-
TPS92391 Boost/SEPIC High Dimming Performance LED Driver with Six 200-mA Channels
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Interface
- 7.3.2 Function Setting
- 7.3.3 Device Supply (VDD)
- 7.3.4 Enable (EN)
- 7.3.5 Charge Pump
- 7.3.6 Boost Controller
- 7.3.7 LED Current Sinks
- 7.3.8 Brightness Control
- 7.3.9
Protection and Fault Detections
- 7.3.9.1 Supply Faults
- 7.3.9.2
Boost Faults
- 7.3.9.2.1 Boost Overvoltage Faults (BSTOVPL, BSTOVPH)
- 7.3.9.2.2 Boost Overcurrent Faults (BSTOCP)
- 7.3.9.2.3 LEDSET Resistor Missing Faults (LEDSET)
- 7.3.9.2.4 MODE Resistor Missing Faults (MODESEL)
- 7.3.9.2.5 FSET Resistor Missing Faults (FSET)
- 7.3.9.2.6 ISET Resistor Out of Range Faults (ISET)
- 7.3.9.2.7 Thermal Shutdown Faults (TSD)
- 7.3.9.3 LED Faults
- 7.3.9.4 Overview of the Fault and Protection Schemes
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.6 Output Diode
- 8.2.1.2.7 Switching FET
- 8.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Power-Line FET
- 8.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.11 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 8.2.1.2.12 Critical Components for Design
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Application With Basic/Minimal Operation
- 8.2.3
SEPIC Mode Application
- 8.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.2 Coupling Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.5 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.6 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.7 Switching FET
- 8.2.3.2.8 Output Diode
- 8.2.3.2.9 Switching Sense Resistor
- 8.2.3.2.10 Power-Line FET
- 8.2.3.2.11 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.3.2.12 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 8.2.3.2.13 Critical Components for Design
- 8.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
TPS92391 Boost/SEPIC High Dimming Performance LED Driver with Six 200-mA Channels
1 Features
- Input voltage operating range 3 V to 48 V
- Six high-precision current sinks
- Up to 200-mA DC current for each current sink
- Current matching 1% (typical)
- Dimming ratio 32 000:1 using 152-Hz LED output PWM frequency
- Up to 16-bit LED dimming resolution with I2C, or PWM input
- 8 Configurable LED strings configuration
- Auto-phase shift PWM dimming
- 12-bit Analog dimming
- Switching frequency 100 kHz to 2.2 MHz
- Boost spread spectrum for reduced EMI
- Boost sync input to set boost switching frequency from an external clock
- Up to 48-V VOUT boost or SEPIC DC/DC
controller
- Switching frequency 100 kHz to 2.2 MHz
- Boost spread spectrum for reduced EMI
- Boost sync input to set boost switching frequency from an external clock
- Extensive fault diagnostics
2 Applications
- Monitor
- TV
- Medical displays
- Industrial backlighting systems in control panels
- Industrial PC
- Test and measurement equipment
3 Description
The TPS92391 is an automotive high-efficiency LED driver with boost controller. The Six high-precision current sinks support phase shifting that is automatically adjusted based on the number of channels in use. LED brightness can be controlled globally through the I²C interface or PWM input.
The boost controller has adaptive output voltage control based on the headroom voltages of the LED current sinks. This feature minimizes the power consumption by adjusting the boost voltage to the lowest sufficient level in all conditions. A wide-range adjustable frequency allows the TPS92391 to avoid disturbance for AM radio band.
The TPS92391 supports built-in hybrid PWM dimming and analog current dimming, which reduces EMI, extends the LED lifetime, and increases the total optical efficiency.
