DLPS202A October 2020 – August 2024 TPS99000S-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics—Transimpedance Amplifier Parameters
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics—Digital to Analog Converters
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics—Analog to Digital Converter
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics—FET Gate Drivers
- 5.9 Electrical Characteristics—Photo Comparator
- 5.10 Electrical Characteristics—Voltage Regulators
- 5.11 Electrical Characteristics—Temperature and Voltage Monitors
- 5.12 Electrical Characteristics—Current Consumption
- 5.13 Power-Up Timing Requirements
- 5.14 Power-Down Timing Requirements
- 5.15 Timing Requirements—Sequencer Clock
- 5.16 Timing Requirements—Host and Diagnostic Port SPI Interface
- 5.17 Timing Requirements—ADC Interface
- 5.18 Switching Characteristics
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1
Illumination Control
- 6.3.1.1 Illumination System High Dynamic Range Dimming Overview
- 6.3.1.2 Illumination Control Loop
- 6.3.1.3 Continuous Mode Operation
- 6.3.1.4
Discontinuous Mode Operation
- 6.3.1.4.1 Discontinuous Mode Pulse Width Limit
- 6.3.1.4.2 COMPOUT_LOW Timer in Discontinuous Operation
- 6.3.1.4.3 Dimming Within Discontinuous Operation Range
- 6.3.1.4.4 Multiple Pulse Heights to Increase Bit Depth
- 6.3.1.4.5 TIA Gain Adjustment
- 6.3.1.4.6 Current Limit in Discontinuous Mode
- 6.3.1.4.7 CMODE Big Cap Mode in Discontinuous Operation
- 6.3.2 Over-Brightness Detection
- 6.3.3 Analog to Digital Converter
- 6.3.4 Power Sequencing and Monitoring
- 6.3.5 DMD Mirror Voltage Regulator
- 6.3.6 Low Dropout Regulators
- 6.3.7 System Monitoring Features
- 6.3.8 Communication Ports
- 6.3.1
Illumination Control
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Register Maps
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PZP|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PZP|100
Orderable Information
7.2.1.2.5 Discontinuous Mode Photo Feedback Considerations
System designs should consider the amount of additional capacitance placed in parallel with the photodiode, and the capacitance of the photodiode itself. While the TPS99000S-Q1 is designed to function with a very wide range of total capacitance, the lowest light level brightness performance is directly impacted by this capacitance. Higher TIA1 input capacitance will result in a brighter minimum brightness achievable by the system due to this light pulse overrun phenomenon. This results in a reduction of the dimming range. (For highest performance, a system designer can minimize total capacitance of the photodiode, photodiode cable, and connector system).
The leading edge of the light pulse in discontinuous mode is controlled by the charging rate of the capacitance in parallel with the LED. The photo feedback DAC sets the threshold to turn on the shunt FET which shunts the current away from the LED. Latency in the photo feedback loop will result in the light climbing higher than the threshold as shown in Figure 7-5. The amount of light that occurs after the threshold is reached (shown as hashed green area) is the majority of the light at the lowest discontinuous mode brightness levels. Figure 7-5 also shows that a reduction in photo feedback DAC level by a factor of two does not reduce the total light pulse power by a factor of two because of the light that occurs after the threshold. The amount of light overrun after the threshold is a function of the photo feedback latency, inductor initial current, capacitance in parallel with the LED, LED voltage to current characteristics and shunt FET timing.
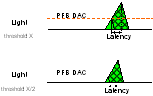 Figure 7-5 Discontinuous Pulse Overrun
Figure 7-5 Discontinuous Pulse Overrun