SLLSE76Q March 2011 – March 2024 TUSB7320 , TUSB7340
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 3.3-V I/O Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Input Clock Specification
- 5.7 Input Clock 1.8-V DC Characteristics
- 5.8 Crystal Specification
- 5.9 TUSB7320 Power Consumption
- 5.10 TUSB7340 Power Consumption
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
-
8 Register Maps
- 8.1
Classic PCI Configuration Space
- 8.1.1 The PCI Configuration Map
- 8.1.2 Vendor ID Register
- 8.1.3 Device ID Register
- 8.1.4 Command Register
- 8.1.5 Status Register
- 8.1.6 Class Code and Revision ID Register
- 8.1.7 Cache Line Size Register
- 8.1.8 Latency Timer Register
- 8.1.9 Header Type Register
- 8.1.10 BIST Register
- 8.1.11 Base Address Register 0
- 8.1.12 Base Address Register 1
- 8.1.13 Base Address Register 2
- 8.1.14 Base Address Register 3
- 8.1.15 Subsystem Vendor ID Register
- 8.1.16 Subsystem ID Register
- 8.1.17 Capabilities Pointer Register
- 8.1.18 Interrupt Line Register
- 8.1.19 Interrupt Pin Register
- 8.1.20 Min Grant Register
- 8.1.21 Max Latency Register
- 8.1.22 Capability ID Register
- 8.1.23 Next Item Pointer Register
- 8.1.24 Power Management Capabilities Register
- 8.1.25 Power Management Control/Status Register
- 8.1.26 Power Management Bridge Support Extension Register
- 8.1.27 Power Management Data Register
- 8.1.28 MSI Capability ID Register
- 8.1.29 Next Item Pointer Register
- 8.1.30 MSI Message Control Register
- 8.1.31 MSI Lower Message Address Register
- 8.1.32 MSI Upper Message Address Register
- 8.1.33 MSI Message Data Register
- 8.1.34 Serial Bus Release Number Register (SBRN)
- 8.1.35 Frame Length Adjustment Register (FLADJ)
- 8.1.36 PCI Express Capability ID Register
- 8.1.37 Next Item Pointer Register
- 8.1.38 PCI Express Capabilities Register
- 8.1.39 Device Capabilities Register
- 8.1.40 Device Control Register
- 8.1.41 Device Status Register
- 8.1.42 Link Capabilities Register
- 8.1.43 Link Control Register
- 8.1.44 Link Status Register
