNR/VOUT | VIN step = ±600 mV Rise/fall time = 10 µs, VOUT < 0.75 V |
0.7 % | 1.4 % | ||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V | 0.5 % | 1.0 % | ||||
| Transient line regulation, (5-A mode), TLNR/VOUT | VIN step = ±600 mV Rise/fall time = 10 µs, VOUT < 0.75 V |
1.0 % | 1.9 % | |||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V | 0.8 % | 1.5 % | ||||
| tON | Off to on | IOUT = 200 mA, VOUT within accuracy limits | 350 | 500 | µs | |
| tOFF | On to off | IOUT = 0, VOUT down to 10% x VOUT | 250 | 500 | µs | |
| With 44 µF output capacitance: IOUT = 0, VOUT down to 10% x VOUT | 800 | |||||
| RPD | Pulldown resistor | Off mode | 3.8 | 7.5 | 15 | Ω |
| SR | Slew rate during rise time | From 0.1 × VOUT to 0.9 × VOUT | 30 | 150 | mV/us | |
| SRDVS | Slew rate | From VOUT = 0.6 V to VOUT = 1.3 V ±5%, ILOAD = ILOADmax, <SMPS>_CFG_STEP = 6 (minimum) | 11 | 12.7 | 14 | mV/µs |
| Output voltage settling time (normal mode) | From VOUT = 0.6 V to VOUT = 1.3 V ±5%, ILOAD = ILOADmax | 50 | 57 | 65 | µs | |
| Overshoot | 100 | mV | ||||
| fSW | Switching frequency | 2.6 | 3 | 3.5 | MHz | |
| IQOFF | Off ground current | Off mode, T = 25°C | 0.1 | 0.25 | µA | |
| Off mode | 0.2 | 1 | ||||
| IQ | On ground current | PFM mode, no switching | 25 | µA | ||
| PWM mode IOUT = 0 mA, VIN = 3.8 V |
12 | mA | ||||
Table 4-2 SMPS2 Switched-Mode Regulator Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | Input capacitor | 0.6 | 4.7 | µF | ||
| CO | Output filter capacitor: (Option 1) | 4 | 10 | 15 | µF | |
| Output filter capacitor: (Option 2) | 11 | 22 | 29 | |||
| Filter capacitor ESR | f = [1 to 10] MHz | 1 | 10 | 20 | mΩ | |
| LO | Filter inductor: (Option 1) | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.3 | µH | |
| Filter inductor: (Option 2) | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.65 | |||
| DCRL | Filter inductor DC resistance | 50 | 100 | mΩ | ||
| Filter inductor Q factor | > 6 MHz | 20 | ||||
| PMOS current limit (high side) | ILIMIT[1:0] = 00 (No current limitation) | – | – | – | mA | |
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 01 (1.4 A) | 2050 | 2550 | 3100 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 10 (1.8 A) | 2400 | 3000 | 3500 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 11 (2.5 A) | 3100 | 3800 | 4400 | |||
| Input current limit under short-circuit conditions | SW = 0 V | 10 | 20 | 30 | mA | |
| VINF | Input voltage (functional) | VSYS | max (VOUT + 0.4, 2.3) | 5.5 | V | |
| VINP | Input voltage (performance) | VSYS | max (VOUT + MinDOV, 2.5) | 3.8 | 4.8 | V |
| MinDOV | Dropout voltage (performance) (DOV = VIN – VOUT) |
IOUT = 0.5 A | 0.3(1) | V | ||
| IOUT = 0.8 A | 0.5 | |||||
| IOUT = 1.0 A | 0.6 | |||||
| IOUT = 1.2 A | 0.7 | |||||
| IOUT = 1.5 A | 0.9 | |||||
| IOUT = 1.8 A | 1.1 | |||||
| IOUT = 2.0 A | 1.2 | |||||
| IOUT = 2.2 A | 1.3 | |||||
| IOUT = 2.5 A (Option 1) | 1.5 | |||||
| IOUT = 2.5 A (Option 2) | 1.7 | |||||
| TDCOV | Total DC output voltage accuracy (Option 1) Includes voltage references, DC load/line regulations, process, and temperature (–1.2%/+2.4%) VOUT > 0.75 V |
0.6 V 1.1 V 1.225 V 1.3 V 1.35 V 1.8 V 1.9 V 2.1 V |
0.601 1.101 1.226 1.301 1.352 1.801 1.902 2.101 |
0.608 1.114 1.241 1.317 1.368 1.823 1.925 2.127 |
0.623 1.141 1.271 1.349 1.401 1.867 1.971 2.178 |
V |
| Total DC output voltage accuracy (Option 2) Includes voltage references, DC load/line regulations, process, and temperature (–1.7%/+2.4%) VOUT > 0.75 V |
0.6 V 1.1 V 1.225 V 1.3 V 1.35 V 1.8 V 1.9 V 2.1 V |
0.598 1.095 1.220 1.295 1.345 1.792 1.892 2.091 |
0.608 1.114 1.241 1.317 1.368 1.823 1.925 2.127 |
0.623 1.141 1.271 1.349 1.401 1.867 1.971 2.178 |
V | |
| IOUT | Rated output current | PWM mode | 2500 | mA | ||
| PFM mode | 200 | |||||
| VOUT | Output voltage, programmable | Low range | 0.6 | 1.3 | V | |
| High range | 0.7 | 1.4 | ||||
| Step size | 12.5 | mV | ||||
| Other selectable voltages | 1.35 1.5 1.8 1.9 2.1 |
V | ||||
| Extended voltage range, multiplier for nominal levels (enabled by OTP bit) | 3.0476 | |||||
| RV | Ripple voltage (Option 1) Measured with 20-MHz LPF |
PWM mode: IOUT = 0 to 2.2 A | 5 | 10 | mVpp | |
| PWM mode: IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 5 | 15 | mVpp | |||
| PFM mode, ∆VOUT/VOUT | 1.0 % | 2.0 % | p-p | |||
| Ripple voltage (Option 2) Measured with 20-MHz LPF |
PWM mode: ILOAD = 0 to IOUTmax | 15 | 25 | mVpp | ||
| PFM mode, VOUT > 0.75 V, ∆VOUT/VOUT | 1.0 % | 2.0 % | p-p | |||
| PFM mode, VOUT < 0.75 V, ∆VOUT/VOUT | 1.5 % | 3.0 % | ||||
| DCLDR | DC load regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | PWM mode, (Option 1): IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 0.25 % | 0.5 % | ||
| PWM mode, (Option 2): IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 0.25 % | 1.2 % | ||||
| DCLNR | DC line regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | PWM mode, VIN = VINPmin to VINPmax, IOUT = IOUTmax | 0.8 % | 1.6 % | ||
| TLDR | Transient load regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT
(Option 1) |
VOUT < 0.75 V IOUT = 0 to 150 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 50 to 250 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 350 to 800 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
3.3 % | 4.2 % | ||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V IOUT = 0 to 150 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 50 to 250 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 350 to 800 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
2.8 % | 3.6 % | ||||
| Transient load regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT
(Option 2) |
VOUT < 0.75 V IOUT = 0 to 150 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 50 to 250 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 350 to 800 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
1.5 % | 3.0 % | |||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V IOUT = 0 to 150 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 50 to 250 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 350 to 800 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
1.3 % | 2.5 % | ||||
| TLNR | Transient line regulation, TLNR/VOUT | VIN step = ±600 mV Rise/fall time = 10 µs, VOUT < 0.75 V |
0.7 % | 1.4 % | ||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V | 0.5 % | 1.0 % | ||||
| tON | Off to on | IOUT = 200 mA, VOUT within accuracy limits | 350 | 500 | µs | |
| tOFF | On to off | IOUT = 0, VOUT down to 10% x VOUT | 250 | 500 | µs | |
| RPD | Pulldown resistor | Off mode | 3.8 | 7.5 | 15 | Ω |
| SR | Slew rate during rise time | From 0.1 × VOUT to 0.9 × VOUT | 30 | 150 | mV/µs | |
| SRDVS | Slew rate | From VOUT = 0.6 V to VOUT = 1.3 V ±5%, ILOAD = ILOADmax, <SMPS>_CFG_STEP = 6 (minimum) | 11 | 12.7 | 14 | mV/µs |
| Output voltage settling time (normal mode) | From VOUT = 0.6 V to VOUT = 1.3 V ±5%, ILOAD = ILOADmax | 50 | 57 | 65 | µs | |
| Overshoot | 100 | mV | ||||
