SLUS223H April 1997 – October 2024 UC1842 , UC1843 , UC1844 , UC1845 , UC2842 , UC2843 , UC2844 , UC2845 , UC3842 , UC3843 , UC3844 , UC3845
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bulk Capacitor and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.2 Transformer Turns Ratio and Maximum Duty Cycle
- 8.2.2.3 Transformer Inductance and Peak Currents
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Current Sensing Network
- 8.2.2.6 Gate Drive Resistor
- 8.2.2.7 VREF Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 RT/CT
- 8.2.2.9 Start-Up Circuit
- 8.2.2.10 Voltage Feedback Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.1 Input Bulk Capacitor and Minimum Bulk Voltage
Bulk capacitance can consist of one or more capacitors connected in parallel, often with some inductance between the capacitors to suppress differential-mode conducted noise. The value of the input capacitor sets the minimum bulk voltage; setting the bulk voltage lower by using minimal input capacitance results in higher peak primary currents leading to more stress on the MOSFET switch, the transformer, and the output capacitors. Setting the bulk voltage higher by using a larger input capacitor results in higher peak current from the input source and the capacitor is physically larger. Compromising between size and component stresses determines the acceptable minimum input voltage. The total required value for the primary-side bulk capacitance, CIN, is selected based upon the power level of the converter, POUT, the efficiency target, η, the minimum input voltage, VIN(min), and is chosen to maintain an acceptable minimum bulk voltage level, VBULK(min), using Equation 9.
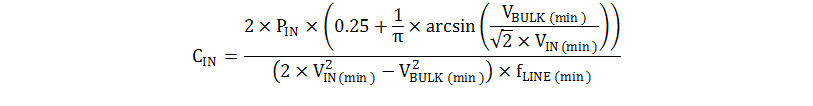
In this equation, VIN(min) is the RMS value of the minimum AC input voltage, 85 VRMS, whose minimum line frequency is denoted as fLINE(min), equal to 47 Hz. Based on the CIN equation, to achieve a minimum bulk voltage of 75 V, assuming 85% converter efficiency, the bulk capacitor must be larger than 126 µF; 180 µF is selected for the design, taking into consideration component tolerances and efficiency estimation.