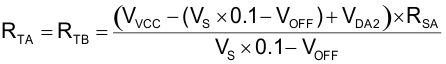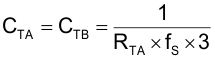SLUSAW0B March 2012 – December 2023 UCC28070A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Interleaving
- 6.3.2 Programming the PWM Frequency and Maximum Duty-Cycle Clamp
- 6.3.3 Frequency Dithering (Magnitude and Rate)
- 6.3.4 External Clock Synchronization
- 6.3.5 Multi-phase Operation
- 6.3.6 VSENSE and VINAC Resistor Configuration
- 6.3.7 VSENSE and VINAC Open-Circuit Protection
- 6.3.8 Current Synthesizer
- 6.3.9 Programmable Peak Current Limit
- 6.3.10 Linear Multiplier and Quantized Voltage Feed Forward
- 6.3.11 Enhanced Transient Response (VA Slew-Rate Correction)
- 6.3.12 Voltage Biasing (VCC and VVREF)
- 6.3.13 PFC Enable and Disable
- 6.3.14 Adaptive Soft Start
- 6.3.15 PFC Start-Up Hold Off
- 6.3.16 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 6.3.17 Zero-Power Detection
- 6.3.18 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.3.19 Current Loop Compensation
- 6.3.20 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.2.1 Output Current Calculation
- 7.2.2.2 Bridge Rectifier
- 7.2.2.3 PFC Inductor (L1 and L2)
- 7.2.2.4 PFC MOSFETs (M1 and M2)
- 7.2.2.5 PFC Diode
- 7.2.2.6 PFC Output Capacitor
- 7.2.2.7 Current-Loop Feedback Configuration (Sizing of the Current-Transformer Turns-Ratio and Sense Resistor (RS))
- 7.2.2.8 Current-Sense Offset and PWM Ramp for Improved Noise Immunity
- 7.2.3 Application Curves
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.2.8 Current-Sense Offset and PWM Ramp for Improved Noise Immunity
To improve noise immunity at extremely light loads, TI recommends adding a PWM ramp with a DC offset to the current-sense signals. Electrical components RTA, RTB, ROA, ROB, CTA, CTB, DPA1, DPA2, DPB1, DPB1 CTA, and CTB form a PWM ramp that is activated and deactivated by the gate drive outputs of the UCC28070A. Resistor ROA and ROB add a DC offset to the CS resistors (RSA and RSB).
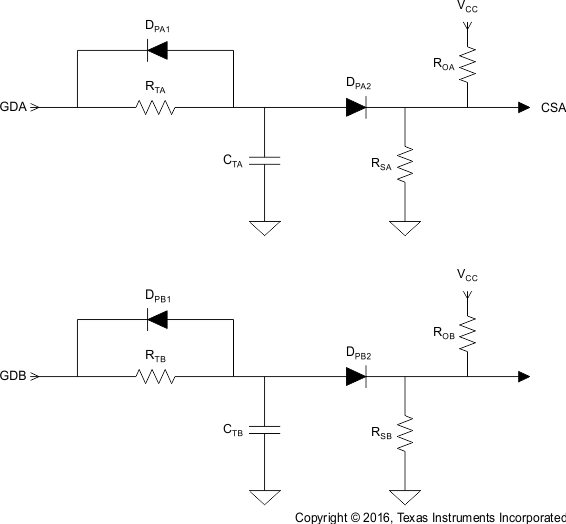 Figure 7-4 PWM Ramp and Offset Circuit
Figure 7-4 PWM Ramp and Offset CircuitWhen the inductor current becomes discontinuous the boost inductors ring with the parasitic capacitances in the boost stages. This inductor current rings through the CTs causing a false current-sense signal. Figure 7-5 shows what the current-sense signal looks like when the inductor current becomes discontinuous.
The inductor current (IL1) and VRsa may vary from this graphical representation depending on how much inductor ringing is in the design when the current becomes discontinuous.
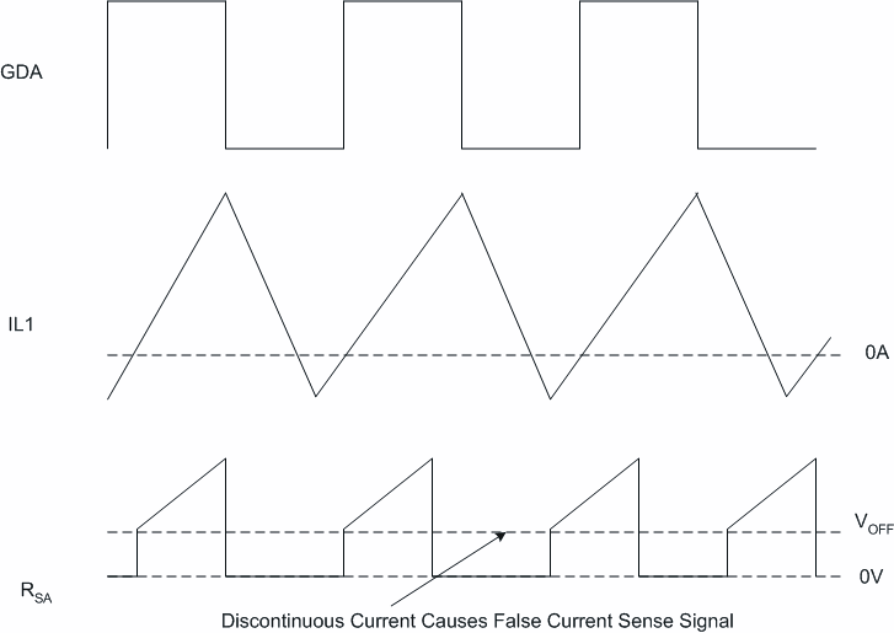 Figure 7-5 False Current-Sense
Signal
Figure 7-5 False Current-Sense
SignalTo counter for the offset (VOFF) just requires adjusting resistors ROA and ROB to ensure that when the unit goes discontinuous the current-sense resistor is not seeing a positive current when it must be zero. Setting the offset to 120mV is a good initial starting point and may need to be adjusted down or up based on evaluation of iTHD.
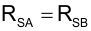
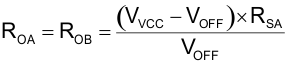
A small PWM ramp that is equal to 10% of the maximum current-sense signal (VS) minus the offset can then be added by properly selecting RTA, RTB, CTA and CTB.