SLUSCG2A March 2016 – March 2016 UCC24636
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The UCC24636 is a high performance controller driver for N-channel MOSFET power devices used for secondary-side synchronous rectification. The UCC24636 is designed to operate as a companion device to a primary-side controller to help achieve efficient synchronous rectification in switching power supplies. The controller features a high-speed driver and provides appropriately timed logic circuitry that seamlessly generates an efficient synchronous rectification system. With its current emulator architecture, the UCC24636 has enough versatility to be applied in DCM and TM operation. The UCC24636 SR on-time adjustability allows optimizing for PSR and SSR applications. Additional features such as pin fault protection, dynamic VPC threshold sensing, and voltage sense blanking time and make the UCC24636 a robust synchronous controller.
9.2 Typical Application
9.2.1 AC-to-DC Adapter, 5 V, 15 W
This design example describes the design of a 15-W off-line flyback converter providing 5 V at 3-A maximum load and operating from a universal AC input. The design uses the UCC28740 AC-to-DC valley-switching primary-side controller in a DCM type flyback converter and achieves over 86% full-load efficiency with the use of the secondary side UCC24636 synchronous rectifier controller.
- The design requirements are detailed in Design Requirements
- The design procedure for selecting the component circuitry for use with the UCC24636 is detailed in Calculation of Component Values.
- Test results shown in Application Waveforms And Curves highlight the unique advantages of using the UCC24636.
 Figure 18. AC-to-DC Charger: 5 V, 15 W
Figure 18. AC-to-DC Charger: 5 V, 15 W
9.2.2 Design Requirements
For this design example, use the parameters listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Performance Specifications AC-to-DC Charger 5 V, 15 W
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VACIN | Input voltage | 90 | 115/230 | 265 | VRMS | |
| fLINE | Frequency | 47 | 50/60 | 64 | Hz | |
| VAC(uvlo) | Brownout voltage | IOUT = IOUT(nom) | 72 | VRMS | ||
| VAC(run) | Brownout recovery voltage | 85 | VRMS | |||
| IIN | Input current | VACIN = VACIN(min), IOUT = IOUT(nom) | 335 | mA | ||
| OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VOUT | Output voltage | VACIN = VACIN(min) to VACIN(max), IOUT = 0 to IOUT(nom) |
4.9 | 5.0 | 5.1 | V |
| IOUT(nom) | Nominal output current | VACIN = VACIN(min) to VACIN(max) | 3.0 | A | ||
| IOUT(min) | Minimum output current | VACIN = VACIN(min) to VACIN(max) | 0 | A | ||
| ΔVOUT | Output voltage ripple | VACIN = VACIN(min) to VACIN(max), IOUT = 0 to IOUT(nom) |
80 | mV | ||
| POUT | Output power | VACIN = VACIN(min), IOUT = IOUT(nom) | 15 | W | ||
| SYSTEM CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| ηavg | Average efficiency | VACIN = VACIN(nom), IOUT = 25%, 50%, 75%, 100% of IOUT(nom) | 85% | 87% | ||
| ƞ10% | 10% Load efficiency | VACIN = VACIN(nom), IOUT = 10% of IOUT(nom) | 73.5% | 82.5% | ||
| PNL | No load power | VACIN = VACIN(nom), IOUT = 0 | 14 | 22 | mW | |
9.2.3 Calculation of Component Values
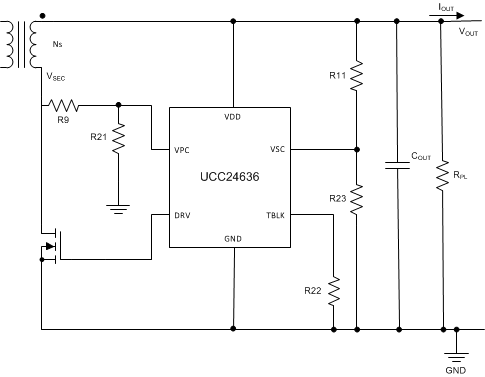 Figure 19. UCC24636 Circuit Design
Figure 19. UCC24636 Circuit Design
For ease of understanding, Figure 19 is a modified version of Figure 15 where the component reference designators are the same as the schematic drawing of Figure 18.
9.2.3.1 VPC Input
For designs operating in constant current (CC) with low VOUT, there are two cases to examine. At maximum power, VIN(MIN) will be lower but VOUT is nominal. In constant current operation, VOUT is the minimum but VIN(MIN) will be higher. Determine R9 for both conditions, and choose the lowest value.
For minimal power dissipation, select:


With R9 = 147 kΩ :
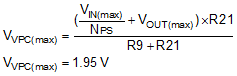
Therefore, VVPC is within the recommended range of 0.45 V to 2.2 V.
9.2.3.2 VSC Input
The value of R23 is recommended to be with the range of 25 kΩ to 50 kΩ.
There is a 10% margin included for the initial value calculation of R11 to provide timing margin during initial operation verification.

