SNAS298G August 2005 – January 2015 ADC128S102
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
- Eight Input Channels
- Variable Power Management
- Independent Analog and Digital Supplies
- SPI/QSPI™/MICROWIRE™/DSP Compatible
- Packaged in 16-Lead TSSOP
- Key Specifications
- Conversion Rate 500 ksps to 1 MSPS
- DNL (VA = VD = 5.0 V) +1.5 / −0.9
- LSB (maximum) INL (VA = VD = 5.0 V) ±1.2 LSB (maximum)
- Power Consumption
- 3V Supply 2.3 mW (typical)
- 5V Supply 10.7 mW (typical)
2 Applications
- Automotive Navigation
- Portable Systems
- Medical Instruments
- Mobile Communications
- Instrumentation and Control Systems
3 Description
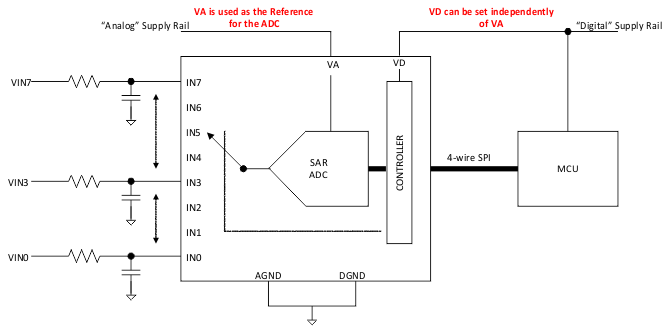
The ADC128S102 is a low-power, eight-channel CMOS 12-bit analog-to-digital converter specified for conversion throughput rates of 500 ksps to 1 MSPS. The converter is based on a successive-approximation register architecture with an internal track-and-hold circuit. It can be configured to accept up to eight input signals at inputs IN0 through IN7.
The output serial data is straight binary and is compatible with several standards, such as SPI, QSPI, MICROWIRE, and many common DSP serial interfaces.
The ADC128S102 may be operated with independent analog and digital supplies. The analog supply (VA) can range from +2.7 V to +5.25 V, and the digital supply (VD) can range from +2.7 V to VA. Normal power consumption using a +3-V or +5-V supply is 2.3 mW and 10.7 mW, respectively. The power-down feature reduces the power consumption to 0.06 µW using a +3-V supply and 0.25 µW using a +5-V supply.
The ADC128S102 is packaged in a 16-lead TSSOP package. Operation over the extended industrial temperature range of −40°C to +105°C is ensured.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| ADC128S102 | TSSOP (16) | 5.00 mm x 4.40 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.
Simplified Schematic