-
DRV8806 Quad Serial Interface Low-Side Driver IC
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
DRV8806 Quad Serial Interface Low-Side Driver IC
1 Features
- 4-Channel Protected Low-Side Driver
- Four NMOS FETs With Overcurrent Protection
- Integrated Inductive Clamp Diodes
- Serial Interface
- Open/Shorted Load Detection
- 2-A (Single Channel On)/1-A (All Channels On) Maximum Drive Current per Channel (at 25°C)
- 8.2-V to 40-V Operating Supply Voltage Range
- Thermally-Enhanced Surface Mount Package
2 Applications
- Relay Drivers
- Unipolar Stepper Motor Drivers
- Solenoid Drivers
- General Low-Side Switch Applications
3 Description
The DRV8806 provides a 4-channel low-side driver with overcurrent protection. It has built-in diodes to clamp turnoff transients generated by inductive loads and can be used to drive unipolar stepper motors, DC motors, relays, solenoids, or other loads.
The DRV8806 can supply up to 2-A (single channel on) or 1-A (all channels on) continuous output current (with adequate PCB heatsinking at 25°C).
A serial interface is provided to control the output drivers. Fault status can be read through the serial interface. Multiple DRV8806 devices can be chained together to use a single serial interface.
Internal shutdown functions are provided for overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, undervoltage lockout, and overtemperature, and faults are indicated by a fault output pin.
The DRV8806 is available in a 16-pin HTSSOP package (Eco-friendly: RoHS & no Sb/Br).
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| DRV8806 | HTSSOP (16) | 5.00 mm × 4.40 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
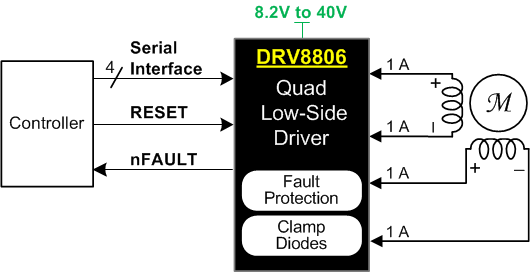
Simplified Schematic
4 Revision History
Changes from B Revision (December 2013) to C Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
Changes from A Revision (November 2013) to B Revision
- Changed (OPEN-DRAIN to PUSH-PULL in the elec chara table section SDATAOUT OUTPUTGo
- Added another row below VOH - merge the first two columns together (VOH and Output high voltage). The second row should have test condition "Io = 100 uA, VM = 8.2 V" and be specified as 2.5 V MINGo
- Added two new rows, ISRC and ISNK in elec chara table, section SDATAOUT OUTPUTGo
- Changed NO. 6 in Timing Requirements table Go
- Added a sentence in second paragraph below Figure 2: A pullup resistor......1 kohm is recommended.Go
Changes from * Revision (June 2012) to A Revision
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | EXTERNAL COMPONENTS OR CONNECTIONS |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| POWER AND GROUND | ||||
| GND | 5, 12, PowerPAD™ | — | Device ground | All pins must be connected to GND. |
| VM | 1 | — | Device power supply | Connect to motor supply (8.2 V - 40 V). |
