SBAS534E July 2011 – January 2016 ADS4249
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 ADS424x, ADS422x Family Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: ADS4249 (250 MSPS)
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 7.7 Digital Characteristics
- 7.8 LVDS and CMOS Modes Timing Requirements
- 7.9 LVDS Timings at Lower Sampling Frequencies
- 7.10 CMOS Timings at Lower Sampling Frequencies
- 7.11 Serial Interface Timing Characteristics
- 7.12 Reset Timing (Only when Serial Interface is Used)
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Serial Register Map
- 8.6.2
Description of Serial Registers
- 8.6.2.1 Register Address 00h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.2 Register Address 01h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.3 Register Address 01h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.4 Register Address 25h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.5 Register Address 29h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.6 Register Address 2Bh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.7 Register Address 3Dh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.8 Register Address 3Fh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.9 Register Address 40h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.10 Register Address 41h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.11 Register Address 42h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.12 Register Address 45h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.13 Register Address 4Ah (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.14 Register Address 58h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.15 Register Address BFh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.16 Register Address C1h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.17 Register Address CFh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.18 Register Address EFh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.19 Register Address F1h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.20 Register Address F2h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.21 Register Address 2h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.22 Register Address D5h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.23 Register Address D7h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.24 Register Address DBh (Default = 00h)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGC|64
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGC|64
発注情報
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
RGC Package (LVDS Mode)
64-Pin VQFN
Top View

NOTE:
The PowerPAD is connected to DRGND.NC = do not connect; must float.
Pin Functions (LVDS Mode)
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 17 | I | Analog ground |
| 18 | |||
| 21 | |||
| 24 | |||
| 27 | |||
| 28 | |||
| 31 | |||
| 32 | |||
| AVDD | 16 | I | Analog power supply |
| 22 | |||
| 33 | |||
| 34 | |||
| CLKM | 26 | I | Differential clock negative input |
| CLKP | 25 | I | Differential clock positive input |
| CLKOUTP | 57 | O | Differential output clock, true |
| CLKOUTM | 56 | O | Differential output clock, complement |
| CTRL1 | 35 | I | Digital control input pins. Together, these pins control the various power-down modes. |
| CTRL2 | 36 | ||
| CTRL3 | 37 | ||
| DA0M | 40 | O | Channel A differential output data pair, D0 and D1 multiplexed |
| DA0P | 41 | ||
| DA2M | 42 | O | Channel A differential output data D2 and D3 multiplexed |
| DA2P | 43 | ||
| DA4M | 44 | O | Channel A differential output data D4 and D5 multiplexed |
| DA4P | 45 | ||
| DA6M | 46 | O | Channel A differential output data D6 and D7 multiplexed |
| DA6P | 47 | ||
| DA8M | 50 | O | Channel A differential output data D8 and D9 multiplexed |
| DA8P | 51 | ||
| DA10M | 52 | O | Channel A differential output data D10 and D11 multiplexed |
| DA10P | 53 | ||
| DA12M | 54 | O | Channel A differential output data D12 and D13 multiplexed |
| DA12P | 55 | ||
| DB0M | 60 | O | Channel B differential output data pair, D0 and D1 multiplexed |
| DB0P | 61 | ||
| DB2M | 62 | O | Channel B differential output data D2 and D3 multiplexed |
| DB2P | 63 | ||
| DB4M | 2 | O | Channel B differential output data D4 and D5 multiplexed |
| DB4P | 3 | ||
| DB6M | 4 | O | Channel B differential output data D6 and D7 multiplexed |
| DB6P | 5 | ||
| DB8M | 6 | O | Channel B differential output data D8 and D9 multiplexed |
| DB8P | 7 | ||
| DB10M | 8 | O | Channel B differential output data D10 and D11 multiplexed |
| DB10P | 9 | ||
| DB12M | 10 | O | Channel B differential output data D12 and D13 multiplexed |
| DB12P | 11 | ||
| DRGND | 49 | I | Output buffer ground |
| PAD | |||
| DRVDD | 1 | I | Output buffer supply |
| 48 | |||
| INM_A | 30 | I | Differential analog negative input, channel A |
| INP_A | 29 | I | Differential analog positive input, channel A |
