SLLSEV7E August 2016 – March 2023 TUSB546-DCI
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 General Register (address = 0x0A) [reset = 00000001]
- 7.6.2 DisplayPort Control/Status Registers (address = 0x10) [reset = 00000000]
- 7.6.3 DisplayPort Control/Status Registers (address = 0x11) [reset = 00000000]
- 7.6.4 DisplayPort Control/Status Registers (address = 0x12) [reset = 00000000]
- 7.6.5 DisplayPort Control/Status Registers (address = 0x13) [reset = 00000000]
- 7.6.6 USB3.1 Control/Status Registers (address = 0x20) [reset = 00000000]
- 7.6.7 USB3.1 Control/Status Registers (address = 0x21) [reset = 00000000]
- 7.6.8 USB3.1 Control/Status Registers (address = 0x22) [reset = 00000100]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RNQ|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
A typical usage of the TUSB564-DCI device is shown in Figure 8-2. The device can be controlled either through its GPIO pins or through its I2C interface. In the example shown below, a Type-C PD controller is used to configure the device through the I2C interface. When configured for I2C mode, pins 29 (RSVD1) and 32 (RSVD2) can be left unconnected. In I2C mode, the equalization settings for each receiver can be independently controlled through I2C registers. For this reason, all of the equalization pins (EQ[1:0], SSEQ[1:0], and DPEQ[1:0]) can be left unconnected. If these pins are left unconnected, the TUSB546-DCI 7-bit I2C target address will be 0x12 because both DPEQ/A1 and SSEQ0/A0 will be at pin level "F". If a different I2C target address is desired, DPEQ/A1 and SSEQ0/A0 pins should be set to a level which produces the desired I2C target address.
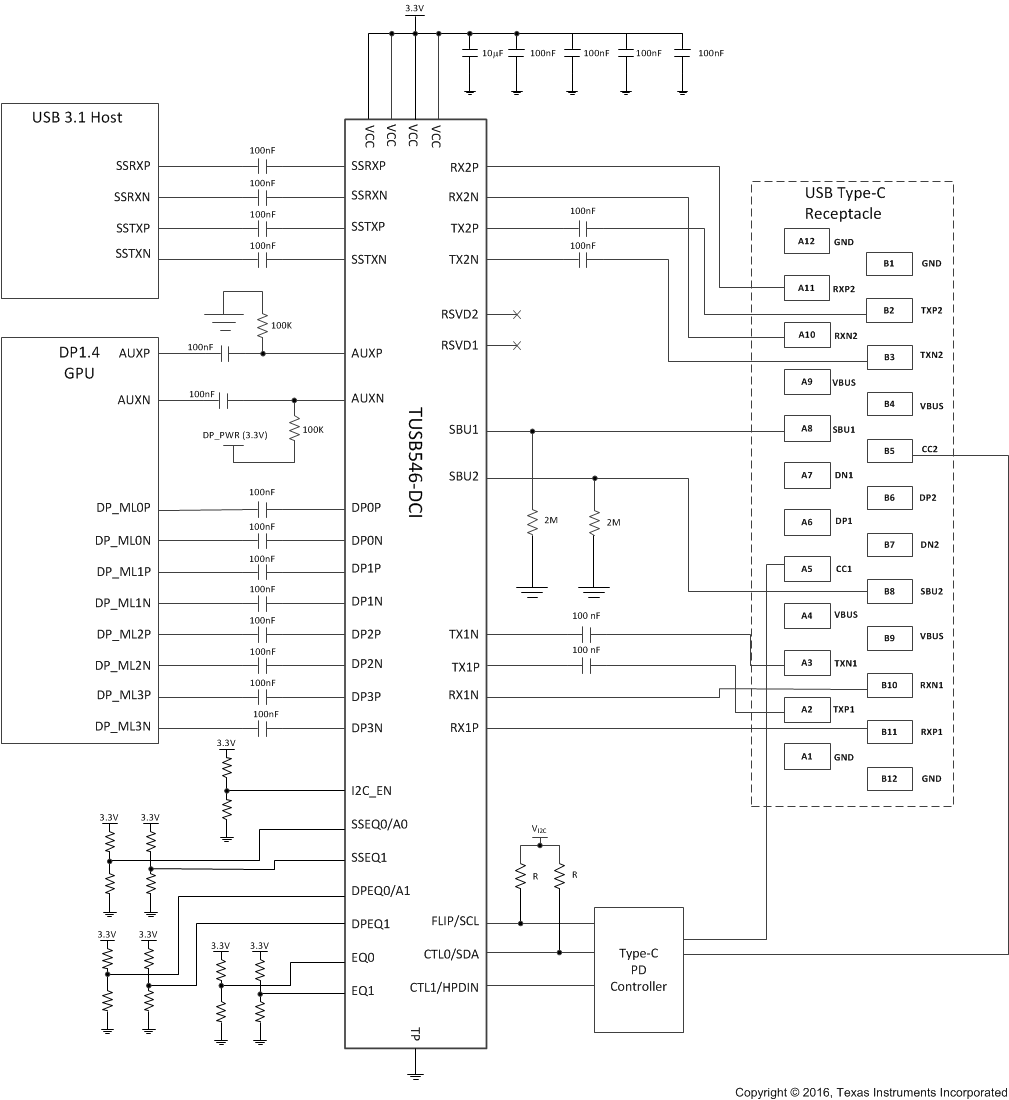 Figure 8-2 Application Circuit
Figure 8-2 Application Circuit