| fSW | Switching frequency | 4.5 | 6 | 6.6 | MHz | |
| IQOFF | Off ground current | Off mode, T = 25°C | 0.1 | 0.25 | µA | |
| Off mode | 0.2 | 1 | ||||
| IQ | On ground current | PFM mode, no switching | 35 | 50 | µA | |
| PWM mode, IOUT = 0 mA, VIN = 3.8 V |
12 | mA | ||||
Table 4-3 SMPS3, SMPS4, SMPS5 Switched-Mode Regulators Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | Input capacitor | 0.6 | 4.7 | µF | ||
| CO | 4 | 10 | 15 | µF | ||
| Filter capacitor ESR | f = [1 to 10] MHz | 1 | 10 | 20 | mΩ | |
| LO | Filter inductor | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.3 | µH | |
| DCRL | Filter inductor DC resistance | 50 | 100 | mΩ | ||
| Filter inductor Q factor | > 6 MHz | 20 | ||||
| PMOS current limit (high side) | ILIMIT[1:0] = 00 (No current limitation) | – | – | – | mA | |
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 01 | 1300 | 1620 | 2000 | |||
| ILIMIT[1:0] = 1X | 1640 | 2050 | 2520 | |||
| Input current limit under short-circuit conditions | SW = 0 V | 10 | 20 | 30 | mA | |
| VINF | Input voltage (functional) | VSYS | max (VOUT + 0.4, 2.3) | 5.5 | V | |
| VINP | Input voltage (performance) | VSYS | max (VOUT + MinDOV, 2.5) | 3.8 | 4.8 | V |
| MinDOV | Dropout voltage (performance) (DOV = VIN – VOUT) |
IOUT = 0.5 A | 0.41(1) | V | ||
| IOUT = 0.8 A | 0.65 | |||||
| IOUT = 1.0 A | 0.9 | |||||
| TDCOV | Total DC output voltage accuracy Includes voltage references, DC load/line regulations, process, and temperature (–1.2%/+2.4%) VOUT > 0.75 V |
0.6 V 1.1 V 1.225 V 1.3 V 1.35 V 1.8 V 1.9 V 2.1 V |
0.601 1.101 1.226 1.301 1.352 1.801 1.902 2.101 |
0.608 1.114 1.241 1.317 1.368 1.823 1.925 2.127 |
0.623 1.141 1.271 1.349 1.401 1.867 1.971 2.178 |
V |
| IOUT | Rated output current | PWM mode | 1100 | mA | ||
| PFM mode | 200 | |||||
| VOUT | Output voltage, programmable | Low range | 0.6 | 1.3 | V | |
| High range | 0.7 | 1.4 | ||||
| Step size | 12.5 | mV | ||||
| Other selectable voltages | 1.35 1.5 1.8 1.9 2.1 |
V | ||||
| Extended voltage range, multiplier for nominal levels (enabled by OTP bit) | 3.0476 | |||||
| RV | Ripple voltage Measured with 20-MHz LPF |
PWM mode: ILOAD = 0 to IOUTmax | 5 | 10 | mVpp | |
| PFM mode, ∆VOUT/VOUT | 1.0 % | 2.0 % | p-p | |||
| DCLDR | DC load regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | PWM mode: IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 0.25 % | 0.5 % | ||
| DCLNR | DC line regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | PWM mode, VIN = VINPmin to VINPmax, IOUT = IOUTmax | 0.8 % | 1.6 % | ||
| TLDR | Transient load regulation, ∆VOUT/VOUT | VOUT < 0.75 V IOUT = 0 to 150 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 50 to 250 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 150 to 400 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
2.0 % | 3.0 % | ||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V IOUT = 0 to 150 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 50 to 250 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns IOUT = 150 to 400 mA, tR/tF = 100 ns |
1.0 % | 1.5 % | ||||
| TLNR | Transient line regulation, TLNR/VOUT | VIN step = ±600 mV Rise/fall time = 10 µs, VOUT < 0.75 V |
0.7 % | 1.4 % | ||
| VOUT ≥ 0.75 V | 0.5 % | 1.0 % | ||||
| tON | Off to on | IOUT = 200 mA, VOUT within accuracy limits | 350 | 500 | µs | |
| tOFF | On to off | IOUT = 0, VOUT down to 10% x VOUT | 250 | 500 | µs | |
| RPD | Pulldown resistor | Off mode | 3.8 | 7.5 | 15 | Ω |
| SR | Slew rate during rise time | From 0.1 × VOUT to 0.9 × VOUT | 30 | 150 | mV/µs | |
| SRDVS | Slew rate SMPS5 |
From VOUT = 0.6 V to VOUT = 1.3 V ±5%, ILOAD = ILOADmax, <SMPS>_CFG_STEP = 6 (minimum) | 11 | 12.7 | 14 | mV/µs |
| Output voltage settling time (normal mode) SMPS5 | From VOUT = 0.6 V to VOUT = 1.3 V ±5%, ILOAD = ILOADmax | 50 | 57 | 65 | µs | |
| Overshoot | 100 | mV | ||||
| fSW | Switching frequency | 5.4 | 6 | 6.6 | MHz | |
| IQOFF | Off ground current | Off mode, T = 25°C | 0.1 | 0.25 | µA | |
| Off mode | 0.2 | 1 | ||||
| IQ | On ground current | PFM mode, no switching | 35 | 50 | µA | |
| PWM mode, IOUT = 0 mA, VIN = 3.8 V |
8 | mA | ||||
4.5.2 LDO Regulators
Table 4-4 lists the LDO regulators electrical characteristics.
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Table 4-4 LDO Regulators Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDO Regulators | ||||||
| CIN | Input filtering capacitor | Connected from LDO_IN to GND. Shared input tank capacitance (depending on platform requirements and power tree) | 0.3 | 2.2 | µF | |
| Connected from CHRG_PMID to GND | 0.9 | 4.7 | 6.5 | |||
| COUT | Output filtering capacitor | Connected from LDO output to GND | 0.6 | 2.2 | 2.7 | µF |
| RESR | Filtering DC capacitor ESR | < 100 kHz | 20 | 100 | 600 | mΩ |
| Filtering AC capacitor ESR | [1 to 10] MHz | 1 | 10 | 20 | mΩ | |
| VINF | Input voltage (functional) | VRTC, VBRTC: VSYS during ACTIVE, SLEEP and WAIT-ON state | 2.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| VRTC, VBRTC: VSYS during BACKUP state | 1.9 | 3.1 | ||||
| VRTC, VBRTC: VBACKUP during BACKUP state | 1.9 | 5.5 | ||||
| LDO1_IN, LDO2_IN, LDO3_IN, LDO4_IN, LDO5_IN, LDO6_IN, LDO7_IN, LDOLN_IN (VOUT ≥ 1.5 V) | TDCOV + DV – 0.2 | 5.5 | ||||
| LDO1_IN, LDO2_IN, LDO3_IN, LDO4_IN, LDO5_IN, LDO6_IN, LDO7_IN, LDOLN_IN (VOUT < 1.5 V) | 1.8 | 5.5 | ||||
| VANA | 2.3 | 5.5 | ||||
| LDOUSB: Supplied from VSYS | 3.5 | 5.5 | ||||
| LDOUSB: Supplied from CHRG_PMID | 3.5 | 6.8 | ||||
| VINP | Input voltage (performance) | VRTC, VBRTC | 2.5 | 3.8 | 4.8 | V |
| VANA | 2.5 | 3.8 | 4.8 | |||
| LDO1_IN, LDO2_IN, LDO3_IN, LDO4_IN, LDO5_IN, LDO6_IN, LDO7_IN, LDOLN_IN (VOUT ≥ 1.5 V) | TDCOV + DV | 3.8 | 4.8 | |||
| LDO1_IN, LDO2_IN, LDO3_IN, LDO4_IN, LDO5_IN, LDO6_IN, LDO7_IN, LDOLN_IN (VOUT < 1.5 V) | 1.8 | 3.8 | 4.8 | |||
| LDOUSB: from VSYS | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.8 | |||
| LDOUSB: from CHRG_PMID, OVV protection | 4.3 | 5.0 | 5.5 | |||
| TDCOV | Total DC output voltage accuracy Includes voltage references, DC load/line regulations, process and temperature (–1.7%/1.2%), _IN ≥ 2.5 V (–3.0%/1.2%), _IN < 2.5 V and VOUT < 1.5 V (except VRTC, VBRTC and VANA) |
1.0 V, _IN ≥ 2.5 V 1.0 V, _IN < 2.5 V 1.2 V, _IN ≥ 2.5 V 1.2 V, _IN < 2.5 V 1.3 V, _IN ≥ 2.5 V 1.3 V, _IN < 2.5 V 1.8 V 1.9 V 2.0 V 2.1 V 2.2 V 2.3 V 2.4 V 2.5 V 2.75 V 2.8 V 2.9 V 3.0 V 3.3 V 3.3 V (LDOUSB) |
1.001 0.987 1.202 1.185 1.301 1.283 1.801 1.902 2.002 2.102 2.203 2.302 2.402 2.503 2.753 2.802 2.903 3.003 3.304 3.245 |
1.018 1.018 1.222 1.222 1.323 1.323 1.832 1.934 2.036 2.138 2.240 2.341 2.443 2.545 2.800 2.850 2.952 3.054 3.359 3.301 |
1.030 1.030 1.236 1.236 1.339 1.339 1.854 1.957 2.060 2.163 2.266 2.369 2.472 2.575 2.834 2.884 2.987 3.090 3.399 3.341 |
V |
| VBRTC VRTC VANA |
1.550 1.801 2.102 |
1.805 1.832 2.138 |
1.854 1.890 2.163 |
V | ||
| DV | Dropout voltage _IN ≥ 2.3 V |
LDO6, LDOLN: IOUT = IOUTmax | 150 | mV | ||
| LDO5, LDO7: IOUT = 50 mA | 140 | |||||
| LDOUSB | 200 | |||||
