-
ADS5263 Quad Channel 16-Bit, 100-MSPS High-SNR ADC
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics, Dynamic Performance - 16-Bit ADC
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics, General - 16-Bit ADC Mode
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics, Dynamic Performance - 14-Bit ADC
- 7.8 Digital Characteristics
- 7.9 Timing Requirements
- 7.10 LVDS Timing at Lower Sampling Frequencies - 2 Wire, 8× Serialization
- 7.11 LVDS Timing for 1 Wire 16× Serialization
- 7.12 LVDS Timing for 2 Wire, 7× Serialization
- 7.13 LVDS Timing for 1 Wire, 14× Serialization
- 7.14 Serial Interface Timing Requirements
- 7.15 Reset Switching Characteristics
- 7.16 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
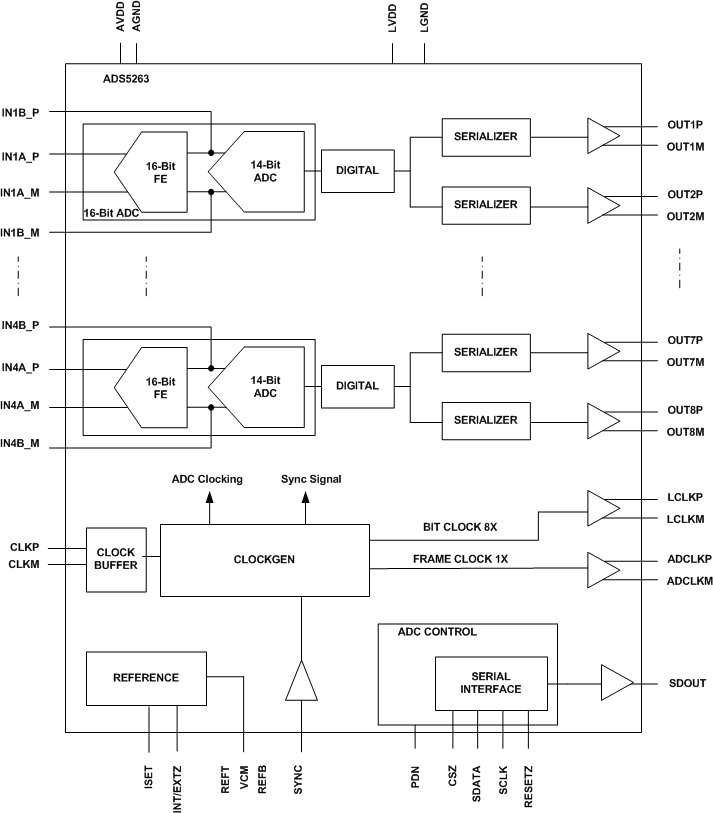
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Orderable Information
ADS5263 Quad Channel 16-Bit, 100-MSPS High-SNR ADC
1 Features
- Maximum Sample Rate: 100 MSPS
- Programmable Device Resolution
- Quad-Channel, 16-Bit, High-SNR Mode
- Quad-Channel, 14-Bit, Low-Power Mode
- 16-Bit High-SNR Mode
- 1.4 W Total Power at 100 MSPS
- 355 mW / Channel
- 4 Vpp Full-scale Input
- 85-dBFS SNR at fin = 3 MHz, 100 MSPS
- 1.4 W Total Power at 100 MSPS
- 14-Bit Low-Power Mode
- 785 mW Total Power at 100 MSPS
- 195 mW/Channel
- 2-Vpp Full-Scale Input
- 74-dBFS SNR at fin = 10 MHz
- Integrated Clamp (for interfacing to CCD sensors)
- 785 mW Total Power at 100 MSPS
- Low-Frequency Noise Suppression
- Digital Processing Block
- Programmable FIR Decimation Filters
- Programmable Digital Gain: 0 dB to 12 dB
- 2- or 4-Channel Averaging
- Programmable Mapping Between ADC Input Channels and LVDS Output Pins—Eases Board Design
- Variety of Test Patterns to Verify Data Capture by FPGA/Receiver
- Serialized LVDS Outputs
- Internal and External References
- 3.3-V Analog Supply
- 1.8-V Digital Supply
- Recovers From 6-dB Overload Within 1 Clock Cycle
- Package:
- CMOS Technology
2 Applications
- Medical Imaging – MRI
- Spectroscopy
- CCD Imaging
3 Description
Using CMOS process technology and innovative circuit techniques, the ADS5263 is designed to operate at low power and give very high SNR performance with a 4-Vpp full-scale input. Using a low-noise 16-bit front-end stage followed by a 14-bit ADC, the device gives 85-dBFS SNR up to 10 MHz and better than 80-dBFS SNR up to 30 MHz.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| ADS5263 | VQFN (64) | 9.00 mm × 9.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
ADS5263 Block Diagram
4 Revision History
Changes from C Revision (January 2013) to D Revision
- Added Register 57 in Register Maps Go
- Added Register CB in Register Maps Go
- Added Typical Applications sectionGo
- Added Layout section Go
- Deleted Ordering Information table. See POA at the end of the data sheet. Go
Changes from B Revision (October 2011) to C Revision
- Changed Pin 54 From: REFB To: NCGo
- Changed Pin 55 From: REFC To: NCGo
- Changed the VCM Pin description To: "Internal reference mode: Outputs the common-mode voltage (1.5 V) that can be used externally to bias the analog input External reference mode: Apply voltage input that sets the reference for ADC operation." From: "Outputs the common-mode voltage (1.5 V) that can be used externally to bias the analog input pins."Go
- Added "Idle channel noise" To SNRGo
- Added "Idle channel noise" To LSBGo
- Changed the INL values- 100 MSPS From: TYP = ±2.2 To: ±5, Added MAX = ±12Go
- to Changed the INL values- 80 MSPS From: TYP = ±2.2 To: ±5Go
- Added From: VCM common-mode output voltage To: VCM common-mode output voltage, Internal reference mode Go