- 8.1.45 Device Capabilities 2 Register
- 8.1.46 Device Control 2 Register
- 8.1.47 Link Control 2 Register
- 8.1.48 Link Status 2 Register
- 8.1.49 Serial Bus Data Register
- 8.1.50 Serial Bus Index Register
- 8.1.51 Serial Bus Target Address Register
- 8.1.52 Serial Bus Control and Status Register
- 8.1.53 GPIO Control Register
- 8.1.54 GPIO Data Register
- 8.1.55 MSI-X Capability ID Register
- 8.1.56 Next Item Pointer Register
- 8.1.57 MSI-X Message Control Register
- 8.1.58 MSI-X Table Offset and BIR Register
- 8.1.59 MSI-X PBA Offset and BIR Register
- 8.1.60 Subsystem Access Register
- 8.1.61 General Control 0 Register
- 8.1.62 General Control 1 Register
- 8.1.63 General Control 2 Register
- 8.1.64 USB Control Register
- 8.1.65 De-Emphasis and Swing Control Register
- 8.1.66 Equalizer Control Register
- 8.1.67 Custom PHY Transmit/Receive Control Register
- 8.2
PCI Express Extended Configuration Space
- 8.2.1 The PCI Express Extended Configuration Map
- 8.2.2 Advanced Error Reporting Capability Register
- 8.2.3 Next Capability Offset / Capability Version Register
- 8.2.4 Uncorrectable Error Status Register
- 8.2.5 Uncorrectable Error Mask Register
- 8.2.6 Uncorrectable Error Severity Register
- 8.2.7 Correctable Error Severity Register
- 8.2.8 Correctable Error Mask Register
- 8.2.9 Advanced Error Capabilities and Control Register
- 8.2.10 Header Log Register
- 8.2.11 Device Serial Number Capability ID Register
- 8.2.12 Next Capability Offset/Capability Version Register
- 8.2.13 Device Serial Number Register
- 8.3
xHCI Memory Mapped Register Space
- 8.3.1 The xHCI Register Map
- 8.3.2
Host Controller Capability Registers
- 8.3.2.1 Capability Registers Length
- 8.3.2.2 Host Controller Interface Version Number
- 8.3.2.3 Host Controller Structural Parameters 1
- 8.3.2.4 Host Controller Structural Parameters 2
- 8.3.2.5 Host Controller Structural Parameters 3
- 8.3.2.6 Host Controller Capability Parameters
- 8.3.2.7 Doorbell Offset
- 8.3.2.8 Runtime Register Space Offset
- 8.3.3
Host Controller Operational Registers
