SLUSD71A April 2018 – May 2018 UCC28742
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 VDD Capacitance, CDD
- 8.2.2.3 VDD Start-Up Resistance, RSTR
- 8.2.2.4 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.5 Transformer Turns Ratio, Inductance, Primary-Peak Current
- 8.2.2.6 Transformer Parameter Verification
- 8.2.2.7 VS Resistor Divider and Line Compensation
- 8.2.2.8 Standby Power Estimate
- 8.2.2.9 Output Capacitance
- 8.2.2.10 Feedback Loop Design Consideration
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
-
11Device and Documentation Support
- 11.1
Device Support
- 11.1.1 Development Support
- 11.1.2
Device Nomenclature
- 11.1.2.1 Capacitance Terms in Farads
- 11.1.2.2 Duty Cycle Terms
- 11.1.2.3 Frequency Terms in Hertz
- 11.1.2.4 Current Terms in Amperes
- 11.1.2.5 Current and Voltage Scaling Terms
- 11.1.2.6 Transformer Terms
- 11.1.2.7 Power Terms in Watts
- 11.1.2.8 Resistance Terms in Ω
- 11.1.2.9 Timing Terms in Seconds
- 11.1.2.10 Voltage Terms in Volts
- 11.1.2.11 AC Voltage Terms in VRMS
- 11.1.2.12 Efficiency Terms
- 11.2 Documentation Support
- 11.3 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates
- 11.4 Community Resources
- 11.5 Trademarks
- 11.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution
- 11.7 Glossary
- 11.1
Device Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.8 Standby Power Estimate
Assuming no-load standby power is a required design parameter, determine the estimated no-load power based on target converter maximum switching frequency and output power rating. The following equation estimates the stand-by power of the converter.

The output preload resistor can be estimated by VOCV and the difference between the converter stand-by power and the no-load bias power PNL_BIAS (that can be set as zero initially and adjust it later, particularly through the bench test), then the preload resistor value is estimated in Equation 24 :

A physical resistor component RPLmay not be needed as other components on the secondary-side such as TL431 can already provide enough preload.
The capacitor bulk voltage for the loss estimation is based on the highest voltage for the standby power measurement, typically as 325 VDC (or AC input of 230 Vrms). Power loss of RSTR is estimated inEquation 25:
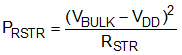
The total standby power, including the converter standby power loss, the start-up resistance power, and the snubber power loss, is estimated in Equation 26:
