-
ISO5852S-Q1 High-CMTI 2.5-A and 5-A Reinforced Isolated IGBT, MOSFET Gate Driver With Split Outputs and Active Protection Features
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Function
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Switching Characteristics
- 7.11 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1 Recommended ISO5852S-Q1 Application Circuit
- 10.2.2.2 FLT and RDY Pin Circuitry
- 10.2.2.3 Driving the Control Inputs
- 10.2.2.4 Local Shutdown and Reset
- 10.2.2.5 Global-Shutdown and Reset
- 10.2.2.6 Auto-Reset
- 10.2.2.7 DESAT Pin Protection
- 10.2.2.8 DESAT Diode and DESAT Threshold
- 10.2.2.9 Determining the Maximum Available, Dynamic Output Power, POD-max
- 10.2.2.10 Example
- 10.2.2.11 Higher Output Current Using an External Current Buffer
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
ISO5852S-Q1 High-CMTI 2.5-A and 5-A Reinforced Isolated IGBT, MOSFET Gate Driver With Split Outputs and Active Protection Features
1 Features
- Qualified for Automotive Applications
- AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results:
- Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to +125°C Ambient Operating Temperature Range
- Device HBM Classification Level 3A
- Device CDM Classification Level C6
- 100-kV/μs Minimum Common-Mode Transient Immunity (CMTI) at VCM = 1500 V
- Split Outputs to Provide 2.5-A Peak Source and
5-A Peak Sink Currents - Short Propagation Delay: 76 ns (Typ),
110 ns (Max) - 2-A Active Miller Clamp
- Output Short-Circuit Clamp
- Soft Turn-Off (STO) during Short Circuit
- Fault Alarm upon Desaturation Detection is Signaled on FLT and Reset Through RST
- Input and Output Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) with Ready (RDY) Pin Indication
- Active Output Pulldown and Default Low Outputs with Low Supply or Floating Inputs
- 2.25-V to 5.5-V Input Supply Voltage
- 15-V to 30-V Output Driver Supply Voltage
- CMOS Compatible Inputs
- Rejects Input Pulses and Noise Transients Shorter Than 20 ns
- Isolation Surge Withstand Voltage 12800-VPK
- Safety-Related Certifications:
- 8000-VPK VIOTM and 2121-VPK VIORM Reinforced Isolation per DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12
- 5700-VRMS Isolation for 1 Minute per UL 1577
- CSA Component Acceptance Notice 5A, IEC 60950–1 and IEC 60601–1 End Equipment Standards
- TUV Certification per EN 61010-1 and EN 60950-1
- GB4943.1-2011 CQC Certification
- All Certifications Complete per UL, VDE, CQC, TUV and Planned for CSA
2 Applications
- Isolated IGBT and MOSFET Drives in:
- HEV and EV Power Modules
- Industrial Motor Control Drives
- Industrial Power Supplies
- Solar Inverters
- Induction Heating
3 Description
The ISO5852S-Q1 device is a 5.7-kVRMS, reinforced isolated gate driver for IGBTs and MOSFETs with split outputs, OUTH and OUTL, providing 2.5-A source and 5-A sink current. The input side operates from a single 2.25-V to 5.5-V supply. The output side allows for a supply range from minimum 15 V to maximum 30 V. Two complementary CMOS inputs control the output state of the gate driver. The short propagation time of 76 ns provides accurate control of the output stage.
An internal desaturation (DESAT) fault detection recognizes when the IGBT is in an overcurrent condition. Upon a DESAT detect, a mute logic immediately blocks the output of the isolator and initiates a soft-turnoff procedure which disables the OUTH pin and pulls the OUTL pin to low over a time span of 2 μs. When the OUTL pin reaches 2 V with respect to the most-negative supply potential, VEE2, the gate-driver output is pulled hard to the VEE2 potential, turning the IGBT immediately off.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| ISO5852S-Q1 | SOIC (16) | 10.30 mm × 7.50 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Functional Block Diagram
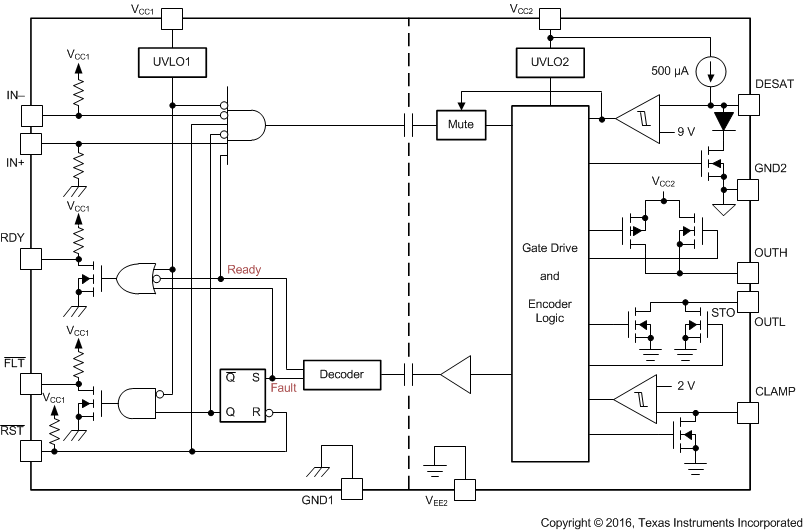
5 Description (continued)