| LDO1, LDO2, LDO3, LDO4, LDO5, LDO7, VRTC: VINPmin = TDCOV + DV | 300 | |||||
| Dropout voltage _IN ≥ 1.8 V |
LDO6, LDOLN: IOUT = IOUTmax | 250 | ||||
| LDO1, LDO2, LDO3, LDO4, LDO5, LDO7: VINPmin = TDCOV + DV | 400 | |||||
| IOUT | Rated output current | VBRTC | 1.5 | mA | ||
| VANA, VRTC | 25 | |||||
| LDOLN | 50 | |||||
| LDO1: VOUT ≤ 2.75 V | 50 | |||||
| LDO1: VOUT ≥ 2.8 V | 80 | |||||
| LDOUSB | 100 | |||||
| LDO2, LDO3, LDO4, LDO5, LDO6, LDO7 | 200 | |||||
| LDO6 (DV = 300 mV, VOUT ≥ 1.8 V) | 250 | |||||
| VOUT | Output voltage, programmable (except VRTC, VBRTC and VANA) |
Range | 1.0 | 3.3 | V | |
| Step size | 100 | mV | ||||
| Additional selectable voltage level | 2.75 | V | ||||
| ILIMIT | Load current limitation | VANA, VRTC, LDO1, LDOLN | 100 | 250 | 400 | mA |
| LDOUSB | 150 | 250 | 600 | |||
| LDO2, LDO3, LDO4, LDO5, LDO6, LDO7 | 400 | 650 | 900 | |||
| DCLDR | DC load regulation, ∆VOUT / VOUT | IOUT = 0 to IOUTmax | 4 | 10 | mV | |
| DCLNR | DC line regulation, ∆VOUT / VOUT | VIN = VINPmin to VINPmax
IOUT = IOUTmax |
0.1 % | 0.2 % | ||
| tON | Turn-on time | IOUT = 0 , VOUT = 0.1 V up to VOUTmin | 100 | 500 | µs | |
| tOFF | Turn-off time (except VRTC and VBRTC) | IOUT = 0, VOUT down to 10% x VOUT | 250 | 500 | µs | |
| RPD | Pulldown resistor (except VRTC and VBRTC) | Off mode | 40 | 60 | 80 | Ω |
| PSRR | Power supply ripple rejection (Except LDO1) |
f = 217 Hz, IOUT = IOUTmax | 45 | 90 | dB | |
| f = 50 kHz, IOUT = IOUTmax | 35 | 45 | ||||
| f = 1 MHz, IOUT = IOUTmax | 20 | 35 | ||||
| Power supply ripple rejection (LDO1: DV > 550 mV) |
f = 217 Hz, IOUT = IOUTmax | 45 | 90 | |||
| f = 50 kHz, IOUT = IOUTmax | 35 | 45 | ||||
| f = 1 MHz, IOUT = IOUTmax | 20 | 35 | ||||
| IQOFF | Off ground current | Off mode, T = 25°C | 0.05 | 0.15 | µA | |
| Off mode | 0.2 | 1 | ||||
| IQ0 | On ground current | IOUT = 0, (except LDOLN, LDOUSB, VANA, VRTC, VBRTC) | 12 | 18 | 29 | µA |
| IOUT = 0, LDOLN | 75 | 150 | 175 | |||
| IOUT = 0, LDOUSB, from VSYS, ACTIVE state | 60 | |||||
| IOUT = 0, LDOUSB, from VSYS, SLEEP state | 40 | |||||
| IOUT = 0, LDOUSB, from CHRG_PMID | 20 | |||||
| αQ | On ground current coefficient On mode, IQOUT = IQ0 + αQ × IOUT |
IOUT < 100 µA | 4 % | |||
| 100 µA < IOUT < 1 mA | 2 % | |||||
| IOUT > 1 mA | 1 % | |||||
| TLDR | Transient load regulation, ∆VOUT / VOUT | On mode, IOUT = 10 mA to IOUTmax / 2, tR = tF = 1 µs |
–25 | 28 | mV | |
| On mode, IOUT = 100 µA to IOUTmax / 2, tR = tF = 1 µs |
–50 | 33 | ||||
| TLNR | Transient line regulation, ∆VOUT / VOUT (except LDO6) | VIN step = 600 mVPP, tR = tF = 10 µs | 0.25 % | 0.6 % | ||
| Transient line regulation, ∆VOUT / VOUT (LDO6) | VIN step = 600 mVPP, tR = tF = 10 µs | 0.25 % | 1.0 % | |||
| Vnoise | Noise (except LDOLN) | 100 Hz < f < 10 kHz | 5000 | 8000 | nV/√Hz | |
| 10 kHz < f < 100 kHz | 1250 | 2500 | ||||
| 100 kHz < f < 1 MHz | 150 | 300 | ||||
| f > 1 MHz | 250 | 500 | ||||
| Noise (LDOLN) | 100 Hz < f < 5 kHz | 200 | 400 | nV/√Hz | ||
| 5 kHz < f < 400 kHz | 62 | 125 | ||||
| 400 kHz < f < 10 MHz | 25 | 50 | ||||
| LDO3 When Used As Vibrator Driver | ||||||
| Output regulated output range | Configurable step of 100 mV | 1.0 | 3.3 | V | ||
| COUT | Output filtering capacitor | Connected between LDO3 output and GND | 0.6 | 2.2 | 2.7 | µF |
| LVibrator | Vibrator load inductance | 70 | 350 | 700 | µH | |
| RVibrator | Vibrator load resistance | 15 | 40 | 50 | Ω | |
4.5.3 Reference Generator
Table 4-5 lists the reference generator electrical characteristics.
Table 4-5 Reference Generator Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COUT | Filtering capacitor | Connected between VBG and REFGND | 30 | 100 | 150 | nF |
| RBias | Biasing resistor (±1%) at 25°C | Connected between IREF and REFGND | 505 | 510 | 515 | kΩ |
| Biasing resistor (±1%) temperature coefficient | 50 | ppm/°C | ||||
| VINP | Input voltage VINP | Performance | 1.9 | 3.8 | 5.5 | V |
| IQ | Ground current | 15 | 20 | 40 | µA | |
| tstartup | Start-up time | 1 | 3 | ms | ||
4.5.4 Crystal Oscillator
Table 4-6 lists the crystal oscillator electrical characteristics.
Table 4-6 Crystal Oscillator Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal Characteristics | ||||||
| fosc | Crystal frequency | at specified load capacitor value | 32768 | Hz | ||
| Crystal tolerance | T = 25°C | –20 | 0 | 20 | ppm | |
| B | Secondary temperature coefficient | –0.04 | –0.035 | –0.03 | ppm/°C2 | |
| RESR | Crystal series resistor | at fundamental frequency | 90 | kΩ | ||
| DL | Operating drive level | 0.1 | 0.5 | µW | ||
| CL | Crystal load capacitor (according to crystal data sheet) | 12.5 | pF | |||
| Cshunt | Shunt capacitor | 1.4 | 2.6 | pF | ||
| Q | Quality factor | 8000 | 80000 | |||
| Crystal Oscillator External Components | ||||||
| VRTC power supply external filtering capacitor | OSC32KCAP | 0.6 | 2.2 | 2.7 | µF | |
| CLoad | Load capacitors on OSC32KIN and OSC32KOUT External capacitor includes the parasitics of PCB |
Normal and high-performance (HP) mode: External capacitor Internal capacitance |
9 8 |
15 10 |
17 12 |
pF |
| Backup mode: External capacitor Internal capacitance |
9 0 |
15 0 |
17 0 |
|||
| Frequency accuracy (taking into account crystal tolerance and internal load capacitors variation) | at 25°C, normal and HP modes | –30 | 0 | 30 | ppm | |
| at 25°C, backup mode | –80 | 0 | 80 | |||
| Oscillator capacitor ratio: COSC32KIN/ COSC32KOUT | 1 | |||||
| Square Wave Input Clock for Bypass | ||||||
| Input bypass clock OSC32KIN input OSC32KOUT floating |
Frequency | 32768 | Hz | |||
| Duty cycle | 40 | 50 % | 60 % | |||
| Rise and fall time (10% to 90%) | 10 | 20 | ns | |||
| Setup time | 1 | ms | ||||
| Crystal Oscillator Characteristics | ||||||
| Frequency temperature coefficient | Oscillator contribution in normal and HP modes (not including the crystal variations) | ±0.5 | ppm/°C | |||
| SSB phase noise at a 1-kHz offset from the carrier | HP mode OSC_HPMODE = 1 | –125 | dBc/Hz | |||
| SSB phase noise at a 100-Hz offset from the carrier | HP mode OSC_HPMODE = 1 | –105 | dBc/Hz | |||
| Cycle jitter short term (peak-to-peak) | Normal mode OSC_HPMODE = 0 | 25 | ns | |||
| Integrated jitter (HP mode) | 20 Hz to 20 kHz flat | 0.86 | nsRMS | |||
| 80 Hz to 20 kHz flat | 0.43 | |||||
| Tstartup | Startup time for power on | Shunt capacitor ≤ 1.4 pF | 300 | ms | ||
| Shunt capacitor 1.4 to 2.6 pF | 400 | |||||
| Sixth harmonic mode rejection RS32/RS200 | Oscillator ratio between negative resistance at 32 kHz and negative resistance at 200 kHz (sixth harmonic) | 10 | ||||
| IQ | Ground current | Crystal mounted: - Backup mode (at 25°C) - Normal mode: OSC_HPMODE = 0 - HP mode: OSC_HPMODE = 1 - Start-up (boost) phase |
1.5 3 5 20 |
µA | ||
| Duty cycle CLK32KAO/CLK32KG | Logic output signal | 40 | 50 % | 60 % | ||
| TRise,TFall | Rise and fall time (10% to 20%) | CLK32KAO/CLK32KG | 5 | 20 | 100 | ns |
4.5.5 RC Oscillators
Table 4-7 lists the RC oscillators electrical characteristics.