| CONTROL | ||||
| LATCH | 11 | I | Latch input | Rising edge latches shift register to output stage, falling edge latches fault data into output shift register – internal pulldown |
| nENBL | 8 | I | Enable input | Active low enables outputs – internal pulldown |
| RESET | 9 | I | Reset input | Active-high reset input initializes internal logic – internal pulldown |
| SCLK | 13 | I | Serial clock | Serial clock input – internal pulldown |
| SDATIN | 14 | I | Serial data input | Serial data input – internal pulldown |
| SDATOUT | 15 | OD | Serial data output | Serial data output; push-pull structure; see serial interface section for details |
| STATUS | ||||
| nFAULT | 16 | OD | Fault | Logic low when in fault condition (overtemperature, overcurrent, open load) - open-drain output |
| OUTPUT | ||||
| OUT1 | 3 | O | Output 1 | Connect to load 1 |
| OUT2 | 4 | O | Output 2 | Connect to load 2 |
| OUT3 | 6 | O | Output 3 | Connect to load 3 |
| OUT4 | 7 | O | Output 4 | Connect to load 4 |
| VCLAMP | 2 | — | Output clamp voltage | Connect to VM supply, or zener diode to VM supply |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VM | Power supply voltage | –0.3 | 43 | V | |
| VOUTx | Output voltage | –0.3 | 43 | V | |
| VCLAMP | Clamp voltage | –0.3 | 43 | V | |
| SDATOUT, nFAULT |
Output current | 20 | mA | ||
| Peak clamp diode current(3) | 2 | A | |||
| DC or RMS clamp diode current(3) | 1 | A | |||
| Digital input pin voltage | –0.5 | 7 | V | ||
| SDATOUT, nFAULT |
Digital output pin voltage | –0.5 | 7 | V | |
| Peak motor drive output current, t < 1 μS | Internally limited | A | |||
| Continuous total power dissipation(3) | See Thermal Information | ||||
| TJ | Operating virtual junction temperature(3) | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –60 | 150 | °C | |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | ±6000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | ±1000 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VM | Power supply voltage | 8.2 | 40 | V | |
| VCLAMP | Output clamp voltage(2) | 0 | 40 | V | |
| IOUT | Continuous output current, single channel on, TA = 25°C(1) | 2 | A | ||
| Continuous output current, four channels on, TA = 25°C(1) | 1 | A | |||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DRV8806 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWP (HTSSOP) | |||
| 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 39.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 24.6 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 20.3 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 20.1 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.3 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
TA = 25°C, over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)6.6 Timing Requirements