When desaturation is active, a fault signal is sent across the isolation barrier, pulling the FLT output at the input side low and blocking the isolator input. Mute logic is activated through the soft-turnoff period. The FLT output condition is latched and can be reset only after the RDY pin goes high, through a low-active pulse at the RST input.
When the IGBT is turned off during normal operation with a bipolar output supply, the output is hard clamp to VEE2. If the output supply is unipolar, an active Miller clamp can be used, allowing Miller current to sink across a low-impedance path which prevents the IGBT from dynamic turnon during high-voltage transient conditions.
The readiness for the gate driver to be operated is under the control of two undervoltage-lockout circuits monitoring the input-side and output-side supplies. If either side has insufficient supply, the RDY output goes low, otherwise this output is high.
The ISO5852S-Q1 device is available in a 16-pin SOIC package. Device operation is specified over a temperature range from –40°C to +125°C ambient.
6 Pin Configuration and Function
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| CLAMP | 7 | O | Miller clamp output |
| DESAT | 2 | I | Desaturation voltage input |
| FLT | 13 | O | Fault output, active-low during DESAT condition |
| GND1 | 9 | — | Input ground |
| 16 | |||
| GND2 | 3 | — | Gate drive common. Connect to IGBT emitter. |
| IN+ | 10 | I | Non-inverting gate drive voltage control input |
| IN– | 11 | I | Inverting gate drive voltage control input |
| OUTH | 4 | O | Positive gate drive voltage output |
| OUTL | 6 | O | Negative gate drive voltage output |
| RDY | 12 | O | Power-good output, active high when both supplies are good. |
| RST | 14 | I | Reset input, apply a low pulse to reset fault latch. |
| VCC1 | 15 | — | Positive input supply (2.25-V to 5.5-V) |
| VCC2 | 5 | — | Most positive output supply potential. |
| VEE2 | 1 | — | Output negative supply. Connect to GND2 for unipolar supply application. |
| 8 | |||
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC1 | Supply-voltage input side | GND1 – 0.3 | 6 | V | ||
| VCC2 | Positive supply-voltage output side | (VCC2 – GND2) | –0.3 | 35 | V | |
| VEE2 | Negative supply-voltage output side | (VEE2 – GND2) | –17.5 | 0.3 | V | |
| V(SUP2) | Total-supply output voltage | (VCC2 – VEE2) | –0.3 | 35 | V | |
| V(OUTH) | Positive gate-driver output voltage | VEE2 – 0.3 | VCC2 + 0.3 | V | ||
| V(OUTL) | Negative gate-driver output voltage | VEE2 – 0.3 | VCC2 + 0.3 | V | ||
| I(OUTH) | Gate-driver high output current | Maximum pulse width = 10 μs, Maximum duty cycle = 0.2%) | 2.7 | A | ||
| I(OUTL) | Gate-driver low output current | Maximum pulse width = 10 μs, Maximum duty cycle = 0.2%) | 5.5 | A | ||
| V(LIP) | Voltage at IN+, IN–,FLT, RDY, RST | GND1 – 0.3 | VCC1 + 0.3 | V | ||
| I(LOP) | Output current of FLT, RDY | 10 | mA | |||
| V(DESAT) | Voltage at DESAT | GND2 – 0.3 | VCC2 + 0.3 | V | ||
| V(CLAMP) | Clamp voltage | VEE2 – 0.3 | VCC2 + 0.3 | V | ||
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | ||
| TSTG | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±4000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | ±1500 | |||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC1 | Supply-voltage input side | 2.25 | 5.5 | V | |
| VCC2 | Positive supply-voltage output side (VCC2 – GND2) | 15 | 30 | V | |
| V(EE2) | Negative supply-voltage output side (VEE2 – GND2) | –15 | 0 | V | |
| V(SUP2) | Total supply-voltage output side (VCC2 – VEE2) | 15 | 30 | V | |
| V(IH) | High-level input voltage (IN+, IN–, RST) | 0.7 × VCC1 | VCC1 | V | |
| V(IL) | Low-level input voltage (IN+, IN–, RST) | 0 | 0.3 × VCC1 | V | |
| tUI | Pulse width at IN+, IN– for full output (CLOAD = 1 nF) | 40 | ns | ||
| tRST | Pulse width at RST for resetting fault latch | 800 | ns | ||
