SLAS989D January 2014 – October 2017 ADC12J4000
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Signal Acquisition
- 7.3.2 The Analog Inputs
- 7.3.3 Clocking
- 7.3.4 Over-Range Function
- 7.3.5 ADC Core Features
- 7.3.6
Digital Down Converter (DDC)
- 7.3.6.1 NCO/Mixer
- 7.3.6.2 NCO Settings
- 7.3.6.3 Decimation Filters
- 7.3.6.4 DDC Output Data
- 7.3.6.5 Decimation Settings
- 7.3.7
Data Outputs
- 7.3.7.1 The Digital Outputs
- 7.3.7.2
JESD204B Interface Features and Settings
- 7.3.7.2.1 Scrambler Enable
- 7.3.7.2.2 Frames Per Multi-Frame (K-1)
- 7.3.7.2.3 DDR
- 7.3.7.2.4 JESD Enable
- 7.3.7.2.5 JESD Test Modes
- 7.3.7.2.6 Configurable Pre-Emphasis
- 7.3.7.2.7 Serial Output-Data Formatting
- 7.3.7.2.8 JESD204B Synchronization Features
- 7.3.7.2.9 SYSREF
- 7.3.7.2.10 SYNC~
- 7.3.7.2.11 Time Stamp
- 7.3.7.2.12 Code-Group Synchronization
- 7.3.7.2.13 Multiple ADC Synchronization
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Map
- 7.6.1 Memory Map
- 7.6.2
Register Descriptions
- 7.6.2.1
Standard SPI-3.0 (0x000 to 0x00F)
- 7.6.2.1.1 Configuration A Register (address = 0x000) [reset = 0x3C]
- 7.6.2.1.2 Configuration B Register (address = 0x001) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.1.3 Device Configuration Register (address = 0x002) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.1.4 Chip Type Register (address = 0x003) [reset = 0x03]
- 7.6.2.1.5 Chip Version Register (address = 0x006) [reset = 0x13]
- 7.6.2.1.6 Vendor Identification Register (address = 0x00C to 0x00D) [reset = 0x0451]
- 7.6.2.2 User SPI Configuration (0x010 to 0x01F)
- 7.6.2.3
General Analog, Bias, Band Gap, and Track and Hold (0x020 to 0x02F)
- 7.6.2.3.1 Power-On Reset Register (address = 0x021) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.3.2 I/O Gain 0 Register (address = 0x022) [reset = 0x40]
- 7.6.2.3.3 IO_GAIN_1 Register (address = 0x023) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.3.4 I/O Offset 0 Register (address = 0x025) [reset = 0x40]
- 7.6.2.3.5 I/O Offset 1 Register (address = 0x026) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.4
Clock (0x030 to 0x03F)
- 7.6.2.4.1 Clock Generator Control 0 Register (address = 0x030) [reset = 0xC0]
- 7.6.2.4.2 Clock Generator Status Register (address = 0x031) [reset = 0x07]
- 7.6.2.4.3 Clock Generator Control 2 Register (address = 0x032) [reset = 0x80]
- 7.6.2.4.4 Analog Miscellaneous Register (address = 0x033) [reset = 0xC3]
- 7.6.2.4.5 Input Clamp Enable Register (address = 0x034) [reset = 0x2F]
- 7.6.2.5 Serializer (0x040 to 0x04F)
- 7.6.2.6
ADC Calibration (0x050 to 0x1FF)
- 7.6.2.6.1 Calibration Configuration 0 Register (address = 0x050) [reset = 0x06]
- 7.6.2.6.2 Calibration Configuration 1 Register (address = 0x051) [reset = 0xF4]
- 7.6.2.6.3 Calibration Background Control Register (address = 0x057) [reset = 0x10]
- 7.6.2.6.4 ADC Pattern and Over-Range Enable Register (address = 0x058) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.6.5 Calibration Vectors Register (address = 0x05A) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.6.6 Calibration Status Register (address = 0x05B) [reset = undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.7 Timing Calibration Register (address = 0x066) [reset = 0x02]
- 7.6.2.7
Digital Down Converter and JESD204B (0x200-0x27F)
- 7.6.2.7.1 Digital Down-Converter (DDC) Control Register (address = 0x200) [reset = 0x10]
- 7.6.2.7.2 JESD204B Control 1 Register (address = 0x201) [reset = 0x0F]