- Added From: VCM output current capability To: VCM output current capability, Internal reference modeGo
- Added From: VCM input voltage To: VCM input current, external reference modeGo
- Added VCM input current, external reference mode Typical value - 80 MSPS of 0.5Go
- Changed EGREF - 100 MSPS MIN value From: ±2.5 To: ±1Go
- Added Temperature Coefficient to EGREF Go
- Added Temperature Coefficient to EGCHANGo
- Changed SNR fin = 5 MHz MIN value From: 68.8 To: to 67.5Go
- Added tA Aperture delay to the Timing Requirements TableGo
- Changed From: 2 WIRE, 16× SERIALIZATION To: 2 WIRE, 8× SERIALIZATIONGo
- Added 100 MSPS to the SAMPLING FREQUENCY, MSPS column of LVDS Timing at Lower Sampling Frequencies - 2 Wire, 8× SerializationGo
- Changed to 8x from 16xGo
- Changed LVDS Timing for 2 Wire, 7× Serialization title From: LVDS Timing for 2 Wire, 14× Serialization To: LVDS Timing for 2 Wire, 7× SerializationGo
- Changed the Digital Filter SectionGo
- Changed Table 9 Description From: Reference voltage must be forced on REFT and REFB pins To: Apply voltage on VCM pin to set the references for ADC operationGo
- Table 10 Added: <EN_HIGH_ADDRS> as bit D4. Added: Register 0x09 to Serial Register Ma;Go
- Table 10 Added: Register bit EXT_REF_VCM. Added: D12 <18x SERIALIZATION>Go
- Table 10 Added: new register entries from Address 5A to 89. Added: new register F0Go
- Added D4 <EN_HIGH_ADDRS>Go
- Added Added register description table (D10 <EN_CLAMP>) for register 0x09Go
- Added description for register EXT_REF_VCM Go
- Added Description for <EN_REG_42>, <PHASE_DDR> and EXT_REF_VCMGo
- Added Decsription for 18b SERIALIZATIONGo
- Changed D11, D10, and D5 To: SERIALIZATION From: SERIAL'NGo
- Changed the register for A7-A0 IN HEXGo
- Added description for register F0 for A7–A0 IN HEXGo
- Replaced the Clamp Function section with the Clamp Functon for CCD Signals sectionGo
- Deleted Figure - CCD Sensor ConnectionsGo
- Added External Reference ModeGo
Changes from A Revision (August 2011) to B Revision
- Added new Figure below Figure 16Go
- Added new Figure below Figure 22 (now Figure 24)Go
- Added new section below Digital Averaging titled: Performance with Didgital Processing BlocksGo
- Added listitem 6. to the OUTPUT LVDS INTERFACE sectionGo
- Added Added new figure in section Output LVDS Interface (Figure 55)Go
- Added new section after Output LVDS Interface titled: Programmable LCLK Phase, also 2 new figures added.Go
- Added register 42 between register 38 and register 45 Go
- Added new figure 52 in Large and Smll Signal Input Bandwidth sectionGo
Changes from * Revision (May 2011) to A Revision
- Added "Non-Magnetic Package Option for MRI Systems" to FeaturesGo
- Changed Features List Item - From: 1.35 W Total Power at 100 MSPS To: 1.4 W Total Power at 100 MSPSGo
- Changed Features List Item - From: 338 mW / Channel To: 355 mW / ChannelGo
- Changed the CLOCK INPUT values in the ROC tableGo
- Changed the ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS, DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE – 16-BIT ADC tableGo
- Changed the ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS, GENERAL – 16-BIT ADC MODE tableGo
- Added the ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS, DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE – 14-BIT ADC tableGo
- Changed the values in DIGITAL OUTPUTS – LVDS INTERFACEGo
- Added LVDS Timing for 1 Wire 16× Serialization, LVDS Timing for 2 Wire, 7× Serialization, and LVDS Timing for 1 Wire, 14× SerializationGo
- Added Figure 25, Figure 26, and Figure 27Go