Table 4-7 RC Oscillators Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32-kHz RC Oscillator | ||||||
| fOUT | Output frequency | 32768 | Hz | |||
| Output frequency accuracy | After trimming | –10 % | 10 % | |||
| Cycle jitter (RMS) | 10 % | |||||
| D | Output duty cycle | 40 % | 50 % | 60 % | ||
| Settling time | 150 | µs | ||||
| IQ | Active current consumption | 4 | 8 | µA | ||
| IQOFF | Power-down current | 30 | nA | |||
| 6-MHz RC Oscillator | ||||||
| fOUT | Output frequency | 6 | MHz | |||
| Output frequency accuracy | After trimming | –10 % | 0 % | 10 % | ||
| Cycle jitter (RMS) | 5 % | |||||
| D | Output duty cycle | 40 % | 50 % | 60 % | ||
| Settling time | 5 | µs | ||||
| IQ | Active current consumption | 35 | 70 | µA | ||
| IQOFF | Power-down current | 50 | nA | |||
4.5.6 CLK32KAUDIO Buffer
Table 4-8 lists the CLK32AUDIO buffer electrical characteristics.
Table 4-8 CLK32KAUDIO Buffer Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Settling time | 25 | 50 | µs | |||
| IQ | Active current consumption | 5 | 7 | 10 | µA | |
| IQOFF | Power down current | 30 | nA | |||
| VHOUT | High output level | VRTC supply | 1.832 | V | ||
| Duty cycle degradation contribution | –2 % | 2 % | ||||
| Integrated jitter contribution | 20 Hz to 20 kHz flat 80 Hz to 20 kHz flat |
25 10 |
50 20 |
psRMS | ||
| CLoad | External output load | 5 | 10 | 50 | pF | |
| TRise, TFall |
Output rise/fall time | Output load = 10 pF | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | ns |
| IOUT | Output drive strength | VOL = 0.2 V | –1 | –2 | mA | |
| VOH = VHOUT – 0.2 V | 1 | 2 | ||||
4.5.7 Backup Battery Charger
Table 4-9 lists the backup battery charger electrical characteristics.
Table 4-9 Backup Battery Charger Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backup Battery Charger | ||||||
| VBACKUP to GPADC input attenuation | VBACKUP from 2.4 to 4.5 V | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.35 | V/V | |
| ICharge | Backup battery charging current | VBACKUP = 0 to 2.6 V BB_CHG_EN = 1 |
350 | 650 | 900 | µA |
| VCharge | End backup battery charging voltage: VBBCHGEND | IVBACKUP = –10 µA, BB_SEL = 00 (VSYS > 3.2 V) | 2.90 | 3.00 | 3.10 | V |
| IVBACKUP = –10 µA, BB_SEL = 01 (VSYS > 2.7 V) | 2.42 | 2.52 | 2.60 | |||
| IVBACKUP = –10 µA, BB_SEL = 10 (VSYS > 3.35 V) | 3.05 | 3.15 | 3.25 | |||
| IVBACKUP = –10 µA, BB_SEL = 11 (VSYS > 2.5 V) | VSYS – 0.3 | VSYS | ||||
| IVBACKUP = –10 µA, BB_SEL = XX (VSYS < 2.5 V) | VSYS – 0.2 | VSYS | ||||
| IQ | Current consumption | BB_CHG_EN = 1, IVBACKUP = 0 µA | 10 | µA | ||
| RSeries | Backup battery serial resistance | Without additional capacitor in parallel | 20 | Ω | ||
| With additional capacitor in parallel | 1500 | |||||
| COUT | Capacitance of the additional capacitor (C44) | 2.0 | 4.7 | µF | ||
4.5.8 Switched-Mode System Supply Regulator
Table 4-10 lists the system supply regulator electrical characteristics.
Table 4-10 System Supply Regulator Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switched-Mode System Supply Regulator | ||||||
| CVBUS | VBUS capacitor (connected between VBUS and PGND) | 0 V < VBUS < 5.25 V | 1.2 | 4.7 | 6.5 | µF |
| 0 V < VBUS < 6 V | 0.9 | 4.7 | 6.5 | µF | ||
| ESR (1 to 10 MHz) | 1 | 10 | 20 | mΩ | ||
| CPMID | PMID capacitor (connected between PMID and PGND) | 0 V < VBUS < 5.25 V | 1.2 | 4.7 | 6.5 | µF |
| 0 V < VBUS < 6 V | 0.9 | 4.7 | 6.5 | |||
| ESR (1 to 10 MHz) | 1 | 10 | 20 | mΩ | ||
| CCSOUT | Output capacitor (connected between CSOUT and PGND) | 0 V < CSOUT < 4.5 V | 3 | 10 | 15 | µF |
| ESR (1 to 10 MHz) | 20 | mΩ | ||||
| CCSIN | Output capacitor (connected between CSIN and PGND) | 0 V < CSIN < 4.5 V | 20 | 100 | 150 | nF |
| ESR (100 kHz) | 400 | mΩ | ||||
| CBOOT | Bootstrap capacitor (connected between BOOT and SW) | 50 | 100 | 200 | nF | |
| ESR (9 MHz) | 200 | mΩ | ||||
| CVREF | Reference voltage capacitor (connected between VREF and PGND) | 0 V < VREF < 6.5 V | 0.7 | 2.2 | 2.86 | µF |
| ESR (1 to 10 MHz) | 20 | mΩ | ||||
| L | Coil (option 1), (connected between SW and CSIN) | Inductance | 0.7 | 1 | 1.45 | µH |
| DCR | 130 | mΩ | ||||
| R9 | Sense resistor (connected between CSIN and CSOUT) | Short circuited with power path | –1% | 68 mΩ | +1% | |
| Maximum output average current | CHRG_SW | 1.5 | 1.545 | A | ||
| IVBUS | VBUS supply current control | VBUS > VBUSmin, PWM switching | 10 | mA | ||
| VBUS > VBUSmin, PWM not switching | 5 | |||||
| 0°C < TJ < 85°C, HZ_MODE= 1, 32S mode | 30 | µA | ||||
| IVBUS_LEAK | Leakage current from battery to VBUS ball | 0°C < TJ < 85°C, CSOUT = 4.2 V, Hi-Z mode | 5 | µA | ||
| VSYS | Output voltage for preconditioning/precharge | 3.8 | V | |||
| Output voltage for full charge mode | VBAT + ΔLIN | V | ||||
| Nominal output voltage, programmable | 20-mV steps | 3.50 | 3.54 | 4.76 | V | |
| Voltage regulation accuracy (except full charge mode), IOUT < 200 mA | T = 25°C | –0.5 % | 0.5 % | |||
| 0°C < T < 125°C | –1.0 % | 1.0 % | ||||
| VICHRG | Nominal output current Without power Path, programmable | With R9 = 68 mΩ | 300 | 1500 | mA | |
| Current accuracy | IOCHARGE ≤ 500 mA | –5 % | 5 % | |||
| IOCHARGE ≥ 600 mA | –3 % | 3 % | ||||
| VAC_DET | VAC detection | VAC_DET rising edge threshold | 2.9 | 3.4 | 3.6 | V |
| VAC_DET falling edge threshold | 2.7 | 3.0 | 3.4 | |||
| Hysteresis | 100 | 135 | 350 | mV | ||
