SLVSFU7B July 2022 – April 2024 TPS929240-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Device Bias and Power
- 6.3.2 Constant Current Output
- 6.3.3 PWM Dimming
- 6.3.4 FAIL-SAFE State Operation
- 6.3.5 On-Chip, 8-Bit, Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 6.3.6
Diagnostic and Protection in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.1 VBAT Undervoltage Lockout Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.2 Low-Supply Warning Diagnostics in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.3 Supply Undervoltage Diagnostics in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.4 Reference Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.5 Pre-Thermal Warning in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.6 Overtemperature Protection in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.7 Overtemperature Shutdown in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.8 LED Open-Circuit Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.9 LED Short-Circuit Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.10 Single-LED Short-Circuit Detection in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.11 EEPROM CRC Error in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.12 Communication Loss Diagnostic in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.13 Fault Masking in NORMAL state
- 53
- 6.3.7
Diagnostic and Protection in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.1 Supply Undervoltage Lockout Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.2 Low-Supply Warning Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.3 Supply Undervoltage Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE State
- 6.3.7.4 Reference Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.5 Pre-Thermal Warning in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.6 Overtemperature Protection in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.7 Overtemperature Shutdown in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.8 LED Open-Circuit Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.9 LED Short-Circuit Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.10 Single-LED Short-Circuit Detection in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.11 EEPROM CRC Error in FAIL-SAFE State
- 6.3.7.12 Fault Masking in FAIL-SAFE state
- Diagnostics Table in FAIL-SAFE State
- 6.3.8 OFAF Setup In FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.9 ERR Output
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6 Register Maps
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCP|38
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DCP|38
Orderable Information
6.3.5 On-Chip, 8-Bit, Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
The TPS929240-Q1 has integrated a successive-approximation-register (SAR) ADC for diagnostics.
To manually read the voltage of an ADC channel as listed in the below table, the user must write the 5-bit register ADCCHSEL to select channel. After ADCCHSEL register is written, the one-time ADC conversion starts and clears FLAG_ADCDONE register. As long as the ADC conversion is completed, the ADC result is available in an 8-bit register ADC_OUT and sets FLAG_ADCDONE to 1. Reading the ADC_OUT register also clears FLAG_ADCDONE and starts a new ADC conversion. The FLAG_ADCDONE is set to 0 after reading completion. TI recommends to write the ADCCHSEL register after turning on or changing current output duty cycle at assigned OUTXn with delay of one PWM cycle time which is set by the PWMFREQ register.
The analog value can be calculated based on the read back binary code with the below equation and table.
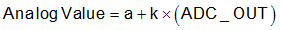
where
- ADC_OUT is a decimal number from 0 to 255.
| CHANNEL NO. | ADCCHSEL | NAME | ADC CALCULATION PARAMETER (a) | ADC CALCULATION PARAMETER (k) | COMMENT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 00h | REF | 0.007V | 0.0101V/LSB | Reference voltage | ||
| 1 | 01h | SUPPLY | 0.1346V | 0.1608V/LSB | SUPPLY voltage | ||
| 2 | 02h | VLDO | 0.0465V | 0.022V/LSB | 5V LDO output voltage | ||
| 3 | 03h | TEMPSNS | –270.312°C | 2.688°C/LSB | Internal temperature sensor | ||
| 4 | 04h | IREF | 0.9969µA | 0.996µA/LSB | Reference current | ||
| 5 | 05h | VBAT | 0.1346V | 0.1608V/LSB | VBAT voltage | ||
| 6 | 06h | MAXOUT | 0.1346V | 0.1608V/LSB | Maximum channel output voltage | ||
| 7 | 07h | RESERVED | RESERVED | RESERVED | RESERVED | ||
| 8 | 08h | OUTA0 | 0.1346V | 0.1608V/LSB | Output voltage channel A0 | ||
| 9 | 09h | OUTA1 | Output voltage channel A1 | ||||
| 10 | 0Ah | OUTA2 | Output voltage channel A2 | ||||
| 11 | 0Bh | OUTB0 | Output voltage channel B0 | ||||
| 12 | 0Ch | OUTB1 | Output voltage channel B1 | ||||
| 13 | 0Dh | OUTB2 | Output voltage channel B2 | ||||
| 14 | 0Eh | OUTC0 | Output voltage channel C0 | ||||
| 15 | 0Fh | OUTC1 | Output voltage channel C1 | ||||
| 16 | 10h | OUTC2 | Output voltage channel C2 | ||||
| 17 | 11h | OUTD0 | Output voltage channel D0 | ||||
| 18 | 12h | OUTD1 | Output voltage channel D1 | ||||
| 19 | 13h | OUTD2 | Output voltage channel D2 | ||||
| 20 | 14h | OUTE0 | Output voltage channel E0 | ||||
| 21 | 15h | OUTE1 | Output voltage channel E1 | ||||
| 22 | 16h | OUTE2 | Output voltage channel E2 | ||||
| 23 | 17h | OUTF0 | Output voltage channel F0 | ||||
| 24 | 18h | OUTF1 | Output voltage channel F1 | ||||
| 25 | 19h | OUTF2 | Output voltage channel F2 | ||||
| 26 | 1Ah | OUTG0 | Output voltage channel G0 | ||||
| 27 | 1Bh | OUTG1 | Output voltage channel G1 | ||||
| 28 | 1Ch | OUTG2 | Output voltage channel G2 | ||||
| 29 | 1Dh | OUTH0 | Output voltage channel H0 | ||||
| 30 | 1Eh | OUTH1 | Output voltage channel H1 | ||||
| 31 | 1Fh | OUTH2 | Output voltage channel H2 | ||||