SLUSAO7C September 2011 – July 2024 UCC28063
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Principles of Operation
- 7.3.2 Natural Interleaving
- 7.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, and Restart Timer
- 7.3.4 Distortion Reduction
- 7.3.5 Zero-Current Detection and Valley Switching
- 7.3.6 Phase Management and Light-Load Operation
- 7.3.7 External Disable
- 7.3.8 Improved Error Amplifier
- 7.3.9 Soft Start
- 7.3.10 Brownout Protection
- 7.3.11 Dropout Detection
- 7.3.12 VREF
- 7.3.13 VCC
- 7.3.14 Control of Downstream Converter
- 7.3.15
System Level Protections
- 7.3.15.1 Failsafe OVP - Output Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.15.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.15.3 Open-Loop Protection
- 7.3.15.4 VCC Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO) Protection
- 7.3.15.5 Phase-Fail Protection
- 7.3.15.6 CS-Open, TSET-Open and -Short Protection
- 7.3.15.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 7.3.15.8 AC-Line Brownout and Dropout Protections
- 7.3.15.9 Fault Logic Diagram
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.2 ZCD Resistor Selection (RZA, RZB)
- 8.2.2.3 HVSEN
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Selecting (RS) For Peak Current Limiting
- 8.2.2.6 Power Semiconductor Selection (Q1, Q2, D1, D2)
- 8.2.2.7 Brownout Protection
- 8.2.2.8 Converter Timing
- 8.2.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 8.2.2.10 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, and Restart Timer
Gate-drive on-time varies proportionately with the error-amplifier output voltage by a factor called KT (in units of μs/V), as shown in Equation 3.

Where:
- VCOMP is the output voltage of the error amplifier and 125 mV is a modulator offset voltage.
The maximum output of the error amplifier is limited to 4.95 V. This value, minus the 125-mV modulator offset, limits maximum on-time as determined by Equation 4.
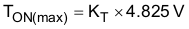
This on-time limit sets the maximum power that can be delivered by the converter at a given input voltage.
At lower power, one boost channel (phase) may be turned off to achieve efficiency benefits (see Phase Management section, below). To provide a smooth transition between two-phase and single-phase operation, KT increases by a factor of two in single-phase mode:

The maximum switching frequency of each phase is limited by minimum-period timers. If inductor current decays to zero before the minimum-period timer elapses, the next turn-on will be delayed, resulting in discontinuous phase current.
A restart timer ensures starting under all circumstances by restarting both phases if the ZCD input of either phase has not transitioned from high-to-low within approximately 200 µs. To prevent the circuit from operating in continuous conduction mode (CCM), the restart timer does not trigger turn-on until both phase-currents return to zero.
The on-time factors (KT, KTS) and the minimum switching period, T(MIN), are proportional to the time-setting resistor RTSET (the resistor from the TSET pin to ground), and these factors can be calculated by Equation 5, Equation 6 and Equation 7:
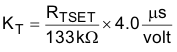
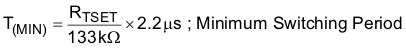
The proper value of RTSET will result in the clamped maximum on-time, TON(max), required by the converter operating at the minimum input line voltage and maximum load.