SLAS468A June 2005 – August 2016 ADS7887 , ADS7888
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Companion Products
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8 Specifications
8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| +IN to AGND | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V | |
| +VDD to AGND | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| Digital input voltage to GND | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| Digital output to GND | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V | |
| Power dissipation, both packages | (TJ(MAX) – TA) / RθJA | |||
| Lead temperature, soldering | Vapor phase (60 s) | 215 | °C | |
| Infrared (15 s) | 220 | |||
| Junction temperature, TJ(MAX) | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
8.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | Operating temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
8.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | ADS7887, ADS7888 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBV (SOT-23) | DCK (SC70) | |||
| 6 PINS | 6 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 114.9 | 150.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 56.6 | 62.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 36.5 | 43 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 5.8 | 1.8 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 36.2 | 42.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
8.5 Electrical Characteristics – ADS7887
+VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C, and fsample = 1.25 MHz (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUT | ||||||
| Full-scale input voltage span(1) | 0 | VDD | V | |||
| Absolute input voltage range | +IN | –0.2 | VDD + 0.2 | V | ||
| Ci | Input capacitance(2) | 21 | pF | |||
| IIlkg | Input leakage current | TA = 125°C | 40 | nA | ||
| SYSTEM PERFORMANCE | ||||||
| Resolution | 10 | Bits | ||||
| No missing codes | 10 | Bits | ||||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | –0.75 | ±0.35 | 0.75 | LSB(3) | |
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | –0.5 | ±0.35 | 0.5 | LSB | |
| EO | Offset error(4)(5)(6) | –1.5 | ±0.5 | 1.5 | LSB | |
| EG | Gain error(5) | –1 | ±0.5 | 1 | LSB | |
| SAMPLING DYNAMICS | ||||||
| Conversion time | 25-MHz SCLK | 530 | 560 | ns | ||
| Acquisition time | 260 | ns | ||||
| Maximum throughput rate | 25-MHz SCLK | 1.25 | MHz | |||
| Aperture delay | 5 | ns | ||||
| Step Response | 160 | ns | ||||
| Overvoltage recovery | 160 | ns | ||||
| DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion(7) | 100 kHz | –84 | –72 | dB | |
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise and distortion | 100 kHz | 60.5 | 61 | dB | |
| SFDR | Spurious free dynamic range | 100 kHz | 73 | 81 | dB | |
| Full power bandwidth | At –3 dB | 15 | MHz | |||
| DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V | VDD – 0.4 | 5.25 | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | VDD = 5 V | 0.8 | V | ||
| VDD = 3 V | 0.4 | |||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | At Isource = 200 µA | VDD – 0.2 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | At Isink = 200 µA | 0.4 | |||
| POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENTS | ||||||
| +VDD | Supply voltage | 2.35 | 3.3 | 5.25 | V | |
| Supply current (normal mode) | At VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V, 1.25-MHz throughput |
2 | mA | |||
| At VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V, static state | 1.5 | |||||
| Power-down state supply current | SCLK off | 1 | µA | |||
| SCLK on (25 MHz) | 200 | |||||
| Power dissipation at 1.25-MHz throughput |
VDD = 5 V | 8 | 10 | mW | ||
| VDD = 3 V | 3.8 | 6 | ||||
| Power dissipation in static state | VDD = 5 V | 5.5 | 7.5 | mW | ||
| VDD = 3 V | 3 | 4.5 | ||||
| Power-down time | 0.1 | µs | ||||
| Power-up time | 0.8 | µs | ||||
| Invalid conversions after power up | 1 | |||||
(1) Ideal input span; does not include gain or offset error.
(2) Refer Figure 31 for details on sampling circuit
(3) LSB means least significant bit
(4) Measured relative to an ideal full-scale input
(5) Offset error and gain error ensured by characterization.