| VBUS_DET | VBUS detection | VBUS_DET rising edge threshold | 2.9 | 3.4 | 3.6 | V |
| VBUS_DET falling edge threshold | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.35 | |||
| Hysteresis | 50 | 135 | 170 | mV | ||
| VAC/VBUS detection deglitch time | 25 | 30 | 36 | ms | ||
| VVBUS_MIN | VBUS input voltage lower limit | Input power source detection for battery charging, threshold for falling edge | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.0 | V |
| Deglitch time for VBUS rising above VVBUS_MIN | Rising voltage, 2-mV overdrive, tR = 100 ns | 4 | 5 | 6 | ms | |
| Hysteresis for VVBUS_MIN | Input voltage rising | 100 | 200 | mV | ||
| VBUS collapse threshold | Input current is automatically reduced, programmable, 80-mV steps | 4.2 | 4.76 | V | ||
| VBUS DPM loop kick-in threshold accuracy | –2 % | 2 % | ||||
| tint | Detection interval | Input power source detection | 1.7 | 2 | 2.6 | s |
| IIN_LIMIT | VBUS input current-limiting threshold | Programmable | 100 | 2250 | mA | |
| Accuracy | –15 % | –9 % | –1 % | |||
| System Supply Regulator, Sleep Comparator (To Detect USB Unplug) | ||||||
| VSLP | SLEEP state entry threshold | VBUS above CSOUT, 2.3 V ≤ CSOUT ≤ VOREG, VBUS falling | 0 | 40 | 100 | mV |
| VSLP_ EXIT | SLEEP state exit hysteresis | 2.3 V ≤ CSOUT ≤ VOREG | 140 | 200 | 260 | mV |
| Deglitch time for VBUS rising above VSLP + VSLP_EXIT | Rising voltage, 2-mV overdrive, tR = 100 ns | 31 | 32 | 34 | ms | |
| System Supply Regulator, Battery Detection (Enabled by OTP Bit) | ||||||
| IDETECT battery detection current before charge done (sink current) | Begins after termination detected, CSOUT ≤ VOREG | –0.45 | mA | |||
| TDETECT battery detection time | 215 | 262 | 335 | ms | ||
| System Supply Regulator, PWM | ||||||
| Internal top reverse blocking MOSFET on-resistance | 100 | 200 | mΩ | |||
| Internal top N-channel switching MOSFET on-resistance | Measured from PMID to SW | 120 | 200 | mΩ | ||
| Internal bottom N-channel MOSFET on-resistance | Measured from SW to PGND | 120 | 240 | mΩ | ||
| fOSC | Oscillator frequency | 2.7 | 3 | 3.3 | MHz | |
| DMIN | Minimum duty cycle | 0 % | ||||
| DMAX | Maximum duty cycle | 93 % | ||||
| Boost Mode for VBUS Voltage Generation | ||||||
| VBUS_B | Boost output voltage (to pin VBUS) | 2.7 V < CHRG_CSOUT < 4.5 V | 4.75 | 5.10 | 5.25 | V |
| IBO1 | Rated output current of the boost, combination of VBUS output current and LDOUSB input current from CHRG_PMID node | VBUS_B = 5.10 V, 2.7 V < CHRG_CSOUT < 4.5 V |
300 | mA | ||
| Rated LDOUSB input current from CHRG_PMID node | VBUS_B = 5.10 V, 2.7 V < CHRG_CSOUT < 4.5 V |
100 | mA | |||
| IBLIMIT | Cycle-by-cycle current limit for boost | VBUS_B = 5.10 V, 2.7 V < CHRG_CSOUT < 4.5 V |
1.0 | A | ||
| VBUSOVP | Overvoltage protection threshold for boost (VBUS pin) | Threshold over VBUS to turn off converter during boost | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.2 | V |
| Hysteresis | VBUS falling from above VBUSOVP | 125 | mV | |||
| Efficiency | CSOUT = 3.6 V, IBO = 200 mA, TA = 25°C, synchronous operation | 85 % | ||||
| IDDQ | Quiescent current | 5 | mA | |||
| VSYSMAX | Maximum system voltage for boost (CSOUT pin) | VCSOUT rising edge during boost | 4.75 | 4.9 | 5.05 | V |
| Hysteresis | VCSOUT falling from above VSYSMAX | 200 | mV | |||
| VSYSMIN | Minimum system voltage for boost (CSOUT pin) | 2.5 | V | |||
| Boost output resistance at HP mode (from VBUS to PGND) | HZ_MODE = 1 | 60 | kΩ | |||
| System Supply, Protection, Current Consumptions | ||||||
| VOVP_ VBUS | VBUS OVP threshold voltage | Threshold over VBUS to turn off converter during charge | 6.3 | 6.5 | 6.7 | V |
| Hysteresis | VBUS falling from above VOVP_VBUS | 140 | mV | |||
| VOVP_ VSYS | System voltage OVP threshold voltage, VCSOUT threshold over VOREG to turn off the regulator during operation | Power Path mode and DCDC in PWM mode | 130 % | 133 % | 136 % | |
| Other cases | 110 % | 117 % | 121 % | |||
| Hysteresis | Lower limit for VCSOUT falling from above VOVP_VSYS | 11 % | ||||
| VOVP_ VBAT | VBAT OVP threshold voltage | Threshold over VBAT to turn off battery charging | 110 % | 117 % | 121 % | |
| Hysteresis | 11 % | |||||
| Debounce time for falling edge | 3 | ms | ||||
| ILIMIT | Cycle-by-cycle current limit for charge | BUCK_HSLIMI = 0: 2.55 A | 2.10 | 2.55 | 3.30 | A |
| BUCK_HSLIMI = 1: 1.90 A default | 1.50 | 1.90 | 2.60 | |||
| VSYS_ SHORT | Short-circuit voltage threshold | CSOUT rising (default) | 2.00 | 2.10 | 2.20 | V |
| Hysteresis | CSOUT falling from above VSYS_SHORT | 100 | mV | |||
| ISYS_ SHORT | Short-circuit detection current | CSOUT ≤ VSYS_SHORT | 20 | 30 | 40 | mA |
| IVBUS | VBUS input current | VBUS = 9.7 V, OVP active | 4 | mA | ||
| Regulator thermal shutdown | Temperature threshold, TCHRGSHTDWN | 148 | °C | |||
| Hysteresis, TCHRGHYS | 10 | |||||
| Analog thermal regulation loop | Threshold to start limiting the current, TCF, IVBUS = 1.5 A |
130 | °C | |||
| Threshold for 0 A current level | TCHRGSHTDWN – 5 | |||||
| Current consumption of the linear charger and supplement mode control | System supply regulator enabled, charger enabled | 1.3 | mA | |||
| System supply regulator enabled, charger disabled | 0.9 | |||||
| System supply regulator disabled, system switch forced to connect | 1 | µA | ||||
4.5.9 Battery Charger
Table 4-11 lists the battery charger electrical characteristics.