| PART NUMBER(1) | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS92391 | QFN (32) | 5 mm × 5 mm |
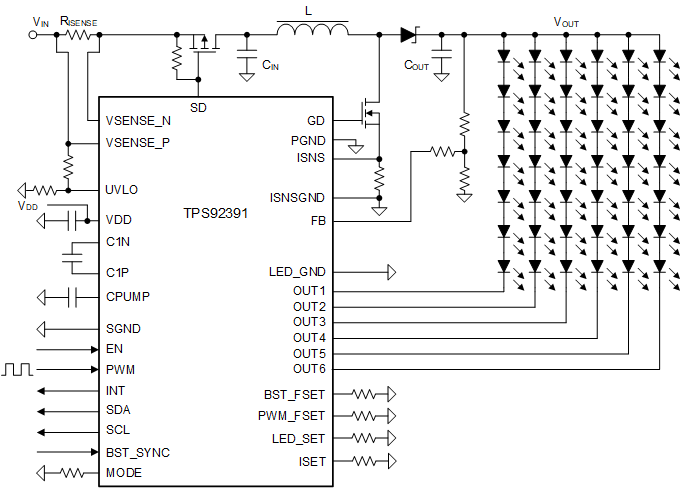 Simplified Schematic
Simplified Schematic System
Efficiency
System
Efficiency4 Revision History
| DATE | REVISION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| March 2021 | * | Initial Release |
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
 Figure 5-1 RHB Package32-PIN QFNTop View
Figure 5-1 RHB Package32-PIN QFNTop View| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | OUT6 | Analog | LED current sink output. If unused tie to ground.. |
| 2 | OUT5 | Analog | LED current sink output. If unused tie to ground.. |
| 3 | OUT4 | Analog | LED current sink output. If unused tie to ground. |
| 4 | LED_GND | GND | LED ground connection. |
| 5 | OUT3 | Analog | LED current sink output. If unused tie to ground. |
| 6 | OUT2 | Analog | LED current sink output. If unused tie to ground. |
| 7 | OUT1 | Analog | LED current sink output. If unused tie to ground. |
| 8 | INT | Analog | Device fault interrupt output, open drain. A 10-kΩ pullup resistor is recommended. |
| 9 | SDA | Analog | SDA for I2C interface. A 10-kΩ pullup resistor is recommended. |
| 10 | SCL | Analog | SCL for I2C interface. A 10-kΩ pullup resistor is recommended. |
| 11 | BST_SYNC | Analog | Input for synchronizing boost. When synchronization is not used, connect this pin to ground to disable spread spectrum or to VDD to enable spread spectrum. |
| 12 | PWM | Analog | PWM input for brightness control. Tie to GND if unused. |
| 13 | SGND | GND | Signal ground. |
| 14 | LED_SET | Analog | LED string configuration through external resistor. Do not leave floating. |
| 15 | PWM_FSET | Analog | LED dimming frequency setup through external resistor. Do not leave floating. |
| 16 | BST_FSET | Analog | Boost switching frequency setup through external resistor. Do not leave floating. |
| 17 | MODE | Analog | Dimming mode setup through external resistor. Do not leave floating. |
| 18 | UVLO | Analog | Input voltage sense for programming input UVLO threshold through external resistor to VIN. |
| 19 | VSENSE_P | Analog | Pin for input voltage detection for OVP protection and positive input for input current sense. |
| 20 | VSENSE_N | Analog | Negative input for input current sense. If input current sense is not used, please tie to VSENSE_P pin. |
| 21 | SD | Analog | Power line FET control. Open Drain output. If unused, leave this pin floating. |
| 22 | VDD | Power | Power supply input for internal analog and digital circuit. Connect a 10-uF capacitor between the VDD pin to GND. |
| 23 | EN | Analog | Enable input. |
| 24 | C1N | Analog | Negative input for charge pump flying capacitor. If feature not used leave this pin floating. |
| 25 | C1P | Analog | Positive input for charge pump flying capacitor. If feature not used leave this pin floating. |
| 26 | CPUMP | Power | Charge pump output pin. Connect to VDD if charge pump is not used. A 4.7-µF decoupling capacitor is recommended on CPUMP pin. |
| 27 | GD | Analog | Gate driver output for external N-FET. |
| 28 | PGND | GND | Power ground. |
| 29 | ISNS | Analog | Boost current sense pin. |
| 30 | ISNSGND | GND | Current sense resistor GND. |
| 31 | ISET | Analog | LED full-scale current setup through external resistor. |
| 32 | FB | Analog | Boost feedback input. |
| DAP | LED_GND | GND | LED ground connection. |