| TA | Ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | ISO5852S-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DW (SOIC) | |||
| 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 99.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 48.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 56.5 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 29.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 56.5 | °C/W |
7.5 Power Ratings
Full-chip power dissipation is derated 10.04 mW/°C beyond 25°C ambient temperature. At 125°C ambient temperature, a maximum of 251 mW total power dissipation is allowed. Power dissipation can be optimized depending on ambient temperature and board design, while ensuring that the junction temperature does not exceed 150°C.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Maximum power dissipation (both sides) | VCC1 = 5.5 V, VCC2 = 30 V, TA = 25°C | 1255 | mW | ||
| PID | Maximum input power dissipation | VCC1 = 5.5 V, VCC2 = 30 V, TA = 25°C | 175 | mW | ||
| POD | Maximum output power dissipation | VCC1 = 5.5 V, VCC2 = 30 V, TA = 25°C | 1080 | mW | ||
7.6 Insulation Specifications
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | VALUE | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GENERAL | ||||
| CLR | External clearance(1) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance through air | 8 | mm |
| CPG | External creepage(1) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance across the package surface | 8 | mm |
| DTI | Distance through the insulation | Minimum internal gap (internal clearance) | 21 | µm |
| CTI | Comparative tracking index | DIN EN 60112 (VDE 0303-11); IEC 60112; Material Group I according to IEC 60664-1; UL 746A | >600 | V |
| Material group | I | |||
| Overvoltage Category | Rated mains voltage ≤ 600 VRMS | I-IV | ||
| Rated mains voltage ≤ 1000 VRMS | I-III | |||
| DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12(2) | ||||
| VIORM | Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage | AC voltage (bipolar) | 2121 | VPK |
| VIOWM | Maximum isolation working voltage | AC voltage (sine wave) Time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) test, see Figure 1 | 1500 | VRMS |
| DC voltage | 2121 | VDC | ||
| VIOTM | Maximum transient isolation voltage | VTEST = VIOTM; t = 60 s (qualification); t = 1 s (100% production) | 8000 | VPK |
| VIOSM | Maximum surge isolation voltage(3) | Test method per IEC 60065, 1.2/50 µs waveform, VTEST = 1.6 × VIOSM = 12800 VPK (qualification) | 8000 | |
| qpd | Apparent charge(4) | Method a: After I/O safety test subgroup 2/3, Vini = VIOTM, tini = 60 s; Vpd(m) = 1.2 × VIORM = 2545 VPK , tm = 10 s |
≤5 | pC |
| Method a: After environmental tests subgroup 1, Vini = VIOTM, tini = 60 s; Vpd(m) = 1.6 × VIORM = 3394 VPK , tm = 10 s |
≤5 | |||
| Method b1: At routine test (100% production) and preconditioning (type test) Vini = VIOTM, tini = 60 s; Vpd(m) = 1.875× VIORM = 3977 VPK , tm = 10 s |
≤5 | |||
| CIO | Barrier capacitance, input to output(5) | VIO = 0.4 sin (2πft), f = 1 MHz | 1 | pF |
| RIO | Isolation resistance, input to output(5) | VIO = 500 V, TA = 25°C | > 1012 | Ω |
| VIO = 500 V, 100°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | > 1011 | |||
| VIO = 500 V at TS = 150°C | > 109 | |||
| Pollution degree | 2 | |||
| UL 1577 | ||||
| VISO | Withstand isolation voltage | VTEST = VISO = 5700 VRMS, t = 60 s (qualification); VTEST = 1.2 × VISO = 6840 VRMS, t = 1 s (100% production) | 5700 | VRMS |
7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
| VDE | CSA | UL | CQC | TUV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certified according to DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12 and DIN EN 61010-1 (VDE 0411-1):2011-07 |
Plan to certify under CSA Component Acceptance Notice 5A, IEC 60950-1, and IEC 60601-1 | Recognized under UL 1577 Component Recognition Program | Certified according to GB4943.1-2011 | Certified according to EN 61010-1:2010 (3rd Ed) and EN 60950-1:2006/A11:2009/A1:2010/ A12:2011/A2:2013 |