(6) First transition of 000H to 001H at 0.5 × (Vref/210)
(7) Calculated on the first nine harmonics of the input frequency
8.6 Electrical Characteristics – ADS7888
+VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C, and fsample = 1.25 MHz (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUT | ||||||
| Full-scale input voltage span(1) | 0 | VDD | V | |||
| Absolute input voltage range | +IN | –0.2 | VDD + 0.2 | V | ||
| Ci | Input capacitance(2) | 21 | pF | |||
| IIlkg | Input leakage current | TA = 125°C | 40 | nA | ||
| SYSTEM PERFORMANCE | ||||||
| Resolution | 8 | Bits | ||||
| No missing codes | 8 | Bits | ||||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | –0.3 | ±0.15 | 0.3 | LSB(3) | |
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | –0.3 | ±0.1 | 0.3 | LSB | |
| EO | Offset error(4) (5) (6) | –0.5 | ±0.15 | 0.5 | LSB | |
| EG | Gain error(5) | –0.5 | ±0.15 | 0.5 | LSB | |
| SAMPLING DYNAMICS | ||||||
| Conversion time | 25-MHz SCLK | 450 | 480 | ns | ||
| Acquisition time | 1.5 MSPS mode, see Figure 34 | 206 | ns | |||
| Maximum throughput rate | 25-MHz SCLK | 1.25 | MHz | |||
| Aperture delay | 5 | ns | ||||
| Step Response | 160 | ns | ||||
| Overvoltage recovery | 160 | ns | ||||
| DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion(7) | 100 kHz | –67.5 | –65 | dB | |
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise and distortion | 100 kHz | 49 | 49.5 | dB | |
| SFDR | Spurious free dynamic range | 100 kHz | 65 | 77 | dB | |
| Full power bandwidth | At –3 dB | 15 | MHz | |||
| DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V | VDD – 0.4 | 5.25 | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | VDD = 5 V | 0.8 | V | ||
| VDD = 3 V | 0.4 | |||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | At Isource = 200 µA | VDD – 0.2 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | At Isink = 200 µA | 0.4 | |||
| POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENTS | ||||||
| +VDD | Supply voltage | 2.35 | 3.3 | 5.25 | V | |
| Supply current (normal mode) | At VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V, 1.25-MHz throughput | 2 | mA | |||
| At VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V, static state | 1.5 | |||||
| Power-down state supply current | SCLK off | 1 | µA | |||
| SCLK on (25 MHz) | 200 | |||||
| Power dissipation at 1.25 MHz throughput | VDD = 5 V | 8 | 10 | mW | ||
| VDD = 3 V | 3.8 | 6 | ||||
| Power dissipation in static state | VDD = 5 V | 5.5 | 7.5 | mW | ||
| VDD = 3 V | 3 | 4.5 | ||||
| Power-down time | 0.1 | µs | ||||
| Power-up time | 0.8 | µs | ||||
| Invalid conversions after power up | 1 | |||||
(1) Ideal input span; does not include gain or offset error.
(2) Refer Figure 31 for details on sampling circuit
(3) LSB means least significant bit
(4) Measured relative to an ideal full-scale input
(5) Offset error and gain error ensured by characterization.