Table 4-11 Battery Charger Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Charger | ||||||
| R2 | Sense resistor of linear charging loop(1) | 15-mΩ resistor allows maximum of 2.0-A charging current 20-mΩ resistor allows maximum of 1.5-A charging current |
15 | 20 | mΩ | |
| IBAT_SHORT | Preconditioning current (for short-circuit detection) | VSYS = 3.6 V, VBAT ≤ VBAT_SHORT | 13 | 20 | 27 | mA |
| VSYS = 3.8 V, VBAT ≤ VBAT_SHORT | 20 | 30 | 40 | |||
| VBAT_SHORT | Preconditioning positive threshold voltage | Programmable: 2.1, 2.45, and 2.8-V voltage levels | 2.1 | 2.8 | V | |
| Hysteresis | 50 | 100 | 150 | mV | ||
| Debounce time | 1 | ms | ||||
| VICHRG_PC | Linear precharge current, programmable | VBAT_SHORT < VBAT < VBAT_FULLCHRG
100-mA steps |
100 | 400 | mA | |
| Accuracy, without autocalibration | –75 % | 0 % | ||||
| Accuracy, with autocalibration | ICHARGE < 300 mA | –10 % | +10 % | |||
| 300 mA ≤ ICHARGE ≤ 400 mA | –5 % | +5 % | ||||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG | Threshold level, low to high transition | VBAT_FULLCHRG = 000 | 2.61 | 2.65 | 2.73 | V |
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 001 | 2.705 | 2.75 | 2.835 | |||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 010 | 2.805 | 2.85 | 2.94 | |||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 011 | 2.905 | 2.95 | 3.04 | |||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 100 | 3.00 | 3.05 | 3.145 | |||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 101 | 3.10 | 3.15 | 3.245 | |||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 110 | 3.20 | 3.25 | 3.35 | |||
| VBAT_FULLCHRG = 111 | 3.295 | 3.35 | 3.455 | |||
| Hysteresis | 50 | 100 | 150 | mV | ||
| VICHRG | Linear full charge current, programmable(1) | VBAT > VBAT_FULLCHRG, 100-mA steps, R2 = 20 mΩ | 100 | 1500 | mA | |
| BAT > VBAT_FULLCHRG, 133-mA steps, R2 = 15 mΩ | 133 | 2000 | ||||
| Accuracy, without autocalibration | ICHARGE ≤ 400 mA | –75 % | –37 % | 0 % | ||
| ICHARGE ≥ 500 mA | –50 % | 0 % | ||||
| Accuracy, with autocalibration | ICHARGE ≤ 400 mA | –5 % | 5 % | |||
| ICHARGE ≥ 500 mA | –3 % | 3 % | ||||
| VOREG | Linear full charge output voltage | Programmable, 20-mV steps | 3.5 | 4.76 | V | |
| Accuracy, with autocalibration | T = 25°C | –0.5 % | 0.5 % | |||
| 0°C < T < 125°C | –1.0 % | 1.0 % | ||||
| VITERM | Charger termination current(1) | Programmable, 50-mA steps R2 = 20 mΩ |
50 | 400 | mA | |
| Programmable, 67-mA steps R2 = 15 mΩ |
67 | 533 | ||||
| Accuracy | –33 % | 33 % | % | |||
| ΔLIN | Charger dropout voltage, voltage between VSYS and VBAT | Programmable, 50-mV steps | 100 | 200 | mV | |
| Accuracy | –20 | 20 | ||||
| DPPM regulation, voltage between VSYS and VBAT | VBAT > VBATMIN_HI | 0.5 × ΔLIN | V | |||
| DPPM regulation, VSYS voltage | VBAT < VBATMIN_HI | 3.4 | V | |||
| VSYS_OVV | System overvoltage detection | Positive threshold | 5.7 | 5.9 | 6.1 | V |
| Hysteresis | 50 | 100 | 200 | mV | ||
| Recharge threshold voltage (in Power Path mode enabled always, in non-Power Path mode enabled when CHARGE_ONCE bit is 0) | Below VOREG | 70 | 120 | 170 | mV | |
| Deglitch time, VBAT decreasing below threshold, tF = 100 ns, 10-mV overdrive | 128 | ms | ||||
| Supplement Mode | ||||||
| PGATE driver time | Fall time, Cgate = 8 nF, VSYS to VSYS – 2 V, VSYS = 3.2 V | 1.0 | µs | |||
| Rise time, Cgate = 8 nF, 0 V to VSYS – 0.1 V, VSYS = 3.2 V | 2.5 | |||||
| Supplement mode threshold level (when entering supplement mode) | VSYS below VBAT, programmable | 20 | 30 | 50 | mV | |
| Accuracy | –10 | 10 | ||||
| Supplement mode threshold level (when exiting supplement mode) | IBAT | 50 | 100 | 150 | mA | |
| Check the need for supplement mode | 100 | ms | ||||
| Charging restart delay | 500 | µs | ||||
| Battery Temperature Measurement | ||||||
| Reference voltage | GPADC_VREF | 1.25 | V | |||
| Low and high threshold voltages | OTP bits, RATIO_LO[2:0], RATIO_HI[2:0] | 0.2 × GPADC_VREF | 0.9 × GPADC_VREF | |||
| Threshold error | 1 % | % | ||||
| Comparator offset | 10 | mV | ||||
| Battery Presence Detector | ||||||
| RBRI | External pulldown resistor | 130 | kΩ | |||
| IBRI | See Table 4-15, GPADC_IN0 current source. | |||||
| VBRIRef | Detection threshold | Threshold | 1.5 | 1.6 | V | |
| Current consumption of the comparator | 10 | µA | ||||
| Delay of the comparator | With > 10-mV overdrive | 10 | µs | |||
4.5.10 Indicator LED Driver
Table 4-12 lists the indicator LED driver electrical characteristics.
Table 4-12 Indicator LED Driver Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator LED Driver | ||||||
| VSYS | 4.8 | V | ||||
| LED current | CURR_LED[1:0] = 00 | 0 | mA | |||
| CURR_LED[1:0] = 01 | 0.85 | 1 | 1.15 | |||
| CURR_LED[1:0] = 10 | 2.125 | 2.5 | 2.875 | |||
| CURR_LED[1:0] = 11 | 4.25 | 5 | 5.75 | |||
| Rise and fall time for the current | Transition on PWM signal, 10 to 90% | 5 | µs | |||
| Startup time | CURR_LED[1:0] from 00 to any other value | 20 | µs | |||
| Quiescent current | Disabled | µA | ||||
| VRTC | 2 | |||||
| VAC (at 20 V) | 70 | |||||
| CHRG_PMID (at 5.25 V) | 20 | |||||
| CHRG_PMID (at 20 V) | 70 | |||||
| CURR_LED[1:0] = 01 (1 mA) | 200 | µA | ||||
| CURR_LED[1:0] = 10 (2.5 mA) | 400 | |||||
| CURR_LED[1:0] = 11 (5 mA) | 750 | |||||
| Pulldown resistance | CURR_LED[1:0] = 00, can be disabled by DIS_PULLDOWN bit | 50 | 100 | 200 | kΩ | |
| Voltage at the output for performance | 3.2 | V | ||||
| Voltage at the output for tolerance | CHRG_LED_TEST pin is driven externally | 5.5 | V | |||
| Dropout voltage Minimum voltage between CHRG_LED_IN and CHRG_LED_TEST |
1 mA | 0.2 | V | |||
| 2.5 mA | 0.4 | |||||
| 5 mA | 0.6 | |||||
| VAC voltage | During operation | 4.1 | V | |||
| VBUS voltage | During operation | 4.0 | V | |||
| CHRG_LED_IN voltage | 2.3 | 5.5 | V | |||
4.5.11 USB OTG
Table 4-13 lists the USB OTG electrical characteristics.
Table 4-13 USB OTG Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pullup and Pulldown Resistors | ||||||
| RID_PU_100K | ID 100k pullup to LDOUSB | 70 | 100 | 130 | kΩ | |
| RID_PU_220K | ID 220k pullup to LDOUSB | 160 | 220 | 280 | kΩ | |
| RID_GND_DRV | ID 10k pulldown to ground | 1 | 10 | 20 | kΩ | |
| RID_ LKG | ID internal leakage without GPADC (7 V) | 350 | nA | |||
| ID internal leakage without GPADC (2 V) | 650 | nA | ||||
| ID external leakage | –1.5 | 0 | 1 | µA | ||
| RA_BUS_IN | A-device VBUS Input Impedance To GND | 10 | 40 | 100 | kΩ | |
| RVBUS_DISCHRG | B-device VBUS SRP pulldown | 5 | 10 | 15 | kΩ | |
| RVBUS_CHRG_VBAT | B-device VBUS SRP pullup on VBAT | 1.5 | 2.5 | 5 | kΩ | |
| RVBUS_CHRG_PMID | B-device VBUS SRP pullup on CHRG_PMID | 1.5 | 2.5 | 5 | kΩ | |
| VVBUS_LKG | OTG device leakage voltage | 0.7 | V | |||
| IB_UNCFG | B-device unconfigured average VBUS input current | 2.5 | mA | |||
| External ID resistances | ||||||
| RID_FLOAT | ID pulldown when ID pin is floating | 220 | kΩ | |||
| RID_A | ACA ID pulldown, OTG device as A-device | 122 | 124 | 126 | ||
| RID_B | ACA ID pulldown, OTG device as B-device, can't connect | 67 | 68 | 69 | ||
| RID_C | ACA ID pulldown, OTG device as B-device, can connect | 36 | 36.5 | 37 | ||
| RID_GND | ID pulldown when ID pin is grounded | 1 | ||||
| Comparators | ||||||
| VID_WK | ID wake-up comparator threshold | No hysteresis | 0.300 | 0.650 | 1.150 | V |
| RID_WK_UP | ID wake-up equivalent threshold resistance | 10 | 100 | 220 | kΩ | |
| VID_CMP1 | ID comparator 1 threshold | No hysteresis | 0.150 | 0.200 | 0.250 | V |
| VID_CMP2 | ID comparator 2 threshold | No hysteresis | 0.683 | 0.720 | 0.757 | V |
| VID_CMP3 | ID comparator 3 threshold | No hysteresis | 1.300 | 1.400 | 1.500 | V |
| VID_CMP4 | ID comparator 4 threshold | No hysteresis | 2.350 | 2.500 | 2.650 | V |
| Current Sources | ||||||
| IID_WK_SRC | ID wake-up current source | VID < 2.75 V | 3.5 | 9 | 25 | µA |
| IID_SRC_16u | ID current source (trimmed) | VID < 2.75 V | 15.5 | 16 | 16.5 | µA |
| IID_SRC_5u | ID current source | VID < 2.75 V | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | µA |
| ADP Comparators | ||||||
| VADP_ PRB | ADP probing voltage threshold | No hysteresis | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.7 | V |
| VADP_ SNS | ADP sensing voltage threshold | No hysteresis | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.55 | V |
| VADP_ DSCHRG | ADP discharge voltage | 0.15 | V | |||
| ADP Current Sources/Sinks | ||||||
| VBUS_IADP_SRC | ADP source current | VBUS < 0.8 V | 1.10 | 1.40 | 1.65 | mA |
| VBUS_IADP_SINK | ADP sink current | 0.5 V < VBUS < 0.8 V | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2 | mA |
| 0.15 V < VBUS < 0.8 V | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2 | |||
| ADP Timings | ||||||
| T_ADP_SINK | ADP sink time | 13 | 14 | 15 | ms | |
| TA_ADP_PRB | ADP probing period, A-device | 1.25 | 1.75 | 1.85 | s | |
| TB_ADP_PRB | ADP probing period, B-device | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.6 | s | |
| T_ADP_SNS | ADP sensing time-out | 3 | s | |||
| Comparators | ||||||
| VVBUS_WKUP_UP | VBUS wake-up comparator | Positive threshold | 2.8 | 3.2 | 3.6 | V |
| Hysteresis | 50 | 100 | 175 | mV | ||
| VA_VBUS_VLD | A-device VBUS valid comparator threshold | Threshold, no hysteresis | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.6 | V |
| VB_SESS_VLD_UP | B-device session valid comparator | Positive threshold | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.6 | V |
| Hysteresis | 20 | 80 | 140 | mV | ||
| VA_SESS_VLD_UP | A-device session valid comparator | Positive threshold | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.3 | V |
| Hysteresis | 10 | 40 | 70 | mV | ||
| VB_SESS_END_UP | B-device session end comparator | Positive threshold | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.8 | V |
| Hysteresis | 10 | 40 | 70 | mV | ||
| VOTG_SESS_VLD_UP | OTG session valid comparator | Positive threshold | 2.90 | 3.10 | 3.40 | V |
| Hysteresis | 20 | 80 | 140 | mV | ||
| VOTG_OVV_UP | OTG overvoltage comparator | Positive threshold | 6.3 | 6.5 | 6.8 | V |
| Hysteresis | 40 | 110 | 180 | mV | ||
4.5.12 Gas Gauge
Table 4-14 lists the gas gauge electrical characteristics.