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)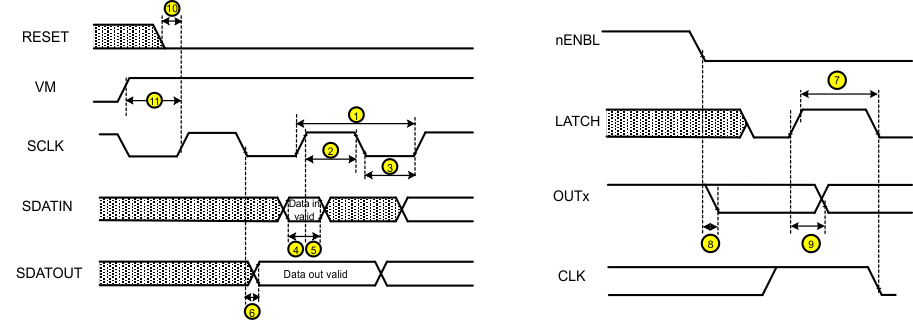
6.7 Typical Characteristics
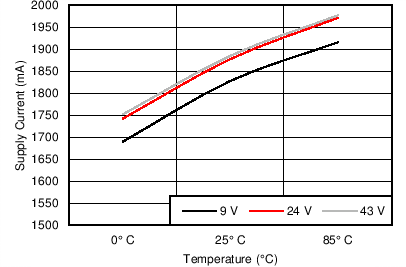
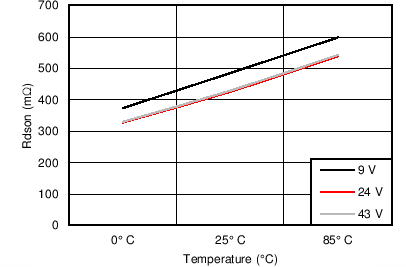
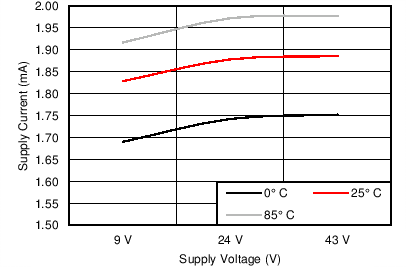
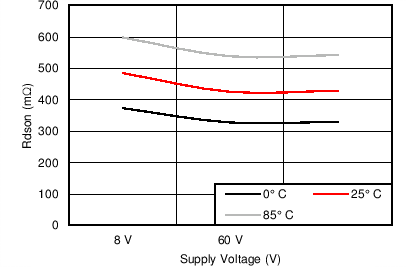
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
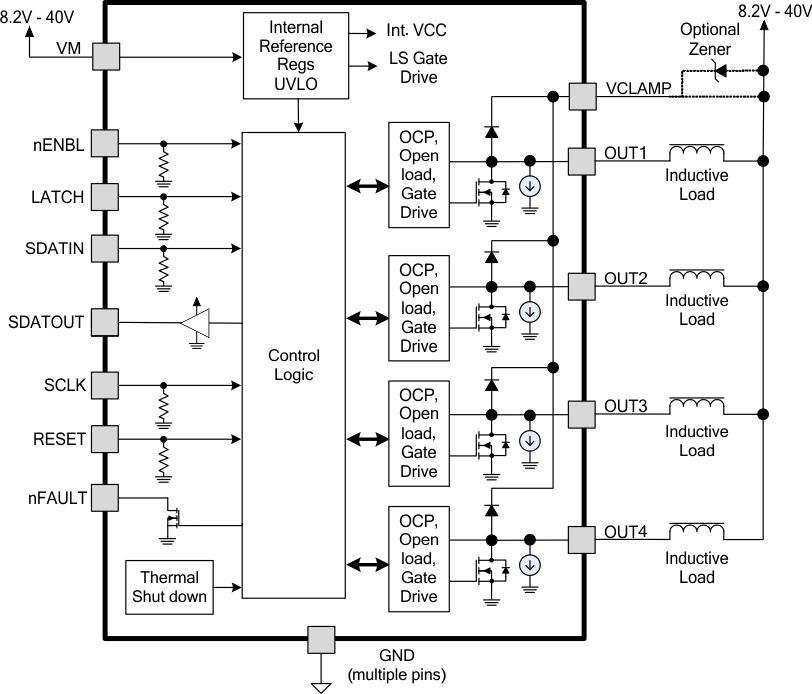
The DRV8806 is an integrated 4-channel low-side driver controlled using a serial interface to change the state of the low-side driver outputs. The low-side driver outputs consist of four N-channel MOSFETs that have a typical RDS(ON) of 500 mΩ. A single motor supply input VM serves as device power and is internally regulated to power the low-side gate drive. Data is shifted into a temporary data register in the device through the SDATIN pin, one bit at each rising edge of SCLK, while LATCH is held low. The outputs of the device can be disabled by pulling nENBL logic high. Several safety features are integrated in the device including overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, undervoltage lockout, and open load protection. The overcurrent protection and open load faults share a fault bit per channel that is set when one of these conditions occurs.
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Output Drivers
The DRV8806 contains four protected low-side drivers. Each output has an integrated clamp diode connected to a common pin, VCLAMP.
VCLAMP can be connected to the main power supply voltage, VM. It can also be connected to a Zener or TVS diode to VM, allowing the switch voltage to exceed the main supply voltage VM. This connection can be beneficial when driving loads that require very fast current decay, such as unipolar stepper motors.
In all cases, the voltage on the outputs must not be allowed to exceed the maximum output voltage specification.
7.3.2 Protection Circuits
The DRV8806 is fully protected against undervoltage, overcurrent and overtemperature events.
7.3.2.1 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
An analog current limit circuit on each FET limits the current through the FET by removing the gate drive. If this analog current limit persists for longer than the tOCP deglitch time (approximately 3.5 µs), the driver will be disabled and the nFAULT pin will be driven low. The driver will remain disabled for the tRETRY retry time (approximately 1.2 ms), then the fault will be automatically cleared. The fault will be cleared immediately if either RESET pin is activated or VM is removed and reapplied.
7.3.2.2 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
If the die temperature exceeds safe limits, all output FETs will be disabled and the nFAULT pin will be driven low. Once the die temperature has fallen to a safe level, operation will automatically resume.