(6) First transition of 000H to 001H at (Vref/28)
(7) Calculated on the first nine harmonics of the input frequency
8.7 Timing Requirements
All specifications typical at TA = –40°C to 125°C and VDD = 2.35 V to 5.25 V (unless otherwise noted; see Figure 32)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS(1) | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tconv | Conversion time | ADS7887 | VDD = 3 V | 14 × tSCLK | ns | ||
| VDD = 5 V | 14 × tSCLK | ||||||
| ADS7888 | VDD = 3 V | 12 × tSCLK | |||||
| VDD = 5V | 12 × tSCLK | ||||||
| tq | Quiet time | Minimum time required from bus 3-state to start of next conversion | VDD = 3 V | 40 | ns | ||
| VDD = 5 V | 40 | ||||||
| td1 | Delay time | CS low to first data (0) out | VDD = 3 V | 15 | 25 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | 13 | 25 | |||||
| tsu1 | Setup time | CS low to SCLK low | VDD = 3 V | 10 | ns | ||
| VDD = 5 V | 10 | ||||||
| td2 | Delay time | SCLK falling to SDO | VDD = 3 V | 15 | 25 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | 13 | 25 | |||||
| th1 | Hold time | SCLK falling to data valid (with 50-pF load) | VDD < 3 V | 7 | ns | ||
| VDD > 5 V | 5.5 | ||||||
| td3 | Delay time | 16th SCLK falling edge to SDO 3-state | VDD = 3 V | 10 | 25 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | 8 | 20 | |||||