- Added section - Large and Small Signal Input BandwidthGo
- Added Section - Board Design ConsiderationsGo
- Added Package Marking ADS5263NM and Ordering Number ADS5263IRGC-NMGo
- Added Section - DEFINITION OF SPECIFICATIONSGo
- Added Section - PackagingGo
5 Description (continued)
ADS5263 has a 14-bit low power mode, where it operates as a quad-channel 14-bit ADC. The 16-bit front-end stage is powered down and the part consumes almost half the power, compared to the 16-bit mode. The 14-bit mode supports a 2-Vpp full-scale input signal, with typical 74-dBFS SNR. The ADS5263 can be dynamically switched between the two resolution modes. This allows systems to use the same part in a high-resolution, high-power mode or a low-resolution, low-power mode.
The device also has a digital processing block that integrates several commonly used digital functions, such as digital gain (up to 12 dB). It includes a digital filter module that has built-in decimation filters (with low-pass, high-pass and band-pass characteristics). The decimation rate is also programmable (by 2, by 4, or by 8). This makes it very useful for narrow-band applications, where the filters can be used to improve SNR and knock-off harmonics, while at the same time reducing the output data rate.
The device includes an averaging mode where two channels (or even four channels) can be averaged to improve SNR. A very unique feature is the programmable mapper module that allows flexible mapping between the input channels and the LVDS output pins. This helps to greatly reduce the complexity of LVDS output routing and can potentially result in cheaper system boards by reducing the number of PCB layers. Specification of device is over industrial temperature range of –40°C to 85°C.
6 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, AVDD | –0.3 | 3.9 | V |
| Supply voltage, LVDD | –0.3 | 2.2 | V |
| Voltage between AGND and DRGND | –0.3 | 0.3 | V |
| Voltage applied to analog input pins – INP_A, INM_A, INP_B, INM_B | –0.3 | minimum (3.6, AVDD + 0.3 V) | V |
| Voltage applied to input pins – CLKP, CLKM, RESET, SCLK, SDATA, CSZ | –0.3 | AVDD + 0.3 | V |
| Voltage applied to reference input pins | –0.3 | 2.8 | V |
| Operating free-air temperature, TA | –40 | 85 | °C |
| Operating junction temperature, TJ | 125 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | ADS5263 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGC (VQFN) | |||
| 64 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 20.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 6.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 2.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 2.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 0.4 | °C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics, Dynamic Performance – 16-Bit ADC
Typical values are at 25°C, AVDD = 3.3V, LVDD = 1.8 V, 50% clock duty cycle, –1-dBFS differential analog input (unless otherwise noted); MIN and MAX values are across the full temperature range TMIN = –40°C to TMAX = 85°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, LVDD = 1.8 V7.6 Electrical Characteristics, General – 16-Bit ADC Mode
Typical values are at 25°C, AVDD = 3.3V, LVDD = 1.8V, 50% clock duty cycle, –1dBFS differential analog input (unless otherwise noted); MIN and MAX values are across the full temperature range TMIN = –40°C to TMAX = 85°C, AVDD = 3.3V, LVDD = 1.8V7.7 Electrical Characteristics, Dynamic Performance – 14-Bit ADC