7.3.2.3 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
If at any time the voltage on the VM pin falls below the undervoltage lockout threshold voltage, all circuitry in the device will be disabled, and internal logic will be reset. Operation will resume when VM rises above the UVLO threshold.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Serial Interface Operation
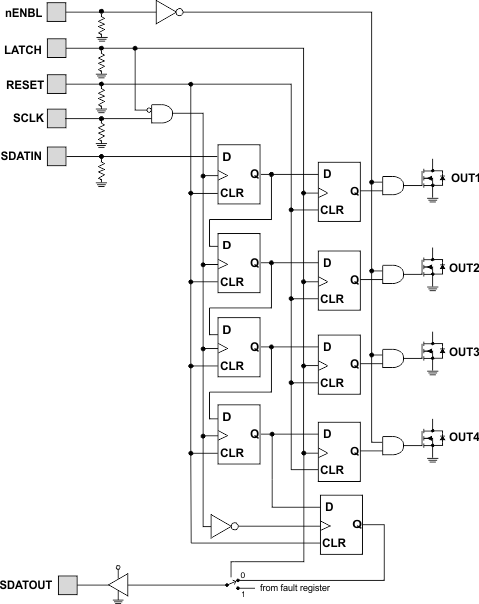
The DRV8806 is controlled with a simple serial interface. Logically, the interface is shown in Figure 6.
Data is shifted into a temporary holding shift register in the part using the SDATIN pin, one bit at each rising edge of the SCLK pin, while LATCH is low. Data is shifted from the last bit to the SDATOUT pin, so multiple devices may be daisy-chained together using a single serial interface.
Note that the SDATOUT pin has a push-pull driver, which can support driving another DRV8806 SDATIN pin at clock frequencies of up to 1 MHz without an external pullup. A pullup resistor can be used between SDATOUT and an external 5-V logic supply to support higher clock frequencies. TI recommends a resistor value of approximately 1 kΩ. The SDATOUT pin is capable of approximately 1-mA source and 5-mA sink. To supply logic signals to a lower-voltage microcontroller, use a resistor divider from SDATOUT to GND.
A rising edge on the LATCH pin latches the data from the temporary shift register into the output stage.
7.4.2 Fault Output Register
The DRV8806 contains circuitry to detect open or shorted loads. The status of the loads can be read through the serial interface. The logic is shown in Figure 7.
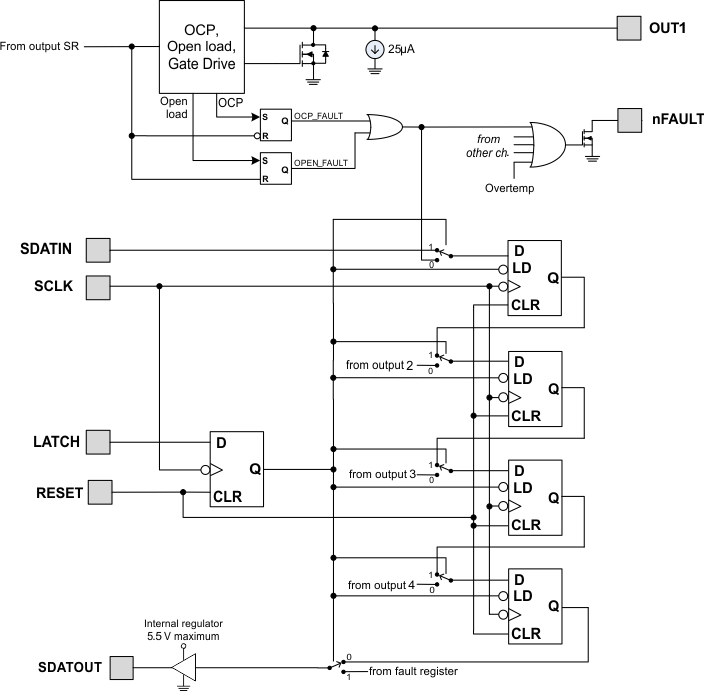 Figure 7. Fault Output
Figure 7. Fault Output
To overcome any leakage currents to accurately sense an open load, a small current source is connected to each output pin. This source pulls approximately 25-µA of current to ground. The voltage on the output pin is sensed during the time that the output is off, and if the voltage on the pin is less than 1.2 V (indicating that there is no load connected) after the open load deglitch time, the OPEN_FAULT latch is set. This latch is cleared whenever the output bit is set.