| Reinforced Insulation Maximum Transient isolation voltage, 8000 VPK; Maximum surge isolation voltage, 8000 VPK, Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage, 2121 VPK |
Isolation Rating of 5700 VRMS; Reinforced insulation per CSA 60950-1- 07+A1+A2 and IEC 60950-1 (2nd Ed.), 800 VRMS max working voltage (pollution degree 2, material group I) ; 2 MOPP (Means of Patient Protection) per CSA 60601-1:14 and IEC 60601-1 Ed. 3.1, 250 VRMS (354 VPK) max working voltage |
Single Protection, 5700 VRMS (1) | Reinforced Insulation, Altitude ≤ 5000m, Tropical climate, 400 VRMS maximum working voltage | 5700 VRMS Reinforced insulation per EN 61010-1:2010 (3rd Ed) up to working voltage of 600 VRMS 5700 VRMS Reinforced insulation per EN 60950-1:2006/A11:2009/A1:2010/ A12:2011/A2:2013 up to working voltage of 800 VRMS |
| Certification completed Certificate number: 40040142 |
Certificate planned | Certification completed File number: E181974 |
Certification completed Certificate number: CQC16001141761 |
Certification completed Client ID number: 77311 |
7.8 Safety Limiting Values
Safety limiting intends to minimize potential damage to the isolation barrier upon failure of input or output circuitry. A failure of the I/O can allow low resistance to ground or the supply and, without current limiting, dissipate sufficient power to overheat the die and damage the isolation barrier, potentially leading to secondary system failures.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | Safety input, output, or supply current | RθJA = 99.6°C/W, VI = 2.75 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 2 | 456 | mA | ||
| RθJA = 99.6°C/W, VI = 3.6 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 2 | 346 | |||||
| RθJA = 99.6°C/W, VI = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 2 | 228 | |||||
| RθJA = 99.6°C/W, VI = 15 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 2 | 84 | |||||
| RθJA = 99.6°C/W, VI = 30 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 2 | 42 | |||||
| PS | Safety input, output, or total power | RθJA = 99.6°C/W, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C, see Figure 3 | 255(1) | mW | ||
| TS | Maximum ambient safety temperature | 150 | °C | |||
The safety-limiting constraint is the maximum junction temperature specified in the data sheet. The power dissipation and junction-to-air thermal impedance of the device installed in the application hardware determines the junction temperature. The assumed junction-to-air thermal resistance in the Thermal Information table is that of a device installed on a high-K test board for leaded surface-mount packages. The power is the recommended maximum input voltage times the current. The junction temperature is then the ambient temperature plus the power times the junction-to-air thermal resistance.
7.9 Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted. All typical values are at TA = 25°C, VCC1 = 5 V, VCC2 – GND2 = 15 V, GND2 – VEE2 = 8 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOLTAGE SUPPLY | |||||||
| VIT+(UVLO1) | Positive-going UVLO1 threshold-voltage input side (VCC1 – GND1) | 2.25 | V | ||||
| VIT-(UVLO1) | Negative-going UVLO1 threshold-voltage input side (VCC1 – GND1) | 1.7 | V | ||||
| VHYS(UVLO1) | UVLO1 Hysteresis voltage (VIT+ – VIT–) input side | 0.2 | V | ||||
| VIT+(UVLO2) | Positive-going UVLO2 threshold-voltage output side (VCC2 – GND2) | 12 | 13 | V | |||
| VIT–(UVLO2) | Negative-going UVLO2 threshold-voltage output side (VCC2 – GND2) | 9.5 | 11 | V | |||
| VHYS(UVLO2) | UVLO2 hysteresis voltage (VIT+ – VIT–) output side | 1 | V | ||||
| IQ1 | Input-supply quiescent current | 2.8 | 4.5 | mA | |||
| IQ2 | Output-supply quiescent current | 3.6 | 6 | mA | |||
| LOGIC I/O | |||||||
| VIT+(IN,RST) | Positive-going input-threshold voltage (IN+, IN–, RST) | 0.7 × VCC1 | V | ||||
