SLUS495J August 2001 – December 2023 UCC29002 , UCC39002
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Differential Current-Sense Amplifier (CS+, CS−, CSO)
- 6.3.2 Load-Share Bus Driver Amplifier (CSO, LS)
- 6.3.3 Load-Share Bus Receiver Amplifier (LS)
- 6.3.4 Error Amplifier (EAO)
- 6.3.5 Adjust Amplifier Output (ADJ)
- 6.3.6 Enable Function (CS+, CS−)
- 6.3.7 Fault Protection on LS Bus
- 6.3.8 Start-Up and Adjust Logic
- 6.3.9 Bias Input and Bias_OK Circuit (VDD)
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7Application and Implementation
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Revision History
- Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.3.9 Bias Input and Bias_OK Circuit (VDD)
The UCC29002 device is built on a high-performance 15V BiCMOS process. Therefore, the absolute maximum voltage across the VDD and GND pins (pin 3 and 4 respectively) is limited to 15V. The recommended maximum operating voltage is 13.5V which corresponds to the minimum tolerance limit of the on-board 14.25V Zener-like active clamp circuit. In case the bias voltage source exceeds the 13.5V limit, the UCC29002 device can be powered through a current-limiting resistor. The total current into the VDD pin (IVDDq + ICLAMP) must be limited to 10mA as listed in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table.
The bypass capacitor for the VDD pin is also the compensation for the input active clamp of the device and, as such, must be placed as close to the device pins (VDD and GND) as possible, using a good-quality, low-ESL capacitor, including trace length. The device is optimized for a capacitor value of 0.1µF to 1µF.
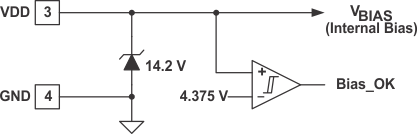 Figure 6-3 VDD Clamp
and Bias Monitor
Figure 6-3 VDD Clamp
and Bias MonitorThe UCC29002 device uses a comparator with hysteresis to monitor the VDD bias voltage for minimum sufficiency. does not have an undervoltage lockout circuit. On initial power-up while VDD < 4.375V, the load-share control functions are disabled. The Bias_OK comparator works as an enable function when VDD rises above the 4.375V enable threshold. After the device is enabled, the Bias_OK signal will remain true until VDD falls below the 4.0V disable threhsold. While this might be inconvenient for some low-voltage applications, this feature is necessary to obtain high accuracy. The load-share accuracy is dependent on working with relatively large signal amplitudes on the load-share bus. If the internal offsets, current-sense error, and ground potential difference between the UCC29002 controllers are comparable in amplitude to the load-share bus voltage, they can cause a significant current-distribution error in the system.
The maximum voltage on the load-share bus is limited to approximately 1.7V below the bias voltage level (VVDD) which would result in an unacceptably low load-share bus amplitude and therefore poor accuracy at low VDD levels. To circumvent this potential design problem, the UCC29002 device does not operate below the previously mentioned 4.0V bias voltage disable threshold. If the system does not have a suitable bias voltage source available to power the UCC29002, TI suggests using an inexpensive charge pump from the output rail which can generate the bias voltage for one or all of the UCC29002 devices in the load-share system.
The maximum VDD of the UCC29002 device is 15V. For load-sharing applications with higher-voltage outputs, use the application solution as recommended in Figure 7-2. A Zener-like clamp on the VDD pin is provided internally so the device can be powered from higher-voltage rails using a minimum number of external components.
The current-sense amplifier (CSA) inputs must be configured so that their absolute maximum voltage ratings are not exceeded. It is not a simple matter to level-shift mV-level current-sense signals from a high-voltage power supply rail down to the CSA inputs without incurring severe distortion from noise, divider tolerances, and offsets. This means that in most high-voltage applications, it is best practice to locate the current-sense resistor RSHUNT in the GND-return path of the power supply output.