| tw1 | Pulse duration | CS | VDD = 3 V | 25 | 40 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | 25 | 40 | |||||
| td4 | Delay time | CS high to SDO 3-state, see Figure 34 | VDD = 3 V | 17 | 30 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | 15 | 25 | |||||
| twH | Pulse duration | SCLK high | VDD = 3 V | 0.4 × tSCLK | ns | ||
| VDD = 5 V | 0.4 × tSCLK | ||||||
| twL | Pulse duration | SCLK low | VDD = 3 V | 0.4 × tSCLK | ns | ||
| VDD = 5 V | 0.4 × tSCLK | ||||||
| Frequency | SCLK | VDD = 3 V | 25 | MHz | |||
| VDD = 5 V | 25 | ||||||
| td5 | Delay time | Second falling edge of clock and CS to enter in power down (use min spec not to accidently enter in power down, see Figure 35) | VDD = 3 V | –2 | 5 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | –2 | 5 | |||||
| td6 | Delay time | CS and 10th falling edge of clock to enter in power down (use max spec not to accidently enter in power down, see Figure 35) | VDD = 3 V | 2 | –5 | ns | |
| VDD = 5 V | 2 | –5 | |||||
(1) 3-V Specifications apply from 2.35 V to 3.6 V, and 5-V specifications apply from 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
8.8 Typical Characteristics
8.8.1 ADS7887 and ADS7888
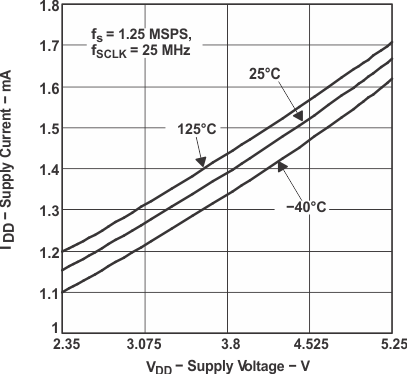 Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
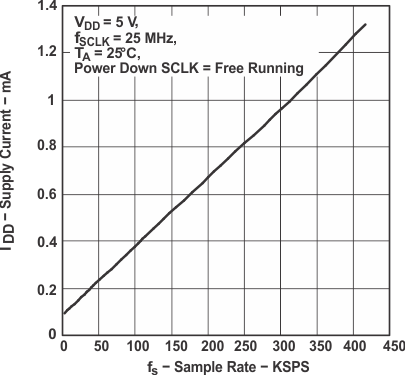 Figure 3. Supply Current vs Sample Rate
Figure 3. Supply Current vs Sample Rate