| VIT–(IN,RST) | Negative-going input-threshold voltage (IN+, IN–, RST) | 0.3 × VCC1 | V | ||||
| VHYS(IN,RST) | Input hysteresis voltage (IN+, IN–, RST) | 0.15 × VCC1 | V | ||||
| IIH | High-level input leakage at (IN+)(1) | IN+ = VCC1 | 100 | µA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input leakage at (IN–, RST)(2) | IN– = GND1, RST = GND1 | -100 | µA | |||
| IPU | Pullup current of FLT, RDY | V(RDY) = GND1, V(FLT) = GND1 | 100 | µA | |||
| V(OL) | Low-level output voltage at FLT, RDY | I(FLT) = 5 mA | 0.2 | V | |||
| GATE DRIVER STAGE | |||||||
| V(OUTPD) | Active output pulldown voltage | I(OUTH/L) = 200 mA, VCC2 = open | 2 | V | |||
| VOUTH | High-level output voltage | I(OUTH) = –20 mA | VCC2 – 0.5 | VCC2 – 0.24 | V | ||
| VOUTL | Low-level output voltage | I(OUTL) = 20 mA | VEE2 + 13 | VEE2 + 50 | mV | ||
| I(OUTH) | High-level output peak current | IN+ = high, IN– = low, V(OUTH) = VCC2 - 15 V |
1.5 | 2.5 | A | ||
| I(OUTL) | Low-level output peak current | IN+ = low, IN– = high, V(OUTL) = VEE2 + 15 V |
3.4 | 5 | A | ||
| I(OLF) | Low-level output current during fault condition | 130 | mA | ||||
| ACTIVE MILLER CLAMP | |||||||
| V(CLP) | Low-level clamp voltage | I(CLP) = 20 mA | VEE2 + 0.015 | VEE2 + 0.08 | V | ||
| I(CLP) | Low-level clamp current | V(CLAMP) = VEE2 + 2.5 V | 1.6 | 2.5 | 3.3 | A | |
| V(CLTH) | Clamp threshold voltage | 1.6 | 2.1 | 2.5 | V | ||
| SHORT CIRCUIT CLAMPING | |||||||
| V(CLP-OUTH) | Clamping voltage (VOUTH – VCC2) |
IN+ = high, IN– = low, tCLP = 10 µs, I(OUTH) = 500 mA | 1.1 | 1.3 | V | ||
| V(CLP-OUTL) | Clamping voltage (VOUTL – VCC2) |
IN+ = high, IN– = low, tCLP = 10 µs, I(OUTL) = 500 mA | 1.3 | 1.5 | V | ||
| V(CLP-CLP) | Clamping voltage (VCLP – VCC2) |
IN+ = high, IN– = low, tCLP = 10 µs, I(CLP) = 500 mA | 1.3 | V | |||
| V(CLP-CLAMP) | Clamping voltage at CLAMP | IN+ = High, IN– = Low, I(CLP) = 20 mA |
0.7 | 1.1 | V | ||
| V(CLP-OUTL) | Clamping voltage at OUTL (VCLP – VCC2) |
IN+ = High, IN– = Low, I(OUTL) = 20 mA |
0.7 | 1.1 | V | ||
| DESAT PROTECTION | |||||||
| I(CHG) | Blanking-capacitor charge current | V(DESAT) – GND2 = 2 V | 0.42 | 0.5 | 0.58 | mA | |
| I(DCHG) | Blanking-capacitor discharge current | V(DESAT) – GND2 = 6 V | 9 | 14 | mA | ||
| V(DSTH) | DESAT threshold voltage with respect to GND2 | 8.3 | 9 | 9.5 | V | ||
| V(DSL) | DESAT voltage with respect to GND2, when OUTH or OUTL is driven low | 0.4 | 1 | V | |||
7.10 Switching Characteristics
Over recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted. All typical values are at TA = 25°C, VCC1 = 5 V, VCC2 – GND2 = 15 V, GND2 – VEE2 = 8 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tr | Output-signal rise time at OUTH | CLOAD = 1 nF | See Figure 44, Figure 45, and Figure 46 | 12 | 18 | 35 | ns |
| tf | Output-signal fall time at OUTL | CLOAD = 1 nF | 12 | 20 | 37 | ns | |
| tPLH, tPHL | Propagation Delay | CLOAD = 1 nF | 76 | 110 | ns | ||
| tsk-p | Pulse skew |tPHL – tPLH| | CLOAD = 1 nF | 20 | ns | |||
| tsk-pp | Part-to-part skew | CLOAD = 1 nF | 30(1) | ns | |||
| tGF (IN,/RST) | Glitch filter on IN+, IN–, RST | CLOAD = 1 nF | 20 | 30 | 40 | ns | |
| tDS (90%) | DESAT sense to 90% VOUTH/L delay | CLOAD = 10 nF | 553 | 760 | ns | ||
| tDS (10%) | DESAT sense to 10% VOUTH/L delay | CLOAD = 10 nF | 2 | 3.5 | μs | ||
| tDS (GF) | DESAT-glitch filter delay | CLOAD = 1 nF | 330 | ns | |||
| tDS (FLT) | DESAT sense to FLT-low delay | See Figure 46 | 1.4 | μs | |||
| tLEB | Leading-edge blanking time | See Figure 44 and Figure 45 | 310 | 400 | 480 | ns | |
| tGF(RSTFLT) | Glitch filter on RST for resetting FLT | 300 | 800 | ns | |||
| CI | Input capacitance(2) | VI = VCC1 / 2 + 0.4 × sin (2πft), f = 1 MHz, VCC1 = 5 V | 2 | pF | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | VCM = 1500 V, see Figure 47 | 100 | 120 | kV/μs | ||
7.11 Insulation Characteristics Curves