When the output is turned on, if an overcurrent (OCP) fault is detected, the channel will be turned off and the OCP_FAULT latch is set. This latch will be cleared whenever the output bit is cleared.
The state of the OCP_FAULT and OPEN_FAULT signals is combined into a single fault bit per channel, and loaded into a shift register while the LATCH pin is low. When the LATCH pin is taken high, the fault data is latched into the shift register at the first falling edge of SCLK. Data may then be shifted out on the SDATOUT pin on each falling edge of the SCLK pin.
Note that the LATCH signal must be high for a minimum of 200 ns before valid data can be clocked out.
The nFAULT pin will be driven active low whenever any of the OCP_FAULT or OPEN_FAULT latches are set, as well as whenever there is an overtemperature condition.
7.4.3 Daisy-Chain Connection
Two or more DRV8806 devices may be connected together to use a single serial interface. The SDATOUT pin of the first device in the chain is connected to the SDATIN pin of the next device. The SCLK, LATCH, RESET, and nFAULT pins are connected together.
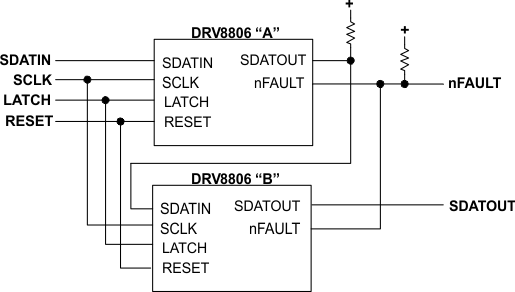 Figure 8. Daisy-Chain Connection
Figure 8. Daisy-Chain Connection
Figure 9 shows an example of a serial transaction, writing the output bits, and then reading the fault status bits, using two devices connected together in a daisy-chain.
Note that the LATCH signal must be high for a minimum of 200 ns before valid data can be clocked out.
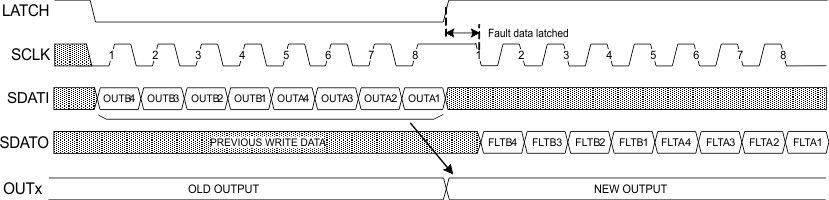 Figure 9. Daisy-Chain Serial Transaction
Figure 9. Daisy-Chain Serial Transaction
7.4.4 nENBL and RESET Operation
The nENBL pin enables or disables the output drivers. nENBL must be low to enable the outputs. nENBL does not affect the operation of the serial interface logic. Note that nENBL has an internal pulldown.
The RESET pin, when driven active high, resets internal logic, including the OCP fault. All serial interface registers are cleared. Note that RESET has an internal pulldown. An internal power-up reset is also provided, so it is not required to drive RESET at power up.
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The DRV8806 can be used to drive one unipolar stepper motor.
8.2 Typical Application
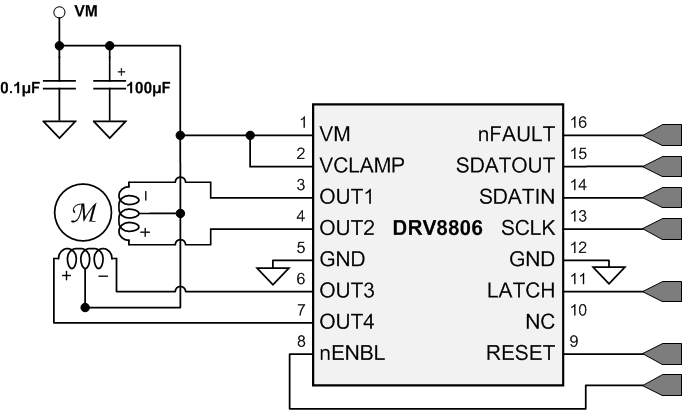 Figure 10. DRV8806 Typical Application
Figure 10. DRV8806 Typical Application
8.2.1 Design Requirements
For this design example, use the parameters listed in Table 1 as the input parameters.