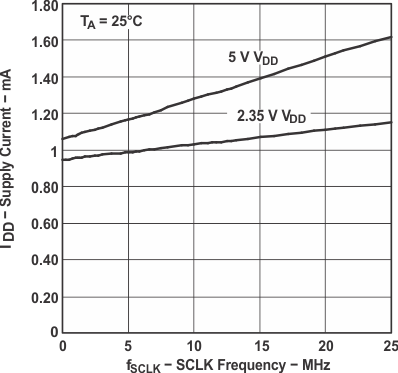 Figure 2. Supply Current vs SCLK Frequency
Figure 2. Supply Current vs SCLK Frequency
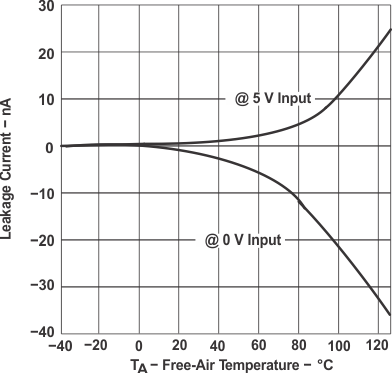 Figure 4. Analog Input Leakage Current
Figure 4. Analog Input Leakage Currentvs Free-Air Temperature
8.8.2 ADS7887 Only
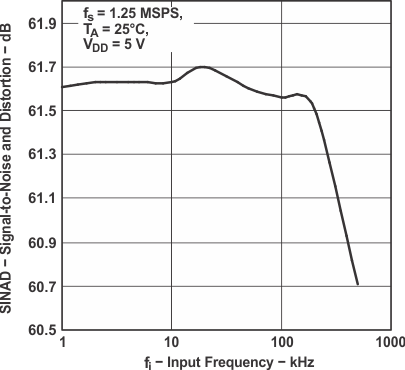 Figure 5. Signal-to-Noise and Distortion
Figure 5. Signal-to-Noise and Distortionvs Input Frequency
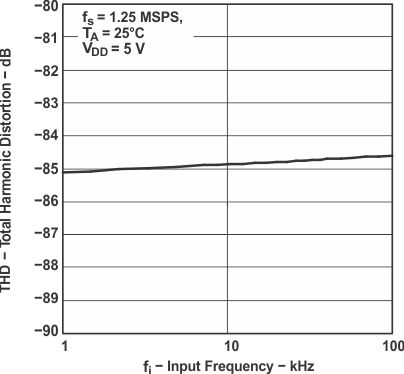 Figure 7. Total Harmonic Distortion
Figure 7. Total Harmonic Distortionvs Input Frequency
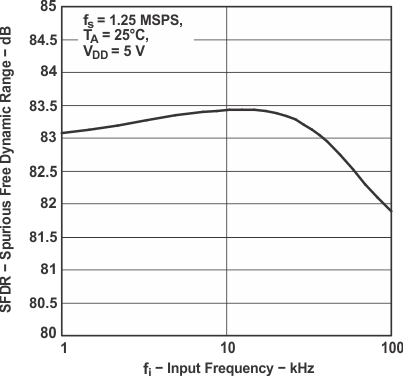 Figure 9. Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Figure 9. Spurious Free Dynamic Rangevs Input Frequency
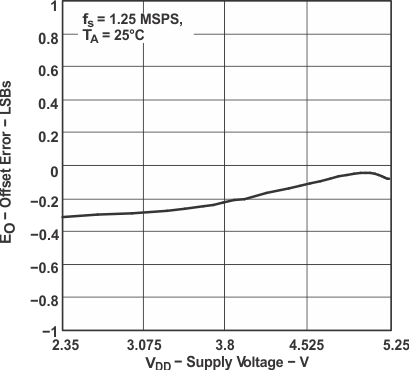 Figure 11. Offset Error vs Supply Voltage
Figure 11. Offset Error vs Supply Voltage
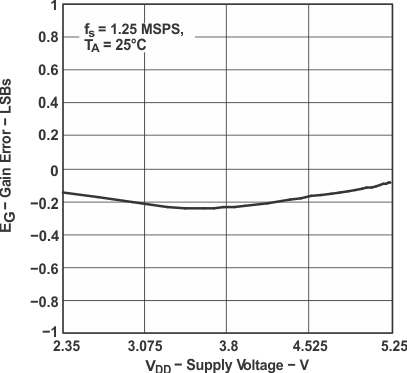 Figure 13. Gain Error vs Supply Voltage
Figure 13. Gain Error vs Supply Voltage
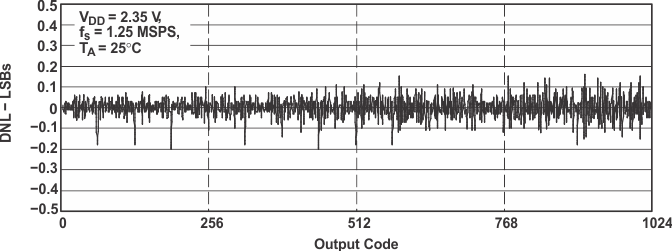 Figure 15. DNL
Figure 15. DNL
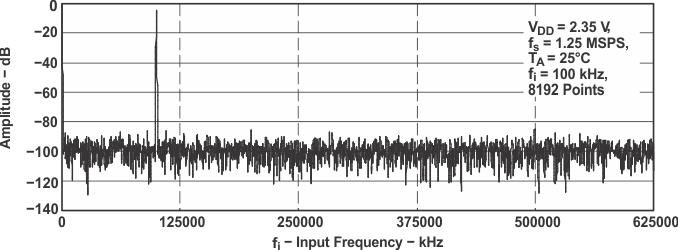 Figure 17. FFT
Figure 17. FFT
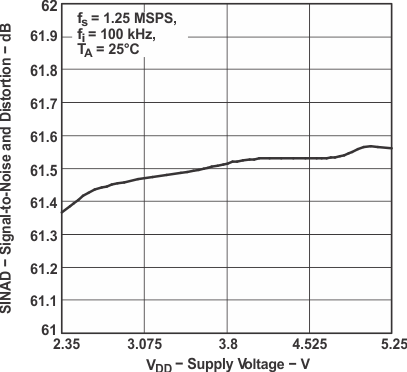 Figure 6. Signal-to-Noise and Distortion
Figure 6. Signal-to-Noise and Distortionvs Supply Voltage
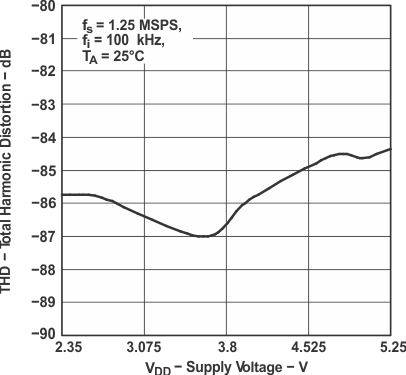 Figure 8. Total Harmonic Distortion