With R11 = 115 kΩ, the operating range of the VSC pin is:


Therefore, VVSC is within the recommended range of 0.3 V to 2.2 V.
The UCC24636 SR timing can be optimized (SR on time increased) by increasing the R115 value after initial operation confirmation. The RatioVPC_VSC parameter has a positive tolerance of 5.3%. Using 1% divider resistors for VPC and VSC should allow reducing the 10% initial SR timing margin.
9.2.3.3 TBLK Input
The blanking time is set with resistor R22.
Select the blanking time to meet the following criteria based on 660-ns minimum primary on-time at high line.
tVPC-BLK = (tPRI × 0.85) – 120 ns
spacer
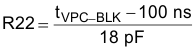
A value of R22 = 20 kΩ results in a blanking time of approximately 460 ns.
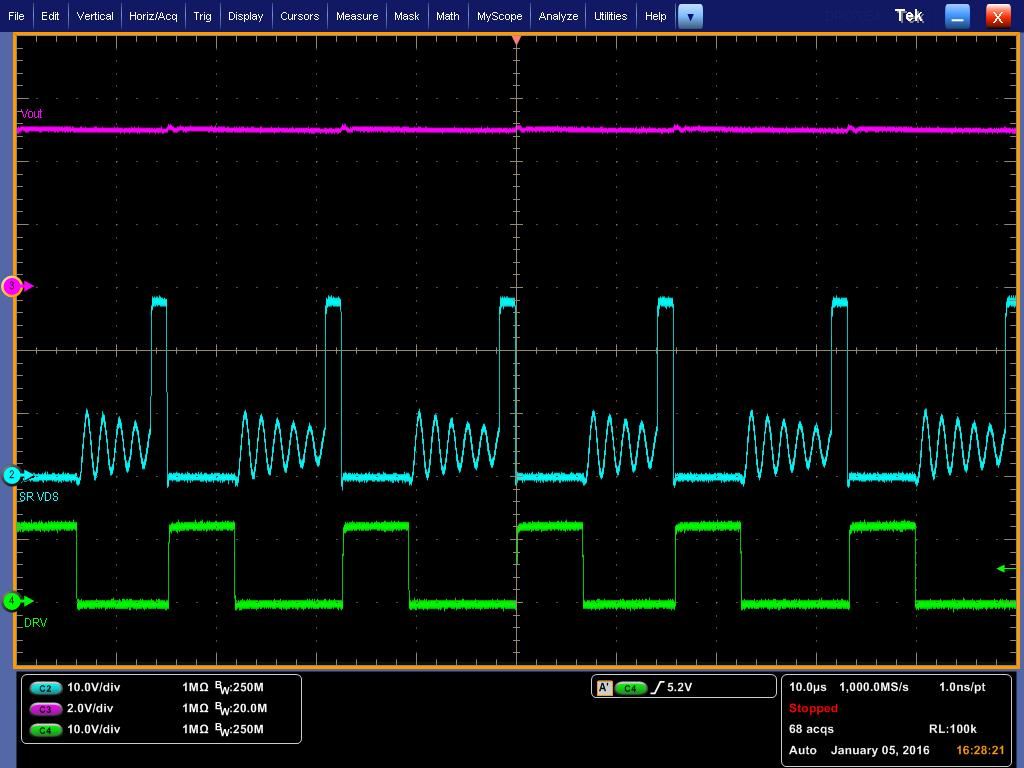
9.2.4 Application Waveforms And Curves

| CH2 (Blue): Drain of synchronous rectifier Q1, 10V/Div | ||
| CH3 (Mag): VOUT, 2V/Div | ||
| CH4 (Green): DRV signal to Q1, 10V/Div |

| CH2 (Blue): Drain of synchronous rectifier Q1, 10V/Div | ||
| CH3 (Mag): VOUT, 2V/Div | ||
| CH4 (Green): DRV signal to Q1, 10V/Div |
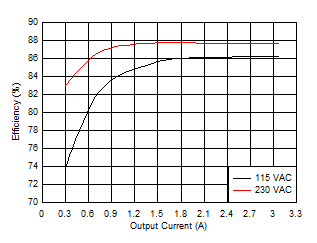 Figure 24. Efficiency vs Output Current
Figure 24. Efficiency vs Output Current
| CH2 (Blue): Drain of synchronous rectifier Q1, 10V/Div | ||
| CH3 (Mag): VOUT, 2V/Div | ||
| CH4 (Green): DRV signal to Q1, 10V/Div |

| CH2 (Blue): Drain of synchronous rectifier Q1, 10V/Div | ||
| CH3 (Mag): VOUT, 2V/Div | ||
| CH4 (Green): DRV signal to Q1, 10V/Div |
 Figure 25. Output Voltage vs Output Current
Figure 25. Output Voltage vs Output Current
9.3 Do's and Don'ts
- Do operate the device within the recommended operating maximum parameters. Consider output overvoltage conditions when determining stress.
- Do consider the guideline for setting the blanking time resistor value illustrated in Figure 16.
- Do not use the UCC24636 in CCM flyback converter designs. For CCM designs, use the UCC24630 with the CCM dead time control function.
- Do not use the UCC24636 in LLC converters as they can operate in CCM.
- Do not add capacitance to the TBLK pin.
- Do not add significant external capacitance to the VPC pin as there will be increased delay of the signal. If filtering is necessary a recommended maximum capacitance is 15 pF with a lower resistor divider network value of 10 kΩ.