JAJSGV3B September 2015 – January 2019 ADC31JB68
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Analog Inputs and Input Buffer
- 9.3.2 Amplitude and Phase Imbalance Correction
- 9.3.3 Over-Range Detection
- 9.3.4 Input Clock Divider
- 9.3.5 SYSREF Detection Gate
- 9.3.6 Serial Differential Output Drivers
- 9.3.7 ADC Core Calibration
- 9.3.8 Data Format
- 9.3.9 JESD204B Supported Features
- 9.3.10 JESD204B Interface
- 9.3.11 Transport Layer Configuration
- 9.3.12 Test Pattern Sequences
- 9.3.13 JESD204B Link Initialization
- 9.3.14 SPI
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Register Map
- 9.5.1
Register Descriptions
- 9.5.1.1 CONFIG_A (address = 0x0000) [reset = 0x3C]
- 9.5.1.2 DEVICE CONFIG (address = 0x0002) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.3 CHIP_TYPE (address = 0x0003 ) [reset = 0x03]
- 9.5.1.4 CHIP_ID (address = 0x0005, 0x0004) [reset = 0x00, 0x1B]
- 9.5.1.5 CHIP_VERSION (address =0x0006) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.6 VENDOR_ID (address = 0x000D, 0x000C) [reset = 0x04, 0x51]
- 9.5.1.7 SPI_CFG (address = 0x0010 ) [reset = 0x01]
- 9.5.1.8 OM1 (Operational Mode 1) (address = 0x0012) [reset = 0xC1]
- 9.5.1.9 OM2 (Operational Mode 2) (address = 0x0013) [reset = 0x20]
- 9.5.1.10 IMB_ADJ (Imbalance Adjust) (address = 0x0014) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.11 OVR_EN (Over-Range Enable) (address = 0x003A) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.12 OVR_HOLD (Over-Range Hold) (address = 0x003B) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.13 OVR_TH (Over-Range Threshold) (address = 0x003C) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.14 DC_MODE (DC Offset Correction Mode) (address = 0x003D) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.15 SER_CFG (Serial Lane Transmitter Configuration) (address = 0x0047) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.16 JESD_CTRL1 (JESD Configuration Control 1) (address = 0x0060) [reset = 0x7F]
- 9.5.1.17 JESD_CTRL2 (JESD Configuration Control 2) (address = 0x0061) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.18 JESD_RSTEP (JESD Ramp Pattern Step) (address = 0x0063, 0x0062) [reset = 0x00, 0x01]
- 9.5.1.19 SER_INV (Serial Lane Inversion Control) (address = 0x0064) [reset = 0x00]
- 9.5.1.20 JESD_STATUS (JESD Link Status) (address = 0x006C) [reset = N/A]
- 9.5.1
Register Descriptions
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RTA|40
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RTA|40
発注情報
10.1.4.1 Output Serial-Lane Interface
The output high speed serial lanes must be AC coupled to the receiving device with 0.01-µF capacitors as shown in Figure 75. DC coupling to the receiving device is not supported. The lane channel on the PCB must be a
100-Ω differential transmission line with dominant coupling recommended between the differential traces instead of to adjacent layers. The lane must terminate at a 100-Ω termination inside the receiving device. Avoid changing the direction of the channel traces abruptly at angles larger than 45°.
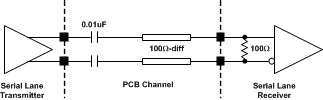 Figure 75. High-Speed Serial-Lane Interface
Figure 75. High-Speed Serial-Lane Interface The recommended spacing between serial lanes is 3× the differential line spacing or greater. High speed serial lanes should be routed on top of or below adjacent, quiet ground planes to provide shielding. TI recommends that other high speed signal traces do not cross the serial lanes on adjacent PCB layers. If absolutely necessary, crossing should occur at a 90° angle with the trajectory of the serial lane to minimize coupling.
The integrity of the data transfer from the transmitter to receiver is limited by the accuracy of the lane impedance and the attenuation as the signal travels down the lane. Inaccurate or varying impedance and frequency dependent attenuation results in increased ISI (part of deterministic jitter) and reduced signal-to-noise ratio, which limits the ability of the receiver to accurately recover the data.
Two features are provided in the ADC31JB68 device serial transmitters to compensate attenuation and ISI caused by the serial lane: voltage swing control (VOD) and de-emphasis (DEM).