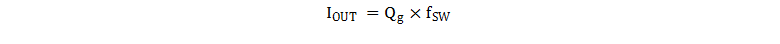SLUS458I July 2000 – June 2024 UCC28C40 , UCC28C41 , UCC28C42 , UCC28C43 , UCC28C44 , UCC28C45 , UCC38C40 , UCC38C41 , UCC38C42 , UCC38C43 , UCC38C44 , UCC38C45
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Detailed Pin Description
- 7.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.3 ±1% Internal Reference Voltage
- 7.3.4 Current Sense and Overcurrent Limit
- 7.3.5 Reduced-Discharge Current Variation
- 7.3.6 Oscillator Synchronization
- 7.3.7 Soft-Start Timing
- 7.3.8 Enable and Disable
- 7.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.10 Voltage Mode
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bulk Capacitor and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.2 Transformer Turns Ratio and Maximum Duty Cycle
- 8.2.2.3 Transformer Inductance and Peak Currents
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Current Sensing Network
- 8.2.2.6 Gate Drive Resistor
- 8.2.2.7 VREF Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 RT/CT
- 8.2.2.9 Start-Up Circuit
- 8.2.2.10 Voltage Feedback Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1.7 VDD
VDD is the power input connection for this device. In normal operation, power VDD through a current limiting resistor. The absolute maximum supply voltage is 20V, including any transients that may be present. If this voltage is exceeded, device damage is likely. This is in contrast to the predecessor bipolar devices, which could survive up to 30V on the input bias pin. Also, because no internal clamp is included in the device, the VDD pin must be protected from external sources which could exceed the 20V level. If containing the start-up and bootstrap supply voltage from the auxiliary winding NA below 20V under all line and load conditions can not be achieved, use a zener protection diode from VDD to GND. Depending on the impedance and arrangement of the bootstrap supply, this may require adding a resistor, RVDD, in series with the auxiliary winding to limit the current into the zener as shown in Figure 7-1. Ensure that over all tolerances and temperatures, the minimum zener voltage is higher than the highest UVLO upper turnon threshold. To prevent noise related problems, filter VDD with a ceramic bypass capacitor to GND. The VDD pin must be decoupled as close to the GND pin as possible.
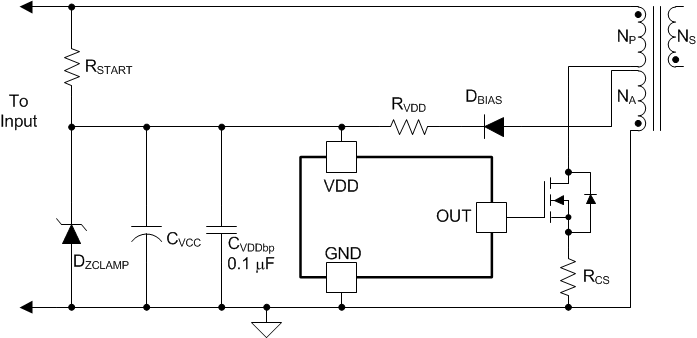 Figure 7-1 VDD Protection
Figure 7-1 VDD ProtectionAlthough nominal VDD operating current is only 2.3mA, the total supply current is higher, depending on the OUT current. Total VDD current is the sum of quiescent VDD current and the average OUT current. Knowing the operating frequency and the MOSFET gate charge (Qg), average OUT current can be calculated from Equation 1.