Typical values are at 25°C, AVDD = 3.3V, LVDD = 1.8 V, 50% clock duty cycle, –1-dBFS differential analog input (unless otherwise noted); MIN and MAX values are across the full temperature range TMIN = –40°C to TMAX = 85°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, LVDD = 1.8 V7.8 Digital Characteristics
The DC specifications refer to the condition where the digital outputs are not switching, but are permanently at a valid logic level 0 or 1. AVDD = 3.3V, LVDD = 1.8V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIGITAL INPUTS – RESET, SCLK, SDATA, CS, PDN, SYNC, INT/EXT | |||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | All digital inputs support 1.8-V and 3.3-V CMOS logic levels. | 1.3 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.4 | V | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | SDATA, SCLK, CS (1) | VHIGH = 1.8 V | 5 | μA | ||
| IIL | Low-level input current | SDATA, SCLK, CS | VLOW = 0 V | 0 | μA | ||
| DIGITAL CMOS OUTPUT – SDOUT | |||||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = 100 µA | AVDD – 0.05 | V | |||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 100 µA | 0.05 | V | |||
| DIGITAL OUTPUTS – LVDS INTERFACE (OUT1P/M TO OUT8P/M, ADCLKP/M, LCLKP/M) | |||||||
| VODH | High-level output differential voltage | With external 100-Ω termination | 275 | 370 | 465 | mV | |
| VODL | Low-level output differential voltage | With external 100-Ω termination | –465 | –370 | –275 | mV | |
| VOCM | Output common-mode voltage | 1000 | 1200 | 1400 | mV | ||
7.9 Timing Requirements(1)
Typical values are at 25°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, LVDD = 1.8 V, sampling frequency = 100 MSPS, sine wave input clock = 1.5 Vpp clock amplitude, CLOAD = 5 pF(2), RLOAD = 100 Ω(3), unless otherwise noted. MIN and MAX values are across the full temperature range, TMIN = –40°C to TMAX = 85°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, LVDD = 1.7 V to 1.9 V| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tj | Aperture jitter | 220 | fs rms | |||
| tA | Aperture delay | Time delay between rising edge of input clock and the actual sampling instant | 3 | ns | ||
| Wake-up time | Time to valid data after coming out of STANDBY mode | 10 | μs | |||
| Time to valid data after coming out of global power down | 60 | |||||
| ADC latency | Latency of ADC alone, excludes the delay from input clock to output clock (tPDI), Figure 3 | 16 | Clock cycles | |||
| 2 WIRE, 8× SERIALIZATION (4) | ||||||
| tsu | Data setup time | Data valid (5) to zero-crossing of LCLKP | 0.23 | ns | ||
| th | Data hold time | Zero-crossing of LCLKP to data becoming invalid(5) | 0.31 | ns | ||
| tPDI | Clock propagation delay | Input clock rising edge crossover to output frame clock ADCLKP rising edge crossover, tPDI = (ts/4) + tdelay | 6.8 | 8.8 | 10.8 | ns |
| Variation of tPDI | Between two devices at same temperature and LVDD supply | ±0.6 | ns | |||
| LVDS bit clock duty cycle | Duty cycle of differential clock, (LCLKP-LCLKM) | 50% | ||||
| tRISE
tFALL |
Data rise time, Data fall time |
Rise time measured from –100 mV to 100 mV, Fall time measured from 100 mV to –100 mV 10 MSPS ≤ Sampling frequency ≤ 100 MSPS |
0.17 | ns | ||
| tCLKRISE
tCLKFALL |
Output clock rise time, Output clock fall time |
Rise time measured from –100 mV to 100 mV Fall time measured from 100 mV to –100 mV 10 MSPS ≤ Sampling frequency ≤ 100 MSPS |
0.2 | ns | ||
7.10 LVDS Timing at Lower Sampling Frequencies - 2 Wire, 8× Serialization
| SAMPLING FREQUENCY, MSPS | SETUP TIME | HOLD TIME | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | ||
| 100 | 0.23 | 0.31 | ns | ||||
| 80 | 0.47 | 0.47 | ns | ||||
| 65 | 0.56 | 0.7 | ns | ||||
| 50 | 0.66 | 1 | ns | ||||
| 20 | 2.7 | 2.8 | ns | ||||
