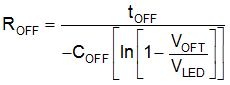SLUSBZ6A April 2016 – August 2016 TPS92515 , TPS92515-Q1 , TPS92515HV , TPS92515HV-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 General Operation
- 8.3.2 Current Sense Comparator
- 8.3.3 OFF Timer
- 8.3.4 OFF-Timer, Shunt FET Dimming or Shunted Output Condition
- 8.3.5 Internal N-channel MOSFET
- 8.3.6 VCC Internal Regulator and Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.7 Analog Adjust Input
- 8.3.8 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.9 Junction Temperature Relative Estimation
- 8.3.10 BOOT and BOOT UVLO
- 8.3.11 PWM (UVLO and Enable)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 General Design Procedure
- 9.2.2 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 9.2.3.2 Calculate OFF-Time Estimate
- 9.2.3.3 Calculate OFF-Time Resistor ROFF
- 9.2.3.4 Calculate the Inductance Value
- 9.2.3.5 Calculate the Sense Resistance
- 9.2.3.6 Calculate Input Capacitance
- 9.2.3.7 Verify Peak Current for Inductor Selection
- 9.2.3.8 Calculate Output Capacitance
- 9.2.3.9 Calculate UVLO Resistance Values
- 9.2.4 Application Curves
- 9.3 Dos and Don'ts
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGQ|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGQ|10
Orderable Information
8.3.3 OFF Timer
The converter OFF-time is controlled via the COFF pin. The output voltage charges a capacitor to 1 V through a resistor creating a delay. Deriving the OFF-time from the output voltage creates a ramp representing the inductor current. If the output voltage cannot be used, another voltage fixed source may be implemented to create a truly constant OFF-time. However, this configuration reduces output current accuracy. When the device is first enabled (when VCC rises above the VCC undervoltage lockout threshold) the pull-down on the COFF pin is disabled, allowing a voltage to build up on the COFF capacitor. At the same time, the maximum off timer begins. If the voltage source is sufficiently above the 1-V threshold, the ramp becomes linear and approximates the inductor current. If the 1-V nominal COFF threshold is reached, or the COFF capacitor charge time duration is greater than tOFF(max) (maximum OFF-time timer expires), a switching cycle starts.
The timer reaches the maximum OFF-time during start-up when the output is completely discharged or when shunt FET dimming and the shunt FET shunts the output for the required period.
Equation 7 calculates ROFF for a desired OFF-time.