Table 4-14 Gas Gauge Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current measurement range | 20-mΩ sense resistor | –3.1 | 3.1 | A | ||
| 15-mΩ sense resistor | -4.13 | 4.13 | ||||
|
Measurement accuracy of single measurement result after calibration. Includes reference, temperature, offset, and 3σ statistical variation. Tolerance of the sense resistor R2 is not included. |
CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 |
–Vmeas × 1% –0.11 –0.28 –0.74 –2.15 |
Vmeas × 1% 0.11 0.28 0.74 2.15 |
mV | ||
| Offset before autocalibration | CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 |
200 200 200 450 |
µV | |||
| Offset after autocalibration (software must calculate the calibrated result) | CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 |
10 10 100 450 |
µV | |||
| Usable input voltage range | –62 | 62 | mV | |||
| Input clock frequency | 32-kHz crystal oscillator | 32768 | Hz | |||
| Current consumption | Power on; FG_EN = 1 | 50 | 70 | µA | ||
| Power off; FG_EN = 0 | 0.2 | |||||
| Integration period (sample counter uses 32-kHz crystal oscillator) | CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 | 250 | ms | |||
| CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 | 62.5 | |||||
| CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 | 15.625 | |||||
| CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 | 3.90625 | |||||
| R2 | External sense resistor | 10 | 20 | mΩ | ||
| Integrator data size (2s complement) | CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 | 1 + 13 | Bit | |||
| CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 | 1 + 11 | |||||
| CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 | 1 + 9 | |||||
| CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 | 1 + 7 | |||||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity (average on 10 measurement results) | CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 |
–3.5 –2.5 –2.0 –1.5 |
3.5 2.5 2.0 1.5 |
LSB | |
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity (average on 10 measurement results) | CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 00 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 01 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 10 CC_ACTIVE_MODE[1:0] = 11 |
–4.0 –2.5 –1.5 –1.0 |
4.0 2.5 1.5 1.0 |
LSB | |
| Accumulator data size | 1 + 31 | Bit | ||||
| Offset data size | 1 + 9 | Bit | ||||
| Sample counter data size | 24 | Bit | ||||
4.5.13 GPADC
Table 4-15 lists the GPADC electrical characteristics.
Table 4-15 GPADC Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQ | Current consumption | GPADC_EN = 1 | 1600 | µA | ||
| IQOFF | Off mode current | GPADC_EN = 0 | 1 | µA | ||
| f | Running frequency | 3 | MHz | |||
| Resolution | 12 | Bit | ||||
| Number of external inputs | 7 | |||||
| Number of internal inputs | 12 | |||||
| Turn on/off time | GPADC_EN 0 to 1 or GPADC_EN 1 to 0 | 10 | 20 | µs | ||
| Gain error without calibration (inputs without scaler) | –2 % | 2 % | ||||
| Gain error without calibration (inputs with scaler) | GPADC_IN10 | –5 % | 3 % | |||
| Others than GPADC_IN10 | –3 | 3 | ||||
| Offset error without calibration | –36 | 36 | LSB | |||
| Gain error with calibration (at 25°C temperature)(1) | GPADC_IN10 | –0.7 % | 0.7 % | |||
| Others than GPADC_IN10 | –0.22 % | 0.22 % | ||||
| Offset error with calibration (at 25°C temperature)(1) | GPADC_IN10 | -3 | 3 | LSB | ||
| Others than GPADC_IN10 | -5 | 5 | ||||
| Gain error drift (Temperature and supply) | GPADC_IN0 - GPADC_IN6, GPADC_IN17 | –0.6 % | 0.25 % | |||
| Other channels | –0.6 % | 0.45 % | ||||
| Offset drift (Temperature and supply) | –2 | 2 | LSB | |||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | Best fitting, GPADC_IN9 | –3 | 4 | LSB | |
| Best fitting, GPADC_IN14 | –16 | 12 | ||||
| Best fitting, other channels | –3 | 3 | ||||
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | –2 | 2 | LSB | ||
| CIN | Input capacitance | GPADC_IN17 | 4 | pF | ||
| Other inputs | 0.5 | |||||
| RExt | Source input impedance (external inputs)(2) | Source resistance without capacitance | 20 | kΩ | ||
| Source capacitance with > 20-kΩ source resistance | 100 | nF | ||||
| GPADC_VREF voltage reference | 1.25 | V | ||||
| GPADC_VREF output current | External load | 200 | µA | |||
| VIN | Input range (Sigma-Delta ADC; the input voltage and nonsaturated ranges of the scaled inputs are described in Table 5-2) | Typical range | 0 | 1.25 | V | |
| Assured range without saturation | 0.01 | 1.215 | ||||
| TConv | Conversion time | 1 channel, sampling = 0 | 210 | µs | ||
| 1 channel, sampling = 1 | 640 | |||||
| 2 channels, sampling = 0 | 290 | |||||
| 2 channels, sampling = 1 | 720 | |||||
| GPADC_IN0 current source | 6.65 | 7 | 7.35 | µA | ||
| GPADC_IN0 with additional current source | GPADC_ISOURCE_EN = 1 | 20.9 | 22 | 23.1 | ||
| GPADC_IN3 current sources | GPADC_REMSENSE[1:0] = 00 | 0 | µA | |||
| GPADC_REMSENSE[1:0] = 01 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 10.5 | |||
| GPADC_REMSENSE[1:0] = 10 | 340 | 380 | 420 | |||
| GPADC_REMSENSE[1:0] = 11 | 675 | 750 | 825 | |||
4.5.14 Thermal Monitoring
Table 4-16 lists the thermal monitoring electrical characteristics.
Table 4-16 Thermal Monitoring Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQOFF | Off ground current (two sensors on the die, specification for one sensor) | Off mode | 0.1 | µA | ||
| at 25°C off mode | 0.5 | |||||
| IQ | On ground current (two sensors on the die, specification for one sensor) | On mode, standard mode | 7 | 15 | µA | |
| On mode, GPADC measurement | 25 | 40 | ||||
| 00 (first hot-die threshold) | Rising temperature | 104 | 117 | 127 | °C | |
| Falling temperature | 95 | 108 | 119 | |||
| 01 (second hot-die threshold) | Rising temperature | 109 | 121 | 132 | °C | |
| Falling temperature | 99 | 112 | 123 | |||
| 10 (third hot-die threshold) | Rising temperature | 113 | 125 | 136 | °C | |
| Falling temperature | 104 | 116 | 128 | |||
| 11 (fourth hot-die threshold) | Rising temperature | 118 | 130 | 141 | °C | |
| Falling temperature | 108 | 120 | 132 | |||
| Thermal shutdown | Rising temperature | 136 | 148 | 160 | °C | |
| Falling temperature | 126 | 138 | 150 | |||
4.5.15 System Control Thresholds
Table 4-17 lists the system control thresholds electrical characteristics.
