SLUS223H April 1997 – October 2024 UC1842 , UC1843 , UC1844 , UC1845 , UC2842 , UC2843 , UC2844 , UC2845 , UC3842 , UC3843 , UC3844 , UC3845
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bulk Capacitor and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.2 Transformer Turns Ratio and Maximum Duty Cycle
- 8.2.2.3 Transformer Inductance and Peak Currents
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Current Sensing Network
- 8.2.2.6 Gate Drive Resistor
- 8.2.2.7 VREF Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 RT/CT
- 8.2.2.9 Start-Up Circuit
- 8.2.2.10 Voltage Feedback Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1.7 VCC
VCC is the power input connection for this device. In normal operation, power VCC through a current-limiting resistor. Although quiescent VCC current is only 0.5 mA, the total supply current is higher, depending on the OUTPUT current. Total VCC current is the sum of quiescent VCC current and the average OUTPUT current. Knowing the operating frequency and the MOSFET gate charge (Qg), average OUTPUT current can be calculated from Equation 4.
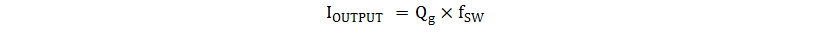
The UCx84x has a VCC supply voltage clamp of 34 V typical, but the absolute maximum value for VCC from a low-impedance source is 30 V. For applications that have a higher input voltage than the recommended VCC voltage, place a resistor in series with VCC to increase the source impedance. The maximum value of this resistor is calculated with Equation 5.
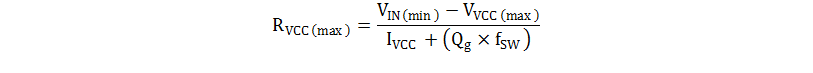
In Equation 5, VIN(min) is the minimum voltage that is used to supply VCC, VVCC(max) is the maximum VCC clamp voltage and IVCC is the IC supply current without considering the gate driver current and Qg is the external power MOSFET gate charge and fSW is the switching frequency.
The turnon and turnoff thresholds for the UCx84x family are significantly different: 16 V and 10 V for the UCx842 and UCx844; 8.4 V and 7.6 V for the UCx843 and UCx855. To protect against noise related problems, filter VCC with an electrolytic and bypass with a ceramic capacitor to ground. Keep the capacitors close to the IC pins.