SLUSCJ9F June 2016 – November 2024 UCC21520
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.9 Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Designing INA/INB Input Filter
- 9.2.2.2 Select External Bootstrap Diode and its Series Resistor
- 9.2.2.3 Gate Driver Output Resistor
- 9.2.2.4 Gate to Source Resistor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Estimate Gate Driver Power Loss
- 9.2.2.6 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 9.2.2.7 Selecting VCCI, VDDA/B Capacitor
- 9.2.2.8 Dead Time Setting Guidelines
- 9.2.2.9 Application Circuits with Output Stage Negative Bias
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
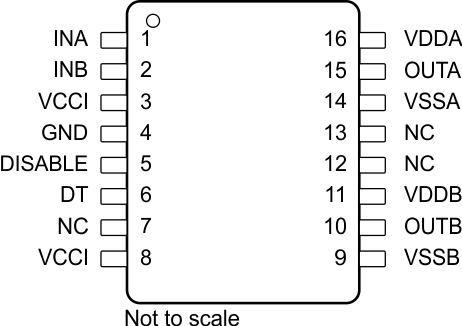 Figure 5-1 DW Package16-Pin SOICTop View
Figure 5-1 DW Package16-Pin SOICTop ViewTable 5-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| DISABLE | 5 | I | Disables both driver outputs if asserted high, enables if set low or left open. This pin is pulled low internally if left open. It is recommended to tie this pin to ground if not used to achieve better noise immunity. Bypass using a ≈1nF low ESR/ESL capacitor close to DIS pin when connecting to a micro controller with distance. |
| DT | 6 | I | Programmable dead time function. Tying DT to VCCI allows the outputs to overlap. Placing a 2-kΩ to 500-kΩ resistor (RDT) between DT and GND adjusts dead time according to: DT (in ns) = 10 x RDT (in kΩ). It is recommended to parallel a ceramic capacitor, ≤1nF, close to the DT pin with RDT to achieve better noise immunity. It is not recommended to leave DT floating. |
| GND | 4 | P | Primary-side ground reference. All signals in the primary side are referenced to this ground. |
| INA | 1 | I | Input signal for A channel. INA input has a TTL/CMOS compatible input threshold. This pin is pulled low internally if left open. It is recommended to tie this pin to ground if not used to achieve better noise immunity. |
| INB | 2 | I | Input signal for B channel. INB input has a TTL/CMOS compatible input threshold. This pin is pulled low internally if left open. It is recommended to tie this pin to ground if not used to achieve better noise immunity. |
| NC | 7 | – | No Internal connection. |
| NC | 12 | – | No internal connection. |
| NC | 13 | – | No internal connection. |
| OUTA | 15 | O | Output of driver A. Connect to the gate of the A channel FET or IGBT. |
| OUTB | 10 | O | Output of driver B. Connect to the gate of the B channel FET or IGBT. |
| VCCI | 3 | P | Primary-side supply voltage. Locally decoupled to GND using a low ESR/ESL capacitor located as close to the device as possible. |
| VCCI | 8 | P | Primary-side supply voltage. This pin is internally shorted to pin 3. |
| VDDA | 16 | P | Secondary-side power for driver A. Locally decoupled to VSSA using a low ESR/ESL capacitor located as close to the device as possible. |
| VDDB | 11 | P | Secondary-side power for driver B. Locally decoupled to VSSB using low ESR/ESL capacitor located as close to the device as possible. |
| VSSA | 14 | P | Ground for secondary-side driver A. Ground reference for secondary side A channel. |
| VSSB | 9 | P | Ground for secondary-side driver B. Ground reference for secondary side B channel. |
(1) P = Power, G = Ground, I = Input, O = Output