JAJSI32 October 2019 ADS1235-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Conversion Control
- 9.4.2 Chop Mode
- 9.4.3 AC-Bridge Excitation Mode
- 9.4.4 ADC Clock Mode
- 9.4.5 Power-Down Mode
- 9.4.6 Reset
- 9.4.7 Calibration
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1 Device Identification (ID) Register (address = 00h) [reset = Cxh]
- 9.6.2 Device Status (STATUS) Register (address = 01h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.3 Mode 0 (MODE0) Register (address = 02h) [reset = 24h]
- 9.6.4 Mode 1 (MODE1) Register (address = 03h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.5 Mode 2 (MODE2) Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.6 Mode 3 (MODE3) Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.7 Reference Configuration (REF) Register (address = 06h) [reset = 05h]
- 9.6.8 Offset Calibration (OFCALx) Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCALx) Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.10 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = FFh]
- 9.6.11 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.12 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.13 PGA Configuration (PGA) Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.14 Input Multiplexer (INPMUX) Register (address = 11h) [reset = FFh]
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.5.5.5 RDATA Command
This command reads conversion data. Because the data are buffered, the data can be read at any time during the conversion phase. If data are read near the completion of the next conversion, old or new conversion data are returned. See the Data Ready (DRDY) section for details.
The response of conversion data varies in length from 3 to 5 bytes depending if the STATUS byte and CRC bytes are included. See the Conversion Data Format section for the numeric data format. See Table 19, Figure 62 (minimum configuration) and Figure 63 (maximum configuration) for operation of the RDATA command.
Table 19. RDATA Command
| DIRECTION | BYTE 1 | BYTE 2 | BYTE 3 | BYTE 4 | BYTE 5 | BYTE 6 | BYTE 7 | BYTE 8 | BYTE 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No CRC mode | |||||||||
| DIN | 12h | Arbitrary | 00h | 00h | 00h | 00h | |||
| DOUT/DRDY | FFh | Echo byte 1 | STATUS (1) | MSB data | MID data | LSB data | |||
| CRC mode | |||||||||
| DIN | 12h | Arbitrary | CRC-2 | 00h | 00h | 00h | 00h | 00h | 00h |
| DOUT/DRDY | FFh | Echo byte 1 | Echo byte 2 | Out CRC-2 | STATUS (1) | MSB data | MID data | LSB data | Out CRC-3 or
Out CRC-4 |
(1) Optional STATUS byte
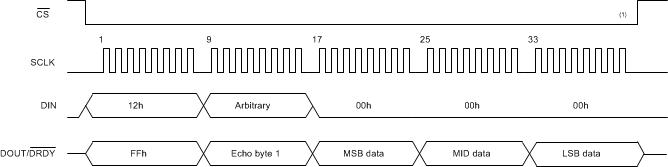
1. CS can be tied low
Figure 62. Conversion Data Read Operation (STATUS Byte and CRC Mode Disabled) 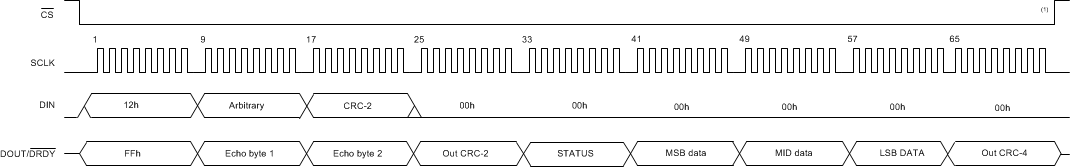
A. CS can be tied low
Figure 63. Conversion Data Read Operation (STATUS Byte and CRC Mode Enabled)