SNVSCI1A October 2023 – December 2023 TPSM365R1 , TPSM365R15
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Enable, Shutdown, and Start-Up
- 7.3.2 External CLK SYNC (With MODE/SYNC)
- 7.3.3 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
- 7.3.4 Power-Good Output Operation
- 7.3.5 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and VOUT/FB Input
- 7.3.6 Bootstrap Voltage and VBOOT-UVLO (BOOT Terminal)
- 7.3.7 Output Voltage Selection
- 7.3.8 Spread Spectrum
- 7.3.9 Soft Start and Recovery from Dropout
- 7.3.10 Current Limit and Short Circuit
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.12 Input Supply Current
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Choosing the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Setting the Output Voltage
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 VCC
- 8.2.2.7 CFF Selection
- 8.2.2.8 External UVLO
- 8.2.2.9 Power-Good Signal
- 8.2.2.10 Maximum Ambient Temperature
- 8.2.2.11 Other Connections
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Best Design Practices
- 8.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.5 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RDN|11
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.7 Output Voltage Selection
In the TPSM365R1x, each variant can be configured as a fixed output voltage or an adjustable output voltage. During device initialization the device configures the target output voltage to an internally selected value or an adjustable version by detecting if feedback resistors are present. When configuring the output voltage to be fixed value, simply connect the VOUT/FB pin to the system output voltage node. See Section 4 for the fixed output voltage setting of each variant.
To configure an adjustable output voltage,
external feedback resistors are required as shown in Figure 7-8. By connecting external feedback resistors with a parallel resistance greater than 5 kΩ
but less than or equal to
10 kΩ (see Equation 2) the output voltage is set according as needed. The internal voltage reference is 1
V. Refer to Section 8.2.2.3 for more details on how to adjust the output voltage.
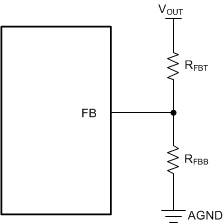 Figure 7-8 Setting Output
Voltage for Adjustable Output Variant
Figure 7-8 Setting Output
Voltage for Adjustable Output Variant- RFBT is the top resistor of the feedback divider
- RFBB is the bottom resistor of the feedback divider
When configured in adjustable output voltage mode, an addition feed-forward capacitor, CFF, in parallel with the RFBT, can be used to optimize the phase margin and transient response. See Section 8.2.2.7 for more details. No additional resistor divider or feed-forward capacitor, CFF, is needed in fixed-output variants.
Please refer to Table 7-4 for selecting passive component values for typical, output voltages.
| VOUT (V) | RFBT (kΩ) | RFBB (kΩ) | RECOMMENDED FSW (kHz) | COUT(MIN) (µF) (EFFECTIVE) | VOUT (V) | RFBT (kΩ) | RFBB (kΩ) | RECOMMENDED FSW (kHz) | COUT(MIN) (µF) (EFFECTIVE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 10 | DNP | 300 | 47 | 3.3 | 33.2 | 14.3 | 1000 | 4.7 | |
| 1.2 | 12.1 | 60.4 | 300 | 47 | 5.0 | 49.9 | 12.4 | 1000 | 4.7 | |
| 1.5 | 15 | 30.1 | 400 | 33 | 7.5 | 75 | 11.5 | 1500 | 2.2 | |
| 1.8 | 18.2 | 22.6 | 500 | 33 | 10 | 100 | 11 | 1800 | 2.2 | |
| 2.0 | 20 | 20 | 500 | 22 | 12 | 121 | 10.7 | 2200 | 2.2 | |
| 2.5 | 24.9 | 16.5 | 500 | 22 | 13 | 130 | 10.7 | 2200 | 2.2 | |
| 3.0 | 30 | 15 | 800 | 4.7 | 15 | 150 | 10.7 | 2200 | 2.2 |