Table 1. Design Parameters
| DESIGN PARAMETER | EXAMPLE VALUE |
|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VM | 24 V |
| Motor winding resistance, RL | 7.4 Ω/phase |
| Motor full step angle, θstep | 1.8°/step |
| Motor rated current, IRATED | 0.75 A |
| SCLK frequency, fSCLK | 1 MHz |
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
8.2.2.1 Motor Voltage
The motor voltage to use will depend on the ratings of the motor selected and the desired torque. A higher voltage shortens the current rise time in the coils of the stepper motor allowing the motor to produce a greater average torque. Using a higher voltage also allows the motor to operate at a faster speed than a lower voltage.
8.2.2.2 Drive Current
The current path is starts from the supply VM, moves through the inductive winding load, and low-side sinking NMOS power FET. Power dissipation losses in one sink NMOS power FET are shown in Equation 1.
The DRV8806 has been measured to be capable of 2-A Single Channel or 1-A Four Channels in a HTSSOP package at 25°C on standard FR-4 PCBs. The maximum RMS current varies based on PCB design and the ambient temperature.
8.2.3 Application Curves
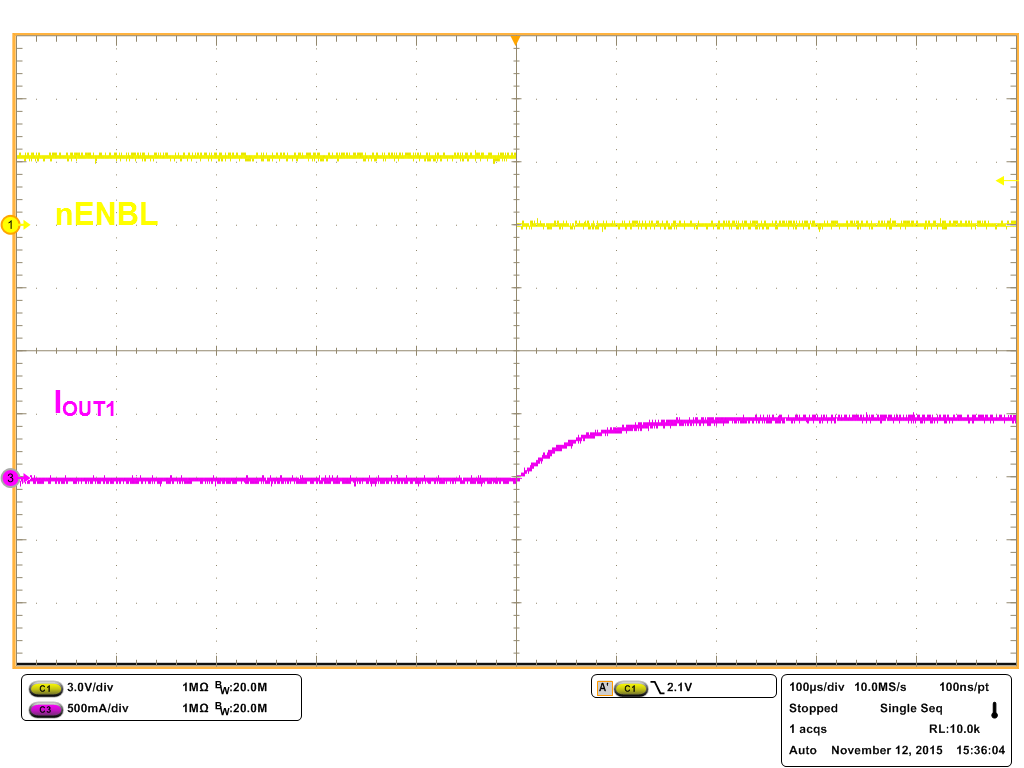
| 16-Ω, 1-mH, RL Load | ||
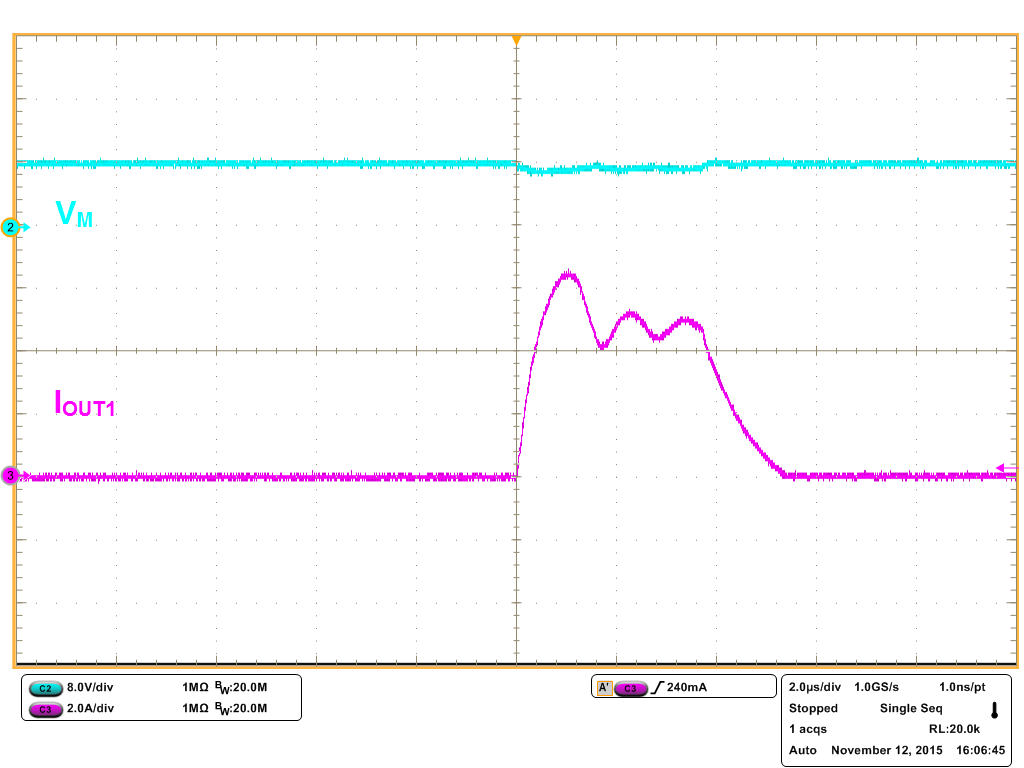
| Output shorted to VM | ||
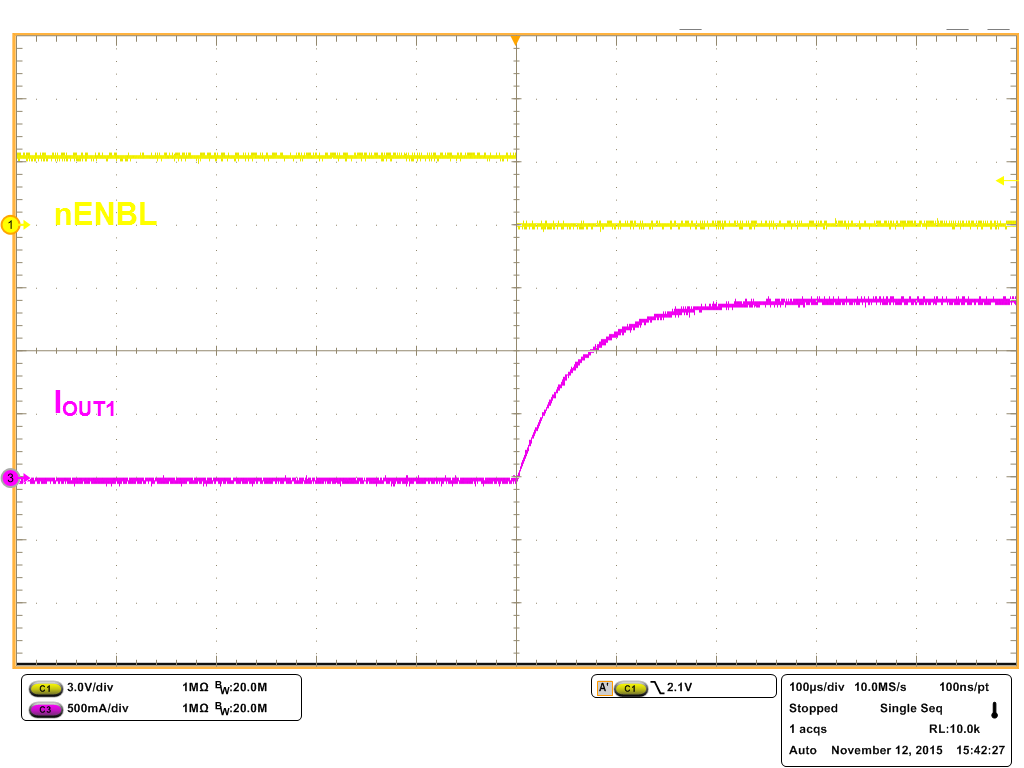
| 16-Ω, 1-mH RL Load | ||
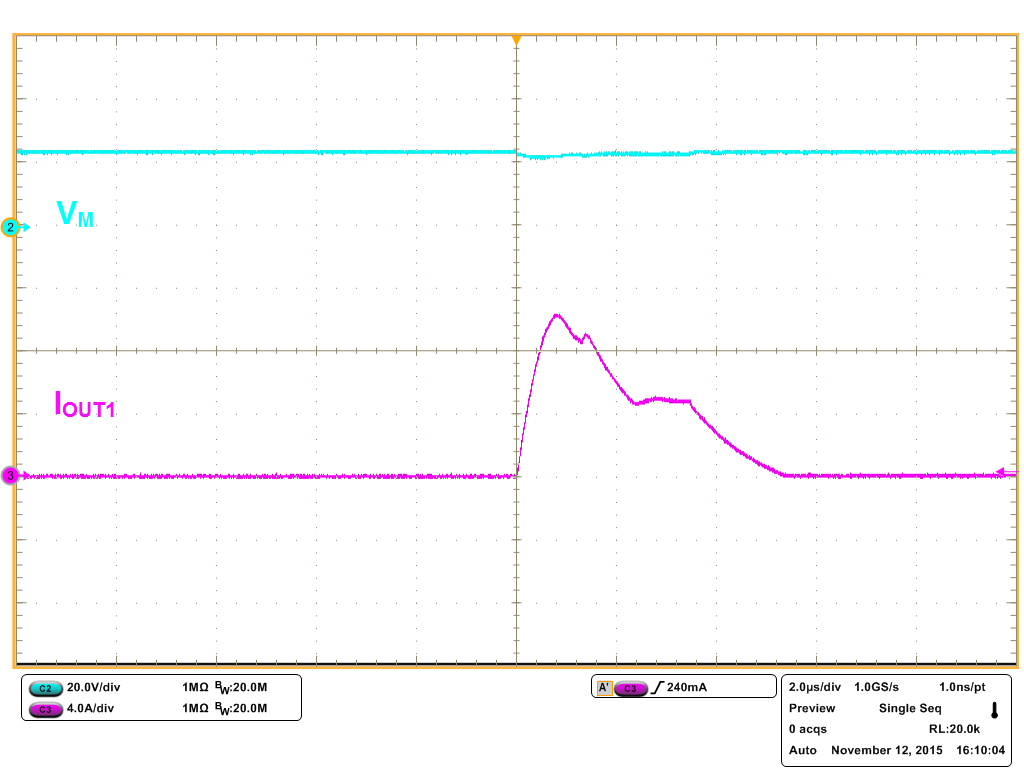
| Output shorted to VM | ||