SLUSCX8C March 2019 – March 2021 TPS92682-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Device Enable
- 7.3.2 Internal Regulator and Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.3 Oscillator
- 7.3.4 Spread Spectrum Function
- 7.3.5 Gate Driver
- 7.3.6 Rail-to-Rail Current Sense Amplifier
- 7.3.7 Transconductance Error Amplifier
- 7.3.8 Switch Current Sense
- 7.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.10 ILED Setting in CC Mode
- 7.3.11 Output Voltage Setting in CV Mode
- 7.3.12 PWM Dimming
- 7.3.13 P-Channel FET Gate Driver Output
- 7.3.14 Soft Start
- 7.3.15 Two-Phase Operation
- 7.3.16 Faults and Diagnostics
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
TPS92682 Registers
- 7.6.1 EN Register
- 7.6.2 CFG1 Register
- 7.6.3 CFG2 Register
- 7.6.4 SWDIV Register
- 7.6.5 ISLOPE Register
- 7.6.6 FM Register
- 7.6.7 SOFTSTART Register
- 7.6.8 CH1IADJ Register
- 7.6.9 CH2IADJ Register
- 7.6.10 PWMDIV Register
- 7.6.11 CH1PWML Register
- 7.6.12 CH1PWMH Register
- 7.6.13 CH2PWML Register
- 7.6.14 CH2PWMH Register
- 7.6.15 ILIM Register
- 7.6.16 IFT Register
- 7.6.17 MFT Register
- 7.6.18 FLT1 Register (read only)
- 7.6.19 FLT2 Register (read only)
- 7.6.20 FEN1 Register
- 7.6.21 FEN2 Register
- 7.6.22 FLATEN Register
- 7.6.23 OV Register
- 7.6.24 LHCFG Register
- 7.6.25 LHCH1IADJ Register
- 7.6.26 LHCH2IADJ Register
- 7.6.27 LHCH1PWML Register
- 7.6.28 LHCH1PWMH Register
- 7.6.29 LHCH2PWML Register
- 7.6.30 LHCH2PWMH Register
- 7.6.31 LHILIM Register
- 7.6.32 LHIFT Register
- 7.6.33 LHMFT Register
- 7.6.34 LHFEN1 Register
- 7.6.35 LHFEN2 Register
- 7.6.36 LHFLATEN Register
- 7.6.37 LHOV Register
- 7.6.38 CAL Register
- 7.6.39 RESET Register
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information General Design Considerations
- 8.2 Application Information CC Mode
- 8.3 Typical Application CV Mode
- 8.4
Typical Application CC Mode
- 8.4.1 CC Boost Design Requirements
- 8.4.2
CC Boost Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.4.2.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 8.4.2.2 Setting Switching Frequency
- 8.4.2.3 Setting Dither Modulation Frequency
- 8.4.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.4.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.2.7 Main N-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.4.2.8 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.4.2.9 Setting ILED and Selecting RCS
- 8.4.2.10 Setting Switch Current Limit
- 8.4.2.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.4.2.12 Compensator Parameters
- 8.4.2.13 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.4.2.14 Series P-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.4.3 CC Buck-Boost Design Requirements
- 8.4.4
CC Buck-Boost Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.4.4.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 8.4.4.2 Setting Switching Frequency
- 8.4.4.3 Setting Dither Modulation Frequency
- 8.4.4.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.4.4.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.4.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.4.7 Main N-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.4.4.8 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.4.4.9 Setting ILED and Selecting RCS
- 8.4.4.10 Setting Switch Current Limit
- 8.4.4.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.4.4.12 Compensator Parameters
- 8.4.4.13 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.4.5 PWM Dimming Consideration
- 8.4.6 Application Curves
- 8.5
Typical Application CV Mode
- 8.5.1 CV Design Requirements
- 8.5.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.5.2.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 8.5.2.2 Setting Switching Frequency
- 8.5.2.3 Setting Dither Modulation Frequency
- 8.5.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.5.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.5.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.5.2.7 Main N-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.5.2.8 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.5.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 8.5.2.10 Setting Switch Current Limit
- 8.5.2.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.5.2.12 Compensator Parameters
- 8.5.2.13 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.5.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.5.1 Serial Interface
The SPI bus consists of four signals: SSN, SCK, MOSI, and MISO. The SSN, SCK, and MOSI pins are TTL inputs into the TPS92682-Q1 while the MISO pin is an open-drain output. The SPI bus can be configured for both star-connect and daisy chain hardware connections.
A bus transaction is initiated by the MCU creating a falling edge on SSN. While SSN is low, the input data present on the MOSI pin is sampled on the rising edge of SCK, with MS-bit first. The output data is asserted on the MISO pin at the falling edge of the SCK. Figure 7-22 shows the data transition and sampling edges of SCK.
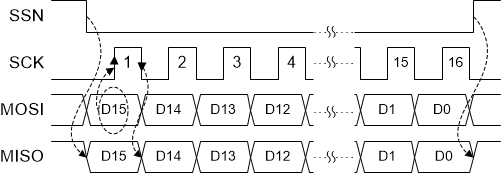 Figure 7-22 SPI DATA Format
Figure 7-22 SPI DATA FormatA valid transfer requires a non-zero integer multiple of 16 SCK cycles (16, 32, 48, and so forth). If SSN is pulsed low and no SCK pulses are issued before SSN rises, a SPI error is reported. Similarly, if SSN is raised before the 16th rising edge of SCK, the transfer is aborted and a SPI error is reported. If SSN is held low after the 16th falling edge of SCK and additional SCK edges occur, the data continues to flow through the TPS92682-Q1 shift register and out of the MISO pin. When SSN transitions from low-to-high, the internal digital block decodes the most recent 16 bits that were received prior to the SSN rising edge.
SSN must transition to high after a multiple of 16 SCK cycles for a transaction to be valid and does not set the SPI error bit. In the case of a write transaction, the TPS92682-Q1 logic performs the requested operation when SSN transitions high. In the case of a read transaction, the read data is output during the next frame, regardless of whether a SPI error has occurred.
The data bit on MOSI is shifted into an internal 16-bit shift register (MS-bit first) while data is simultaneously shifted out of the MISO pin. While SSN is high (bus idle), MISO is tri-stated by the open-drain driver. While SSN is low, MISO is driven according to the 16-bit data pattern being shifted out based on the prior received command. At the falling edge of the SSN, to begin a new transaction, MISO is driven with the MS-bit of the outbound data, and is updated on each subsequent falling edge of SCK.