| TA up to 150°C | Stress-voltage frequency = 60 Hz | |


7.12 Typical Characteristics



| Unipolar: VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 |



| CL = 1 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 20 V | ||

| CL = 100 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 20 V | ||

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 20 V | ||

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 15 V | DESAT = 220 pF | |

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 30 V | DESAT = 220 pF | |

| IN+ = High | IN– = Low |


| No CL |

| CL = 1 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC1 = 5 V |

| RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω | VCC1 = 5 V |

| RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω | VCC1 = 5 V |

| RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω | VCC1 = 5 V |

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |





| VCC2 = 15 V | DESAT = 6 V |

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 20 V | ||

| CL = 1 nF | RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 20 V | ||

| CL = 100 nF | RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 20 V | ||

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 15 V | DESAT = 220 pF | |

| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 – VEE2 = VCC2 – GND2 = 30 V | DESAT = 220 pF | |

| IN+ = Low | IN– = Low |

| Input frequency = 1 kHz |

| RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω, 20 kHz |

| CL = 1 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |
| VCC2 = 15 V |

| RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω | VCC1 = 5 V |

| RGH = 10 Ω | RGL = 5 Ω | VCC1 = 5 V |


| CL = 10 nF | RGH = 0 Ω | RGL = 0 Ω |




8 Parameter Measurement Information
 Figure 44. OUTH and OUTL Propagation Delay, Non-Inverting Configuration
Figure 44. OUTH and OUTL Propagation Delay, Non-Inverting Configuration
 Figure 45. OUTH and OUTL Propagation Delay, Inverting Configuration
Figure 45. OUTH and OUTL Propagation Delay, Inverting Configuration
 Figure 46. DESAT, OUTH/L, FLT, RST Delay
Figure 46. DESAT, OUTH/L, FLT, RST Delay
 Figure 47. Common-Mode Transient Immunity Test Circuit
Figure 47. Common-Mode Transient Immunity Test Circuit