7.11 LVDS Timing for 1 Wire 16× Serialization
| SAMPLING FREQUENCY, MSPS | SETUP TIME | HOLD TIME | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | ||
| 65 | 0.15 | 0.31 | ns | ||||
| 50 | 0.27 | 0.35 | ns | ||||
| 40 | 0.45 | 0.55 | ns | ||||
| 20 | 1.1 | 1.4 | ns | ||||
| Clock Propagation Delay tPDI = (ts/8) + tdelay 10 MSPS < Sampling Frequency < 65 MSPS |
tdelay | ns | |||||
| MIN | TYP | MAX | ns | ||||
| 6.8 | 8.8 | 10.8 | ns | ||||
7.12 LVDS Timing for 2 Wire, 7× Serialization
| SAMPLING FREQUENCY, MSPS | SETUP TIME | HOLD TIME | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | ||
| 100 | 0.29 | 0.39 | ns | ||||
| 80 | 0.51 | 0.60 | ns | ||||
| 65 | 0.58 | 0.82 | ns | ||||
| 50 | 0.85 | 1.20 | ns | ||||
| 20 | 3.2 | 3.3 | ns | ||||
| Clock Propagation Delay tPDI = (ts/3.5) + tdelay 10 MSPS < Sampling Frequency < 100 MSPS |
tdelay | ns | |||||
| MIN | TYP | MAX | ns | ||||
| 6.8 | 8.8 | 10.8 | ns | ||||
7.13 LVDS Timing for 1 Wire, 14× Serialization
| SAMPLING FREQUENCY, MSPS | SETUP TIME | HOLD TIME | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | MIN | TYP | MAX | ||
| 65 | 0.19 | 0.28 | ns | ||||
| 50 | 0.37 | 0.42 | ns | ||||
| 30 | 0.70 | 1.0 | ns | ||||
| 20 | 1.3 | 1.5 | ns | ||||
| Clock Propagation Delay tPDI = (ts/7) + tdelay 10 MSPS < Sampling Frequency < 65 MSPS |
tdelay | ns | |||||
| MIN | TYP | MAX | ns | ||||
| 6.8 | 8.8 | 10.8 | ns | ||||
7.14 Serial Interface Timing Requirements
Typical values at 25°C, MIN and MAX values across the full temperature range TMIN = –40°C to TMAX = 85°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, LVDD = 1.8 V, unless otherwise noted.| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fSCLK | SCLK frequency (= 1/ tSCLK) | > DC | 20 | MHz | |
| tSLOADS | CS to SCLK setup time | 25 | ns | ||
| tSLOADH | SCLK to CS hold time | 25 | ns | ||
| tDS | SDATA setup time | 25 | ns | ||
| tDH | SDATA hold time | 25 | ns | ||
7.15 Reset Switching Characteristics
Typical values at 25°C, MIN and MAX values across the full temperature range TMIN = –40°C to TMAX = 85°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 | Power-on delay | Delay from power up of AVDD and LVDD to RESET pulse active | 1 | ms | ||
| t2 | Reset pulse duration | Pulse duration of active RESET signal | 50 | ns | ||
| t3 | Register write delay | Delay from RESET disable to CS active | 100 | ns | ||

NOTE:
A high-going pulse on RESET pin is required in serial interface mode in case of initialization through hardware reset. For parallel interface operation, RESET has to be tied permanently HIGH. Figure 2. LVDS Timing
Figure 2. LVDS Timing
 Figure 3. Latency Diagram
Figure 3. Latency Diagram
 Figure 4. LVDS Output Voltage Levels
Figure 4. LVDS Output Voltage Levels
7.16 Typical Characteristics
7.16.1 Typical Characteristic – 16-Bit ADC Mode
All plots are at 25°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, LVDD = 1.8 V, maximum-rated sampling frequency, sine-wave input clock = 1.5 VPP differential clock amplitude, 50% clock duty cycle, –1 dBFS differential analog input, internal reference mode, 0 dB gain, 32k point FFT (unless otherwise noted). Figure 5. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 40 MSPS
Figure 5. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 40 MSPS
 Figure 7. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 80 MSPS
Figure 7. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 80 MSPS
 Figure 9. FFT for 65-MHz Input Signal, fS = 80 MSPS
Figure 9. FFT for 65-MHz Input Signal, fS = 80 MSPS
 Figure 11. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