- 8.3.3.1 USB Command Register
- 8.3.3.2 USB Command Register
- 8.3.3.3 USB Status Register
- 8.3.3.4 Page Size Register
- 8.3.3.5 Device Notification Control Register
- 8.3.3.6 Command Ring Control Register
- 8.3.3.7 Device Context Base Address Array Pointer Register
- 8.3.3.8 Configure Register
- 8.3.3.9 Port Status and Control Register
- 8.3.3.10 Port PM Status and Control Register (USB 3.0 Ports)
- 8.3.3.11 Port PM Status and Control Register (USB 2.0 Ports)
- 8.3.3.12 Port Link Info Register
- 8.3.4 Host Controller Runtime Registers
- 8.3.5 Host Controller Doorbell Registers
- 8.3.6
xHCI Extended Capabilities Registers
- 8.3.6.1 USB Legacy Support Capability Register
- 8.3.6.2 USB Legacy Support Control/Status Register
- 8.3.6.3 xHCI Supported Protocol Capability Register (USB 2.0)
- 8.3.6.4 xHCI Supported Protocol Name String Register (USB 2.0)
- 8.3.6.5 xHCI Supported Protocol Port Register (USB 2.0)
- 8.3.6.6 xHCI Supported Protocol Capability Register (USB 3.0)
- 8.3.6.7 xHCI Supported Protocol Name String Register (USB 3.0)
- 8.3.6.8 xHCI Supported Protocol Port Register (USB 3.0)
- 8.4 MSI-X Memory Mapped Register Space
- 8.5 The MSI-X Table and PBA in Memory Mapped Register Space
- 8.1
Classic PCI Configuration Space
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RKM|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RKM|100
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
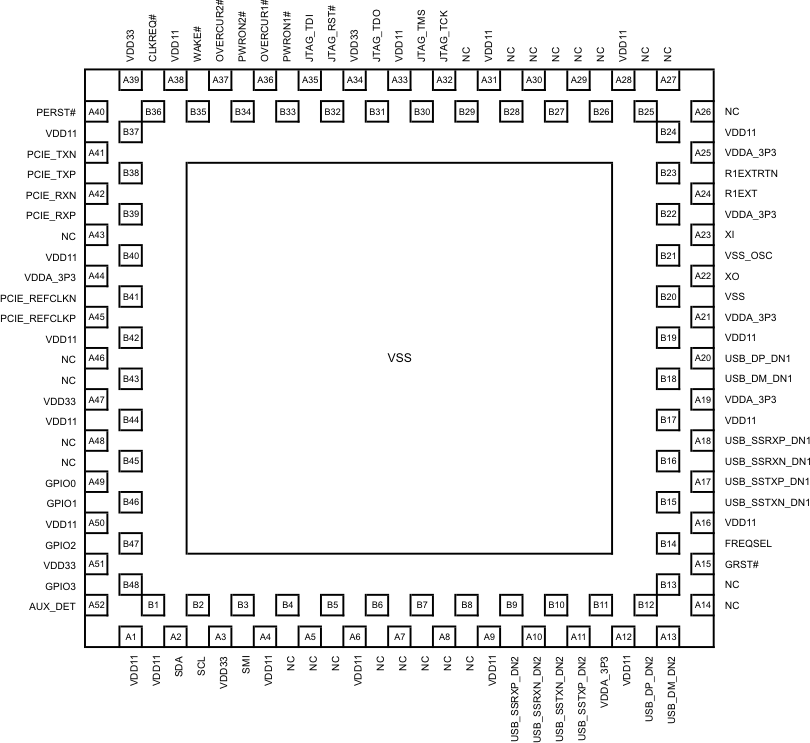 Figure 4-1 RKM Package,100-Pin WQFN-MR Exposed
Thermal PadTUSB7320 (Top
View)
Figure 4-1 RKM Package,100-Pin WQFN-MR Exposed
Thermal PadTUSB7320 (Top
View)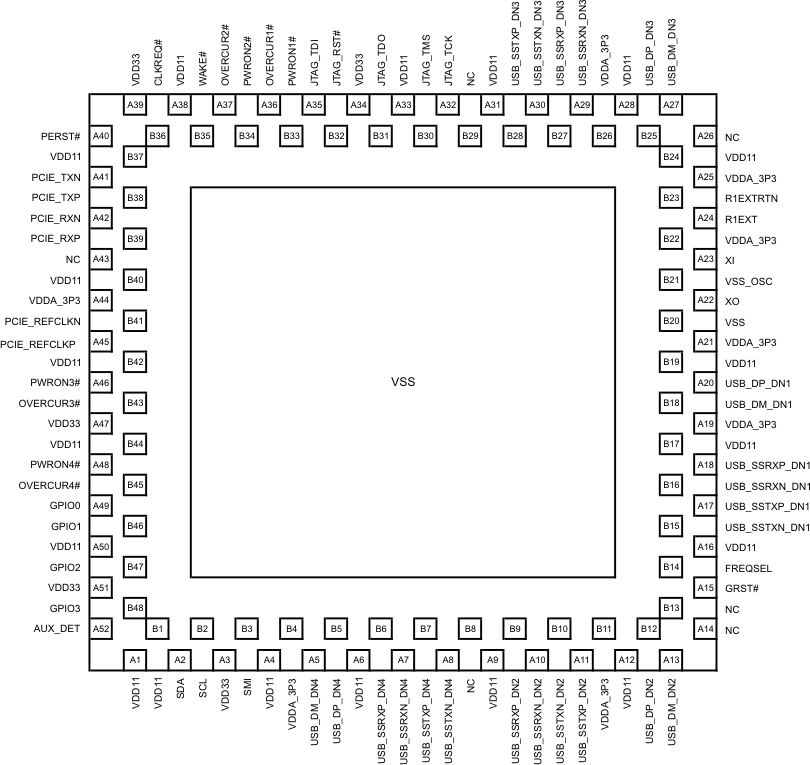 Figure 4-2 RKM Package,100-Pin WQFN-MR Exposed
Thermal PadTUSB7340 (Top
View)
Figure 4-2 RKM Package,100-Pin WQFN-MR Exposed
Thermal PadTUSB7340 (Top
View)The following tables give a description of the terminals. These terminals are grouped in tables by functionality. Each table includes the terminal name, terminal number, I/O type, and terminal description.
| TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| I | Input |
| O | Output |
| I/O | Input/Output |
| PD, PU | Internal pull-down/pullup |
| S | Strapping pin |
| P | Power supply |
| G | Ground |
Table 4-1 Clock and Reset Signals
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | TUSB7320 | TUSB7340 | ||
| CLOCK AND RESET SIGNALS | ||||
| GRST# | A15 | A15 | I PU | Global power reset. This reset brings all of the TUSB73x0 internal registers to their default states. When GRST# is asserted, the device is completely nonfunctional. GRST# should be asserted until all power rails are valid at the device. If a 24 MHz or 48 MHz reference clock is used instead of a crystal, GRST# must remain asserted until the 24 MHz or 48 MHz clock is stable. |
| XI | A23 | A23 | I | Crystal input. This terminal is the crystal input for the internal oscillator. The input may alternately be driven by the output of an external oscillator. When using a crystal a 2-MΩ feedback resistor is required between XI and XO. |
| XO | A22 | A22 | O | Crystal output. This terminal is crystal output for the internal oscillator. If XI is driven by an external oscillator this pin may be left unconnected. When using a crystal a 2-MΩ feedback resistor is required between XI and XO. |
| FREQSEL | B14 | B14 | I | Frequency select. This terminal indicates the oscillator input frequency and is used to configure the correct PLL multiplier. This pin should be set low for normal operation. |
| PCIE_REFCLKP | A45 | A45 | I | PCI Express Reference Clock. PCIE_REFCLKP and PCIE_REFCLKN comprise the differential input pair for the 100-MHz system reference clock. |
| PCIE_REFCLKN | B41 | B41 | I | |
| PERST# | A40 | A40 | I | PCI Express Reset Input. The PERST# signal is used to signal when the system power is stable. The PERST# signal is also used to generate an internal power on reset |
| PCI EXPRESS SIGNALS | ||||
| PCIE_TXP | B38 | B38 | O | PCI Express transmitter differential pair (positive). |
| PCIE_TXN | A41 | A41 | O | PCI Express transmitter differential pair (negative). |
| PCIE_RXP | B39 | B39 | I | PCI Express receiver differential pair (positive). |
| PCIE_RXN | A42 | A42 | I | PCI Express receiver differential pair (negative). |
| WAKE# | B35 | B35 | O | Wake. Wake is an active low signal that is driven low to reactivate the PCI Express link hierarchy’s main power rails and reference clocks. Note: WAKE# is not a failsafe I/O and should not be connected to a 3.3-V auxiliary supply while VDD33 is not present. |
| CLKREQ# | B36 | B36 | O | PCI Express REFCLK Request signal. Note: CLKREQ# is not a failsafe I/O and should not be connected to a 3.3-V auxiliary supply while VDD33 is not present. |
| USB DOWNSTREAM SIGNALS | ||||
| USB_SSTXP_DN1 | A17 | A17 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 1 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSTXN_DN1 | B15 | B15 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 1 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXP_DN1 | A18 | A18 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 1 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXN_DN1 | B16 | B16 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 1 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_DP_DN1 | A20 | A20 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (positive). |
| USB_DM_DN1 | B18 | B18 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (negative). |
| PWRON1# | B33 | B33 | O PD | USB DS Port 1 Power On Control for Downstream Power. The terminal is used to control the downstream power switch. If the PWRON_POLARITY bit is set to 1, this pin is active high and the internal pull-down is disabled. This pin may be at low impedance when power rails are removed. |
| OVERCUR1# | A36 | A36 | I PU | USB DS Port 1 Overcurrent Detection. 0: overcurrent detected; 1: overcurrent not detected |
| USB_SSTXP_DN2 | A11 | A11 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 2 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSTXN_DN2 | B10 | B10 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 2 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXP_DN2 | B9 | B9 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 2 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXN_DN2 | A10 | A10 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 2 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_DP_DN2 | B12 | B12 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (positive). |
| USB_DM_DN2 | A13 | A13 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (negative). |
| PWRON2# | B34 | B34 | O PD | USB DS Port 2 Power On Control for Downstream Power. The terminal is used for control of the downstream power switch. If the PWRON_POLARITY bit is set to 1, this pin is active high and the internal pull-down is disabled. This pin may be at low impedance when power rails are removed. |
| OVERCUR2# | A37 | A37 | I PU | USB DS Port 2 Overcurrent Detection. 0: overcurrent detected; 1: overcurrent not detected |