Table 4-17 System Control Thresholds Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSYSMIN_HI threshold, rising edge | Programmable, step size is 50 mV | 2.5 | 3.55 | V | ||
| VSYSMIN_HI threshold accuracy | –1.6 % | +3.2 % | ||||
| VSYSMIN_LO threshold, falling edge | Programmable, step size is 50 mV | 2.3 | 3.1 | V | ||
| VSYSMIN_LO threshold accuracy | –1.6 % | +3.2 % | ||||
| POR rising-edge threshold | 2.00 | 2.15 | 2.50 | V | ||
| POR fallng-edge threshold | 1.90 | 2.00 | 2.10 | V | ||
| POR hysteresis | Rising edge to falling edge | 40 | 150 | 350 | mV | |
4.5.16 Current Consumption
Table 4-18 lists the current consumption electrical characteristics.
Table 4-18 Current Consumption Electrical Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backup Mode | ||||||
| IVBACKUP(Backup) | VBACKUP, supplied on VBACKUP | VSYS = 0 V VBACKUP = 3.2 V |
8 | 10 | µA | |
| IVSYS(Backup) | VSYS, supplied on VSYS | VBACKUP = 0 V VSYS = 2.7 V |
12 | 19 | µA | |
| WAIT-ON State | ||||||
| IVSYS(WAIT-ON) | VSYS = 3.8 V, VRTC in a low-power mode | 20 | 30 | µA | ||
| SLEEP State | ||||||
| IVSYS(SLEEP) | SMPS2 and SMPS3 enabled, no load | VSYS = 3.8 V | 110 | µA | ||
4.5.17 Digital Input Signal Electrical Parameters
Table 4-19 lists the digital input signal electrical parameters.
Table 4-19 Digital Input Signal Electrical Parameters
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWRON, RPWRON | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage related to VSYS/VDD | –0.3 | 0 | 0.35 × VSYS | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage related to VSYS/VDD | 0.65 × VSYS | VSYS | VSYS + 0.3 ≤ 5.5 | V | |
| GPADC_START, MMC, MSECURE, NRESWARM, PREQ1, PREQ2, PREQ3, SIM, TESTEN | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage related to VIO | –0.3 | 0 | 0.35 × VIO | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage related to VIO | 0.65 × VIO | VIO | VIO + 0.3 | V | |
| BOOT0, BOOT1, BOOT2, CHRG_EXTCHRG_STATZ, OSC32KIN | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage related to VRTC | –0.3 | 0 | 0.35 × VRTC | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage related to VRTC | 0.65 × VRTC | VRTC | VRTC + 0.3 | V | |
| CTLI2C_SCL, CTLI2C_SDA, DVSI2C_SCL, DVSI2C_SDA | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage related to VIO | –0.3 | 0 | 0.3 × VIO | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage related to VIO | 0.7 × VIO | VIO | VIO + 0.3 | V | |
| Hysteresis | 0.1 × VIO | V | ||||
| 1.2-V Specific Related I/Os: PREQ3(1)(2) | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage related to VIO | –0.3 | 0 | 0.3 × VIO | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage related to VIO | 0.7 × VIO | VIO | VIO + 0.3 | V | |
4.5.18 Digital Output Signal Electrical Parameters
Table 4-20 lists the digital output signal electrical parameters.
Table 4-20 Digital Output Signal Electrical Parameters
| PARAMETER(1) | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REGEN1, REGEN2, VBUS_DET | ||||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 100 µA | 0 | 0.2 × VSYS | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = 100 µA | 0.8 × VSYS | VSYS | V | |
| BATREMOVAL, CLK32KAO, CLK32KG, INT, NRESPWRON, PWM1, PWM2, SYSEN | ||||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage related to VIO | IOL = 2 mA | 0 | 0.45 | V | |
| VOL | Low-level output voltage related to VIO | IOL = 100 µA | 0 | 0.2 | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage related to VIO | IOH = 2 mA | VIO – 0.45 | VIO | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage related to VIO | IOH = 100 µA | VIO – 0.2 | VIO | V | |
| CLK32KAUDIO, CHRG_EXTCHRG_ENZ | ||||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage related to VRTC | IOL = 2 mA | 0 | 0.45 | V | |
| VOL | Low-level output voltage related to VRTC | IOL = 100 µA | 0 | 0.2 | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage related to VRTC | IOH = 2 mA | VRTC – 0.45 | VRTC | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage related to VRTC | IOH = 100 µA | VRTC – 0.2 | VRTC | V | |
| CTLI2C_SDA, DVSI2C_SDA | ||||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage related to VIO | 3-mA sink current | 0 | 0.2 × VIO | V | |
4.5.19 Digital Output Signal Timing Characteristics
Table 4-21 lists the digital output signal timing characteristics.
Table 4-21 Digital Output Signal Timing Characteristics
| BALL NAME/OUTPUT BUFFER | LOAD (pF) | RISE/FALL TIME (ns) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | NOM | MAX | |
| CHRG_EXTCHRG_ENZ | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| INT | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| BATREMOVAL | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| NRESPWRON | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| PWM1 | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| PWM2 | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| REGEN1 | 5 | 35 | 5 | 25 | |
| REGEN2 | 5 | 35 | 5 | 25 | |
| SYSEN | 5 | 35 | 5 | 15 | |
| VRTC supply output buffer and VIO supply output buffer |
5 | 1 | 6 | ||
| 20 | 4 | 11 | |||
| 35 | 5 | 15 | |||
| 50 | 8 | 20 | |||
| VSYS supply output buffer | 5 | 1 | 9 | ||
| 20 | 3 | 17 | |||
| 35 | 5 | 25 | |||
| 50 | 6 | 34 | |||
| CLK32KAO output buffer and CLK32KG output buffer |
5 | 5 | 15 | ||
| 20 | 8 | 30 | |||
| 35 | 10 | 45 | |||
| 50 | 15 | 100 | |||
4.6 Typical Characteristics
Figure 4-1 shows the 5.0-A SMPS regulator efficiency. Figure 4-2 shows 1.1-A SMPS regulator efficiency.
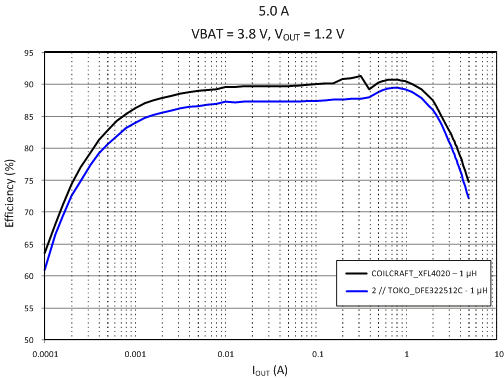
| 5.0 A | VBAT = 3.8 V | |
| VOUT = 1.2 V |
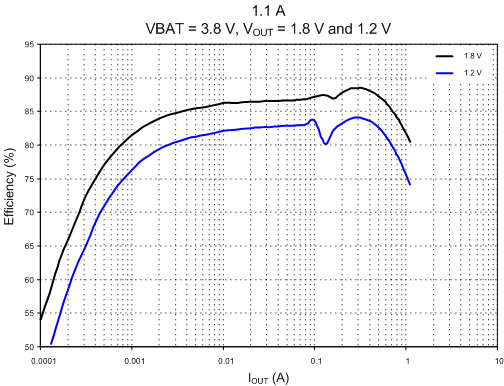
| 1.1 A | VBAT = 3.8 V | |
| VOUT = 1.8 V and 1.2 V |
Figure 4-3 and Figure 4-4 show 2.5-A SMPS regulator efficiencies with two different inductor options.
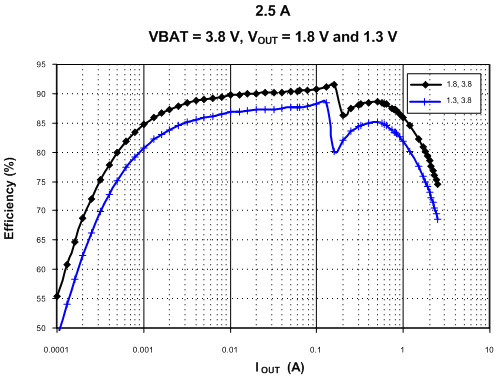
| 2.5 A | VBAT = 3.8 V | |
| VOUT = 1.8 V and 1.3 V |
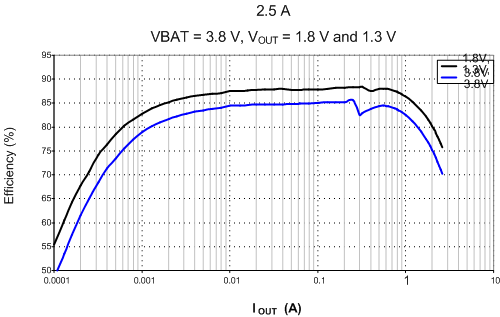
| 2.5 A | VBAT = 3.8 V | |
| VOUT = 1.8 V and 1.3 V |