SBAS741B October 2015 – April 2020 ADS1018-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.1.6 Pseudo Code Example
The flow chart in Figure 22 shows a pseudo-code sequence with the required steps to set up communication between the device and a microcontroller to take subsequent readings from the ADS1018-Q1. As an example, the default Config register settings are changed to set up the device for FSR = ±0.512 V, continuous-conversion mode, and a 920-SPS data rate.
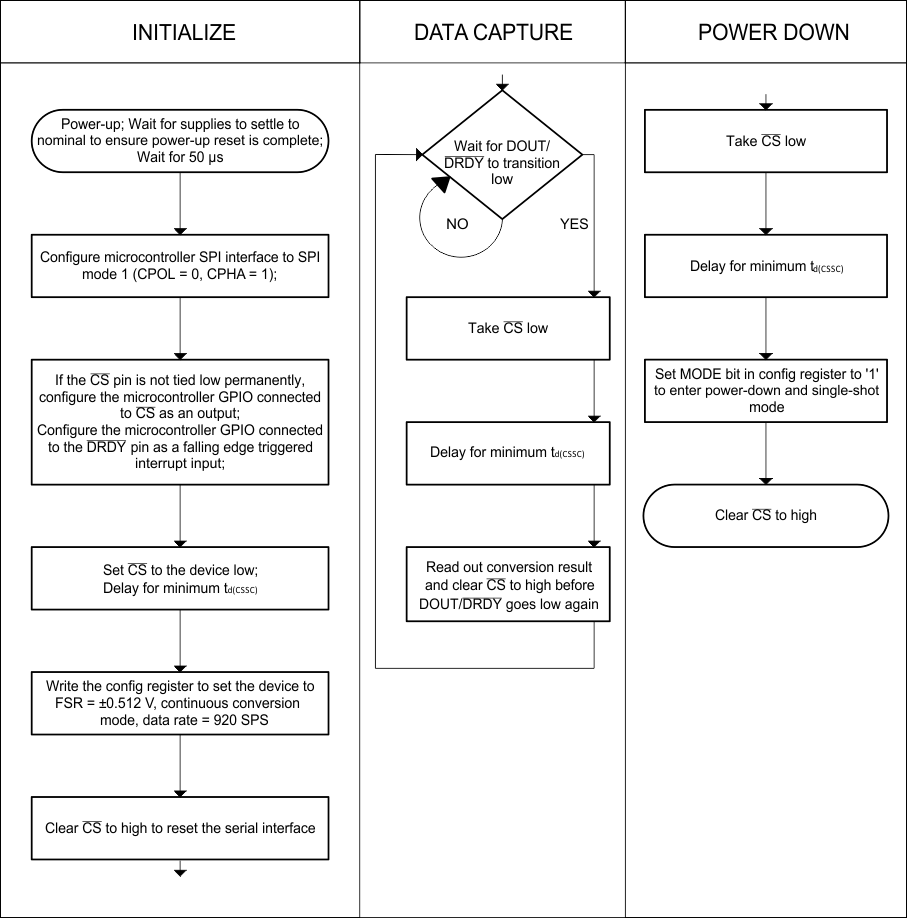 Figure 22. Pseudo-Code Example Flowchart
Figure 22. Pseudo-Code Example Flowchart