| USB_SSTXP_DN3 | — | B28 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 3 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSTXN_DN3 | — | A30 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 3 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXP_DN3 | — | B27 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 3 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXN_DN3 | — | A29 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 3 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_DP_DN3 | — | B25 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (positive). |
| USB_DM_DN3 | — | A27 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (negative). |
| PWRON3# | — | A46 | O PD | USB DS Port 3 Power On Control for Downstream Power. The terminal is used for control of the downstream power switch. If the PWRON_POLARITY bit is set to 1, this pin is active high and the internal pull-down is disabled. This pin may be at low impedance when power rails are removed. |
| OVERCUR3# | — | B43 | I PU | USB DS Port 3 Overcurrent Detection. 0: overcurrent detected; 1: overcurrent not detected |
| USB_SSTXP_DN4 | — | B7 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 4 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSTXN_DN4 | — | A8 | O | USB SuperSpeed transmitter differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 4 SSTX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXP_DN4 | — | B6 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (positive). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 4 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_SSRXN_DN4 | — | A7 | I | USB SuperSpeed receiver differential pair (negative). Note: When routing, it is permissible to swap the positive and negative signals in Port 4 SSRX differential pair. |
| USB_DP_DN4 | — | B5 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (positive). |
| USB_DM_DN4 | — | A5 | I/O | USB High-speed differential transceiver (negative). |
| PWRON4# | — | A48 | O PD | USB DS Port 4 Power On Control for Downstream Power. The terminal is used for control of the downstream power switch. If the PWRON_POLARITY bit is set to 1, this pin is active high and the internal pull-down is disabled. This pin may be at low impedance when power rails are removed. |
| OVERCUR4# | — | B45 | I PU | USB DS Port 4 Overcurrent Detection. 0: overcurrent detected; 1: overcurrent not detected |
| I2C SIGNALS | ||||
| SCL | B2 | B2 | I/O | I2C Clock – If no I2C device is present, pull this line down to disable. |
| SDA | A2 | A2 | I/O | I2C Data – If no I2C device is present, pull this line down to disable. |
| TEST AND MISCELLANEOUS SIGNALS | ||||
| JTAG_TCK | A32 | A32 | I PD | JTAG test clock |
| JTAG_TDI | A35 | A35 | I PU | JTAG test data in |
| JTAG_TDO | B31 | B31 | O PD | JTAG test data out |
| JTAG_TMS | B30 | B30 | I PU | JTAG test mode select |
| JTAG_RST# | B32 | B32 | I PD | JTAG reset. Should be pulled low for normal operation. |
| GPIO0 | A49 | A49 | I/O PU | General purpose I/O |
| GPIO1 | B46 | B46 | I/O PU | |
| GPIO2 | B47 | B47 | I/O PU | |
| GPIO3 | B48 | B48 | I/O PU | |
| SMI | B3 | B3 | O | System management interrupt Note: This pin is active high and should not be pulled up/down. |
| R1EXT | A24 | A24 | OI | High precision external resistor used for calibration. A resister value of 9.09 KΩ ±1% accuracy is connected between the terminals R1EXT and R1EXTRTN. |
| R1EXTRTN | B23 | B23 | OI | |
| AUX_DET | A52 | A52 | I | Auxiliary power detect. This pin indicates if the TUSB73X0 is enabled for wakeup from D3cold. Note: If this feature is implemented, AUX_DET must be pulled to VDD33 to prevent leakage. |
| NC | B4, A5, B5, B6, A7, B7, A8, B8, B13, A14, B25, A26, B26, A27, B27, B28, A29, B29, A30, A43, B43, B45, A46, A48 | A14, B8, B13, A26, B29, A43 | I/O | Pins are not connected internally. Note: TUSB7320 pins B4 and B26 may be connected to VDDA_3P3 to support a dual-layout option with the TUSB7340. |
| POWER SIGNALS | ||||
| VDD33 | A3, A34, A39, A47, A51 | A3, A34, A39, A47, A51 | PWR | 3.3-V I/O power rail |
| VDDA_3P3 | B11, A19, A21, A25, B22, A44 | B4, B11, A19, A21, A25, B22, B26, A44 | PWR | 3.3-V analog power rail |
| VDD11 | A1, B1, A4, A6, A9, A12, A16, B17, B19, B24, A28, A33, A31, A38, B37, B40, B42, B44, A50 | A1, B1, A4, A6, A9, A12, A16, B17, B19, B24, A28, A33, A31, A38, B37, B40, B42, B44, A50 | PWR | 1.1-V core power rail |
| VSS | B20, A53 | B20, A53 | PWR | Ground. The ground pad is labeled A53 for schematic purposes. |
| VSS_NC | C1, C2, C3, C4 | C1, C2, C3, C4 | PWR | The corner pins, which are for mechanical stability of the package, are connected to ground internally. These pins may be connected to VSS or left unconnected. |
| VSS_OSC | B21 | B21 | PWR | Oscillator return. If using a crystal, the load capacitors should use this signal as the return path and it should not be connected to the PCB ground. If using an oscillator, this should be connected to PCB Ground. |