SLUS270G March 1999 – May 2020 UCC2800 , UCC2801 , UCC2802 , UCC2803 , UCC2804 , UCC2805
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Detailed Pin Description
- 9.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.3 Self-Biasing, Active Low Output
- 9.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 9.3.5 Oscillator
- 9.3.6 Synchronization
- 9.3.7 PWM Generator
- 9.3.8 Minimum Off-Time Setting (Dead-Time Control)
- 9.3.9 Leading Edge Blanking
- 9.3.10 Minimum Pulse Width
- 9.3.11 Current Limiting
- 9.3.12 Overcurrent Protection and Full Cycle Restart
- 9.3.13 Soft Start
- 9.3.14 Slope Compensation
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.1.4 RC
RC is the oscillator timing pin. For fixed frequency operation, set timing capacitor charging current by connecting a resistor from REF to RC. Set frequency by connecting timing capacitor from RC to GND. For the best performance, keep the timing capacitor lead to GND as short and direct as possible. If possible, use separate ground traces for the timing capacitor and all other functions.
The UCC280x’s oscillator allows for operation to 1 MHz versus 500 kHz with the UC3842 family. Both devices make use of an external resistor to set the charging current for the capacitor, which determines the oscillator frequency. For the UCC2802 and UCC2804, use Equation 4.
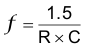
For the UCC2803 and UCC2805, use Equation 5.
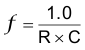
In these two equations, switching frequency (f) is in Hz, R is in Ω, and C is in farads.
The two equations are different due to different reference voltages. The recommended range of timing resistor values is between 10 kΩ and 200 kΩ; the recommended range of timing capacitor values is between 100 pF and 1000 pF. The peak-to-peak amplitude of the oscillator waveform is 2.45 V versus 1.7 V in UC3842 family. For best performance, keep the timing capacitor lead to GND as short as possible. TI recommends separate ground traces for the timing capacitor and all other pins. The maximum duty cycle for the UCC2802 and UCC2803 is approximately 99%; the maximum duty cycle for the UCC2803 and UCC2804 is approximately 49%. The duty cycle cannot be easily modified by adjusting RT and CT, unlike the UC3842A family. The maximum duty cycle limit is set by the ratio of the external oscillator charging resistor RT and the internal oscillator discharge transistor on-resistance, like the UC3842. However, maximum duty cycle limits less than 90% (for the UCC2802 and UCC2803) and less than 45% (for the UCC2804 and UCC2805) can not reliably be set in this manner. For better control of maximum duty cycle, consider using the UCCx807.