Figure 11. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
 Figure 15. SFDR vs Input Frequency
Figure 15. SFDR vs Input Frequency
 Figure 17. SFDR Across Gain
Figure 17. SFDR Across Gain
 Figure 19. Performance Across Input Amplitude,
Figure 19. Performance Across Input Amplitude, Single Tone
 Figure 21. Performance vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 21. Performance vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
 Figure 23. SNR Across Temperature vs AVDD Supply, Sample Rate = 80 MSPS
Figure 23. SNR Across Temperature vs AVDD Supply, Sample Rate = 80 MSPS
 Figure 27. Performance Across LVDD Supply
Figure 27. Performance Across LVDD Supply Sample Rate = 100 MSPS
 Figure 29. Performance Across Input Clock Duty Cycle,
Figure 29. Performance Across Input Clock Duty Cycle, Sample Rate = 100 MSPS
 Figure 31. Far-Channel Crosstalk Spectrum
Figure 31. Far-Channel Crosstalk Spectrum
 Figure 33. Differential Non-Linearity
Figure 33. Differential Non-Linearity
 Figure 6. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 40 MSPS
Figure 6. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 40 MSPS
 Figure 8. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 80 MSPS
Figure 8. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 80 MSPS
 Figure 10. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
Figure 10. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
 Figure 12. FFT for 65-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
Figure 12. FFT for 65-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
 Figure 14. FFT for 2-Tone Input Signal
Figure 14. FFT for 2-Tone Input Signal
 Figure 16. SNR vs Input Frequency
Figure 16. SNR vs Input Frequency
 Figure 18. SNR Across Gain
Figure 18. SNR Across Gain
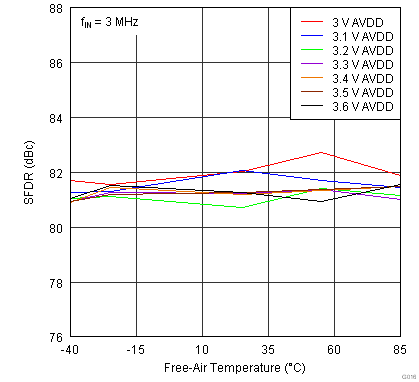 Figure 22. SFDR Across Temperature vs AVDD Supply, Sample Rate = 80 MSPS
Figure 22. SFDR Across Temperature vs AVDD Supply, Sample Rate = 80 MSPS
 Figure 24. Performance Across LVDD Supply Voltage,
Figure 24. Performance Across LVDD Supply Voltage, Sample Rate = 80 MSPS
 Figure 26. SNR Across Temperature
Figure 26. SNR Across Temperature Sample Rate = 100 MSPS
 Figure 28. Performance Across Input Clock Amplitude, Sample Rate = 100 MSPS
Figure 28. Performance Across Input Clock Amplitude, Sample Rate = 100 MSPS
 Figure 30. Near-Channel Crosstalk Spectrum,
Figure 30. Near-Channel Crosstalk Spectrum, Sample Rate = 100 MSPS
 Figure 32. Integral Non-Linearity
Figure 32. Integral Non-Linearity
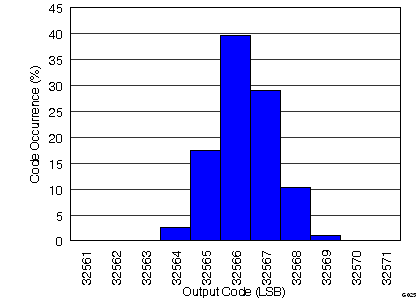
with Analog Inputs Shorted
7.16.2 Typical Characteristic – 14-Bit ADC Mode
 Figure 35. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
Figure 35. FFT for 3-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
 Figure 37. FFT for 65-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
Figure 37. FFT for 65-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
 Figure 36. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
Figure 36. FFT for 15-MHz Input Signal, fS = 100 MSPS
7.16.3 Typical Characteristics – Common Plots
 Figure 38. 16-Bit Digital Power Across Sampling Frequencies
Figure 38. 16-Bit Digital Power Across Sampling Frequencies

 Figure 42. SNR Contour Across Sampling and Input Frequencies, 14-Bit ADC
Figure 42. SNR Contour Across Sampling and Input Frequencies, 14-Bit ADC
 Figure 39. 14-Bit Digital Power Across Sampling Frequencies
Figure 39. 14-Bit Digital Power Across Sampling Frequencies

 Figure 43. SFDR Contour Across Sampling and Input Frequencies, 14-Bit ADC
Figure 43. SFDR Contour Across Sampling and Input Frequencies, 14-Bit ADC


