SGLS378G March 2008 – October 2017 ADS5463-SP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: ADS5463-RHA
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADS5463-RHA
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: ADS5463-RHA
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: ADS5463-SP
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics: ADS5463-SP
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics: ADS5463-SP
- 6.11 Timing Requirements
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Device and Documentation Support
11.1 Device Support
11.1.1 Definition of Specifications
-
Analog Bandwidth The analog input frequency at which the power of the fundamental is reduced by 3 dB with respect to the low-frequency value
-
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay
-
Clock Pulse Duration/Duty Cycle
The duty cycle of a clock signal is the ratio of the time the clock signal remains at a logic high (clock pulse duration) to the period of the clock signal. Duty cycle is typically expressed as a percentage. A perfect differential sine wave clock results in a 50% duty cycle.
-
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) An ideal ADC exhibits code transitions at analog input values spaced exactly 1 LSB apart. DNL is the deviation of any single step from this ideal value, measured in units of LSB.
-
Effective Resolution Bandwidth The highest input frequency where the SNR (dB) is dropped by 3 dB for a full-scale input amplitude.
-
Gain Error Gain error is the deviation of the ADC actual input full-scale range from its ideal value. Gain error is given as a percentage of the ideal input full-scale range.
-
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
INL is the deviation of the ADC transfer function from a best-fit line determined by a least-squares curve fit of that transfer function. The INL at each analog input value is the difference between the actual transfer function and this best-fit line, measured in units of LSB.
-
Maximum Conversion Rate The maximum sampling rate at which certified operation is given. All parametric testing is performed at this sampling rate unless otherwise noted.
-
Minimum Conversion Rate The minimum sampling rate at which the ADC functions
-
Offset Error Offset error is the deviation of output code from mid-code when both inputs are tied to common-mode.
-
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (SINAD)
SINAD is the ratio of the power of the fundamental (PS) to the power of all the other spectral components including noise (PN) and distortion (PD), but excluding dc.
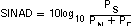
-
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
SNR is the ratio of the power of the fundamental (PS) to the noise floor power (PN), excluding the power at dc and in the first five harmonics.
SNR is given either in units of dBc (dB to carrier) when the absolute power of the fundamental is used as the reference, or dBFS (dB to full scale) when the power of the fundamental is extrapolated to the converter’s full-scale range.
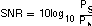
SINAD is given either in units of dBc (dB to carrier) when the absolute power of the fundamental is used as the reference, or dBFS (dB to Full Scale) when the power of the fundamental is extrapolated to the converter’s full-scale range.
-
Temperature Drift
Temperature drift (with respect to gain error and offset error) specifies the change from the value at the nominal temperature to the value at TMIN or TMAX. It is computed as the maximum variation the parameters over the whole temperature range divided by TMIN
-
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) THD is the ratio of the power of the fundamental (PS) to the power of the first five harmonics (PD).
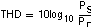
THD is typically given in units of dBc (dB to carrier).
-
Two-Tone Intermodulation Distortion
IMD3 is the ratio of the power of the fundamental (at frequencies f1, f2) to the power of the worst spectral component at either frequency 2f1 – f2 or 2f2 – f1). IMD3 is either given in units of dBc (dB to carrier) when the absolute power of the fundamental is used as the reference, or dBFS (dB to full scale) when the power of the fundamental is extrapolated to the converter’s full-scale range.
11.2 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates
To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on ti.com. In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any product information that has changed. For change details, review the revision history included in any revised document.
11.3 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
Design Support TI's Design Support Quickly find helpful E2E forums along with design support tools and contact information for technical support.
11.4 Trademarks
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
11.5 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
11.6 Glossary
SLYZ022 — TI Glossary.
This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.