- 7.6.2.7.3 JESD204B Control 2 Register (address = 0x202) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.7.4 JESD204B Device ID (DID) Register (address = 0x203) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.7.5 JESD204B Control 3 Register (address = 0x204) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.7.6 JESD204B and System Status Register (address = 0x205) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.7.7 Overrange Threshold 0 Register (address = 0x206) [reset = 0xF2]
- 7.6.2.7.8 Overrange Threshold 1 Register (address = 0x207) [reset = 0xAB]
- 7.6.2.7.9 Overrange Period Register (address = 0x208) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.7.10 DDC Configuration Preset Mode Register (address = 0x20C) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.7.11 DDC Configuration Preset Select Register (address = 0x20D) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.7.12 Rational NCO Reference Divisor Register (address = 0x20E to 0x20F) [reset = 0x0000]
- 7.6.2.7.13 NCO Frequency (Preset x) Register (address = see ) [reset = see ]
- 7.6.2.7.14 NCO Phase (Preset x) Register (address = see ) [reset = see ]
- 7.6.2.7.15 DDC Delay (Preset x) Register (address = see ) [reset = see ]
- 7.6.2.1
Standard SPI-3.0 (0x000 to 0x00F)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NKE|68
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
- Excellent Noise and Linearity up to and beyond FIN = 3 GHz
- Configurable DDC
- Decimation Factors from 4 to 32 (Complex Baseband Out)
- Usable Output Bandwidth of 800 MHz at
4x Decimation and 4000 MSPS - Usable Output Bandwidth of 100 MHz at
32x Decimation and 4000 MSPS - Bypass Mode for Full Nyquist Output Bandwidth
- Low Pin-Count JESD204B Subclass 1 Interface
- Automatically Optimized Output Lane Count
- Embedded Low Latency Signal Range Indication
- Low Power Consumption
-
Key Specifications:
- Max Sampling Rate: 4000 MSPS
- Min Sampling Rate: 1000 MSPS
- DDC Output Word Size: 15-Bit Complex (30 bits total)
- Bypass Output Word Size: 12-Bit Offset Binary
- Noise Floor: −149 dBFS/Hz or −150.8 dBm/Hz
- IMD3: −64 dBc (FIN = 2140 MHz ± 30 MHz at −13 dBFS)
- FPBW (–3 dB): 3.2 GHz
- Peak NPR: 46 dB
- Supply Voltages: 1.9 V and 1.2 V
- Power Consumption
- Bypass (4000 MSPS): 2 W
- Decimate by 10 (4000 MSPS): 2 W
- Power Down Mode: <50 mW
2 Applications
- Wireless Infrastructure
- RF-Sampling Software Defined Radio
- Wideband Microwave Backhaul
- Military Communications
- SIGINT
- RADAR and LIDAR
- DOCSIS / Cable Infrastructure
- Test and Measurement
3 Description
The ADC12J4000 device is a wideband sampling and digital tuning device. Texas Instruments' giga-sample analog-to-digital converter (ADC) technology enables a large block of frequency spectrum to be sampled directly at RF. An integrated DDC (Digital Down Converter) provides digital filtering and down-conversion. The selected frequency block is made available on a JESD204B serial interface. Data is output as baseband 15-bit complex information for ease of downstream processing. Based on the digital down-converter (DDC) decimation and link output rate settings, this data is output on 1 to 5 lanes of the serial interface.
A DDC bypass mode allows the full rate 12-bit raw ADC data to also be output. This mode of operation requires 8 lanes of serial output.
The ADC12J4000 device is available in a 68-pin VQFN package. The device operates over the Industrial (–40°C ≤ TA ≤ 85°C) ambient temperature range.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| ADC12J4000 | VQFN (68) | 10.00 mm × 10.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.
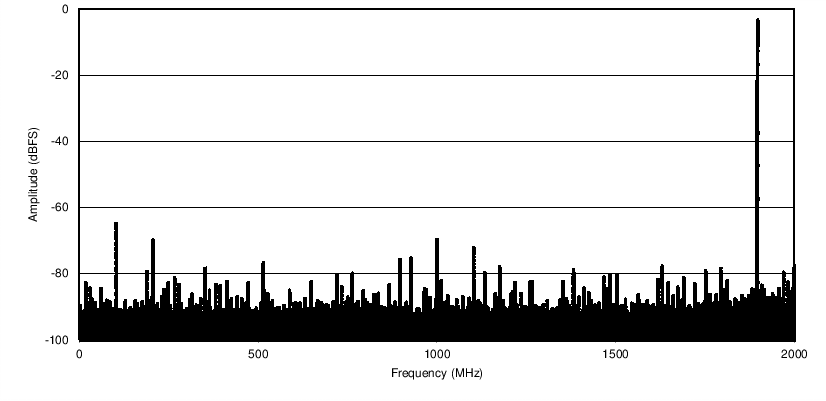
Bypass — Spectral Response
ƒS = 4 GHz, FIN = 1897 MHz