SLUSBP5E March 2014 – July 2018 TPS92601-Q1 , TPS92602-Q1
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope-Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Boost-Current Limit
- 7.3.4 Oscillator and PLL
- 7.3.5 Control Loop Compensation
- 7.3.6 LED Open-Circuit Detection
- 7.3.7 Output Short-Circuit and Overcurrent Detection
- 7.3.8 Measuring LED Current During a Non-Failure Condition
- 7.3.9 LED Dimming Options
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Boost Regulator With Separate or Paralleled Channels
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Maximum Output-Current Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Overvoltage-Protection Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.4 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.1.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.10 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2
Boost-to-Battery Regulator
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2.2 Maximum Output-Current Set Point
- 8.2.2.2.3 Output Overvoltage-Protection Set Point
- 8.2.2.2.4 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.2.2.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.9 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.2.2.10 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.2.2.11 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.2.3 TPS92602y-Q1 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Boost Regulator With Separate or Paralleled Channels
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
7.3.9.2 PWM Dimming
To change the brightness of an LED string by a certain magnitude without affecting the lighting-color of the LED, it is necessary to use PWM dimming topology. Turning the LEDs ON and OFF at a certain frequency with a certain duty cycle reduces the brightness without changing the LED current (so not affecting the color).
The integrated high-side PMOS-FET gate driver turns the LED string ON and OFF following the supplied signal frequency and duty cycle on the PWMIN pin. During the OFF time of the FET, the device stops the internal control loop by disconnecting the loop internally and then stores the value of the compensation network. This technique allows fastest recovery of the regulator with the following ON time, as the control loop restarts from the point at which it stopped. The average LED current during ON time is almost the same as the LED current with no PWM dimming (duty cycle 100%). For very low duty cycles, the time required by the controller to ramp up the inductor current form 0 A becomes more significant relative to the overall ON time, leading to lower average current. So for very low duty cycles, the relation between average current and duty cycle is no longer linear.
One must maintain a minimum on-time in order for PWM dimming to operate in the linear region of its transfer function. Because of disabling the controller during dimming, the PWM pulse must be long enough that the energy intercepted from the input is greater than or equal to the energy being put into the LEDs. For boost and boost-to-battery topologies, the minimum ON time (in seconds) for which the PWM dimming operates in the linear region is:
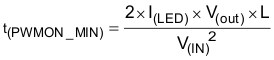
To ensure that the applied dimming-pulse duration matches with the effective dimming-pulse duration, TI recommends synchronizing the dimming pulses with the switching clock of the boost converter. Choose the external inductor and output capacitors according to the requirements for the minimum duty cycle.