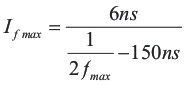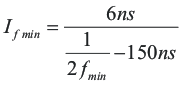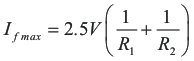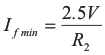SLUS846D September 2008 – August 2024 UCC25600
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Glossary
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.3 Oscillator
With variable switching frequency control, UCC25600 relies on the internal oscillator to vary the switching frequency. The oscillator is controlled by the current flowing out of the RT pin. Except during soft start, the relationship between the gate signal frequency and the current flowing out of the RT pin can be represented as:
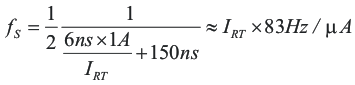
Because the switching frequency is proportional to the current, by limiting the maximum and minimum current flowing out of the RT pin, the minimum and maximum switching frequency of the converter could be easily limited. As shown in Figure 8-7, putting a resistor from the RT pin to ground limits the minimum current and putting a resistor in series with the opto-coupler limits the maximum current.
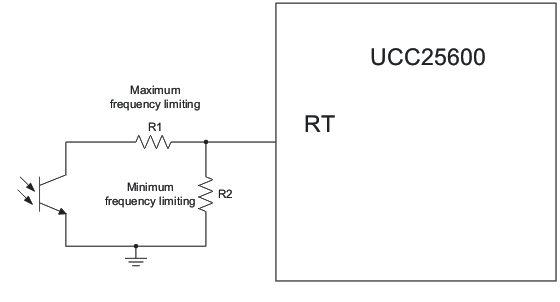 Figure 8-7 Maximum and Minimum Frequency Setting for UCC25600
Figure 8-7 Maximum and Minimum Frequency Setting for UCC25600The frequency limiting resistor can be calculated based on following equations.