| INM_B | 20 | I | Differential analog negative input, channel B |
| INP_B | 19 | I | Differential analog positive input, channel B |
| NC | 38 | — | Do not connect, must be floated |
| 39 | |||
| 58 | |||
| 59 | |||
| RESET | 12 | I | Serial interface RESET input. When using the serial interface mode, the internal registers must be initialized through a hardware RESET by applying a high pulse on this pin or by using the software reset option; see the Serial Interface Configuration section. In parallel interface mode, the RESET pin must be permanently tied high. SCLK and SEN are used as parallel control pins in this mode. This pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-down resistor. |
| SCLK | 13 | I | This pin functions as a serial interface clock input when RESET is low. SCLK controls the low-speed mode selection when RESET is tied high; see Table 7 for detailed information. This pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-down resistor. |
| SDATA | 14 | I | Serial interface data input; this pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-down resistor. |
| SDOUT | 64 | O | This pin functions as a serial interface register readout when the READOUT bit is enabled. When READOUT = 0, this pin is put into a high-impedance state. |
| SEN | 15 | I | This pin functions as a serial interface enable input when RESET is low. SEN controls the output interface and data format selection when RESET is tied high; see Table 8 for detailed information. This pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-up resistor to AVDD. |
| VCM | 23 | O | This pin outputs the common-mode voltage (0.95 V) that can be used externally to bias the analog input pins |
RGC Package (CMOS Mode)
64-Pin VQFN
Top View
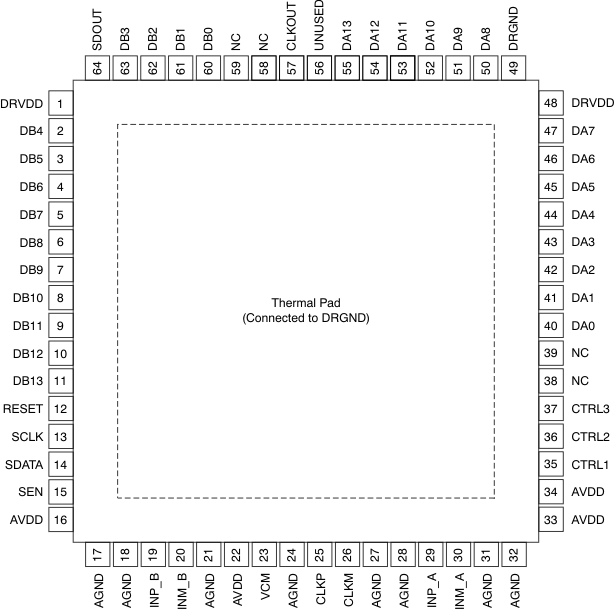
NOTE:
The PowerPAD is connected to DRGND.NC = do not connect; must float.
Pin Functions (CMOS Mode)
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 17 | I | Analog ground |
| 18 | |||
| 21 | |||
| 24 | |||
| 27 | |||
| 28 | |||
| 31 | |||
| 32 | |||
| AVDD | 16 | I | Analog power supply |
| 22 | |||
| 33 | |||
| 34 | |||
| CLKM | 26 | I | Differential clock negative input |
| CLKP | 25 | I | Differential clock positive input |
| CLKOUT | 57 | O | CMOS output clock |
| CTRL1 | 35 | I | Digital control input pins. Together, these pins control various power-down modes. |
| CTRL2 | 36 | ||
| CTRL3 | 37 | ||
| DA0 | 40 | O | Channel A ADC output data bits, CMOS levels |
| DA1 | 41 | ||
| DA2 | 42 | ||
| DA3 | 43 | ||
| DA4 | 44 | ||
| DA5 | 45 | ||
| DA6 | 46 | ||
| DA7 | 47 | ||
| DA8 | 50 | ||
| DA9 | 51 | ||
| DA10 | 52 | ||
| DA11 | 53 | ||
| DA12 | 54 | ||
| DA13 | 55 | ||
| DB0 | 60 | O | Channel B ADC output data bits, CMOS levels |
| DB1 | 61 | ||
| DB2 | 62 | ||
| DB3 | 63 | ||
| DB4 | 2 | ||
| DB5 | 3 | ||
| DB6 | 4 | ||
| DB7 | 5 | ||
| DB8 | 6 | ||
| DB9 | 7 | ||
| DB10 | 8 | ||
| DB11 | 9 | ||
| DB12 | 10 | ||
| DB13 | 11 | ||
| DRGND | 49 | I | Output buffer ground |
| PAD | |||
| DRVDD | 1 | I | Output buffer supply |
| 48 | |||
| INM_A | 30 | I | Differential analog negative input, channel A |
| INP_A | 29 | I | Differential analog positive input, channel A |
| INM_B | 20 | I | Differential analog negative input, channel B |
| INP_B | 19 | I | Differential analog positive input, channel B |
| NC | 38 | — | Do not connect, must be floated |
| 39 | |||
| 58 | |||
| 59 | |||
| RESET | 12 | I | Serial interface RESET input. When using the serial interface mode, the internal registers must be initialized through a hardware RESET by applying a high pulse on this pin or by using the software reset option; see the Serial Interface Configuration section. In parallel interface mode, the RESET pin must be permanently tied high. SDATA and SEN are used as parallel control pins in this mode. This pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-down resistor. |
| SCLK | 13 | I | This pin functions as a serial interface clock input when RESET is low. SCLK controls the low-speed mode when RESET is tied high; see Table 7 for detailed information. This pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-down resistor. |
| SDATA | 14 | I | Serial interface data input; this pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-down resistor. |
| SDOUT | 64 | O | This pin functions as a serial interface register readout when the READOUT bit is enabled. When READOUT = 0, this pin is put into a high-impedance state. |
| SEN | 15 | I | This pin functions as a serial interface enable input when RESET is low. SEN controls the output interface and data format selection when RESET is tied high; see Table 8 for detailed information. This pin has an internal 150-kΩ pull-up resistor to AVDD. |
| UNUSED | 56 | — | This pin is not used in the CMOS interface |
| VCM | 23 | O | This pin outputs the common-mode voltage (0.95 V) that can be used externally to bias the analog input pins |