Figure 8. Total Harmonic Distortionvs Supply Voltage
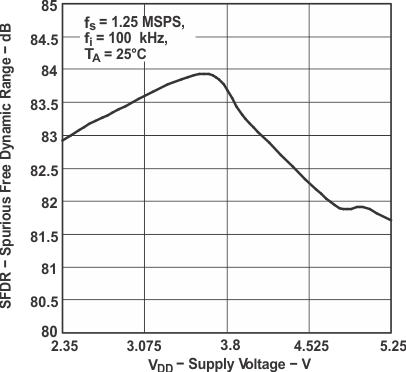 Figure 10. Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Figure 10. Spurious Free Dynamic Rangevs Supply Voltage
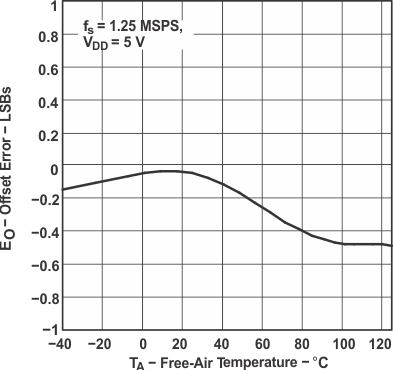 Figure 12. Offset Error vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 12. Offset Error vs Free-Air Temperature
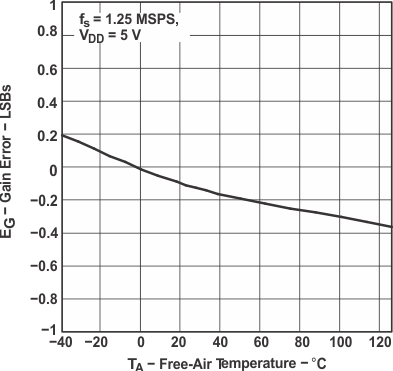 Figure 14. Gain Error vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 14. Gain Error vs Free-Air Temperature
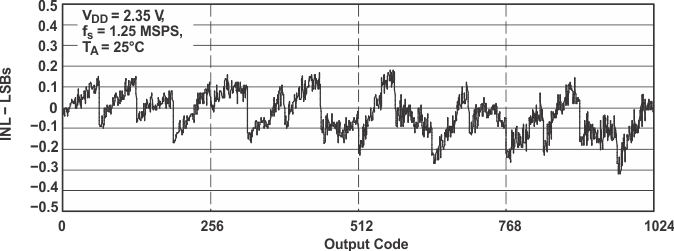 Figure 16. INL
Figure 16. INL
8.8.3 ADS7888 Only
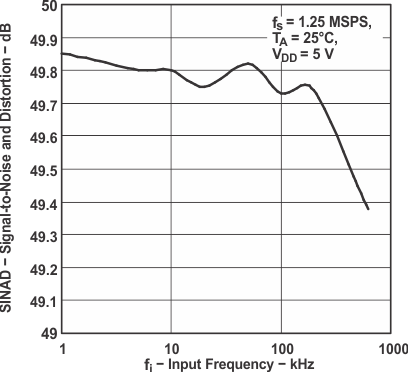 Figure 18. Signal-to-Noise and Distortion
Figure 18. Signal-to-Noise and Distortionvs Input Frequency
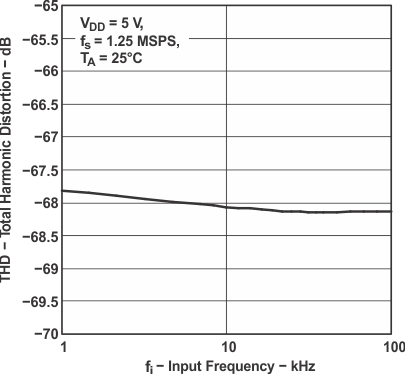 Figure 20. Total Harmonic Distortion
Figure 20. Total Harmonic Distortionvs Input Frequency
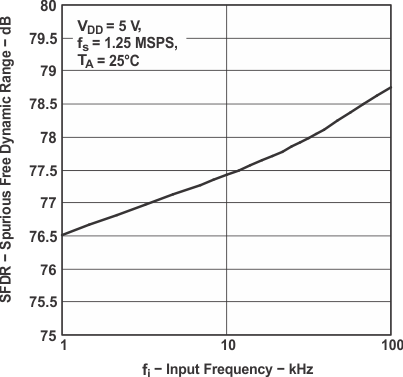 Figure 22. Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Figure 22. Spurious Free Dynamic Rangevs Input Frequency
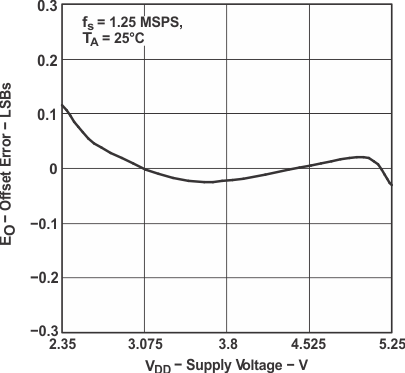 Figure 24. Offset Error vs Supply Voltage
Figure 24. Offset Error vs Supply Voltage
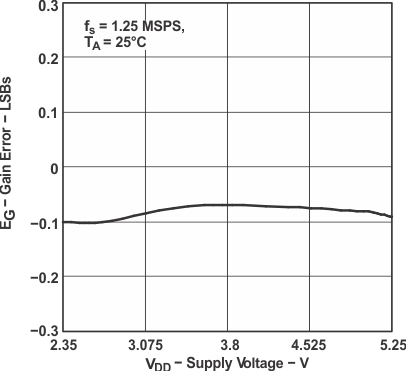 Figure 26. Gain Error vs Supply Voltage
Figure 26. Gain Error vs Supply Voltage
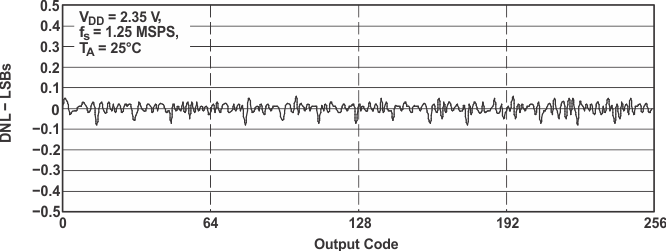 Figure 28. DNL
Figure 28. DNL
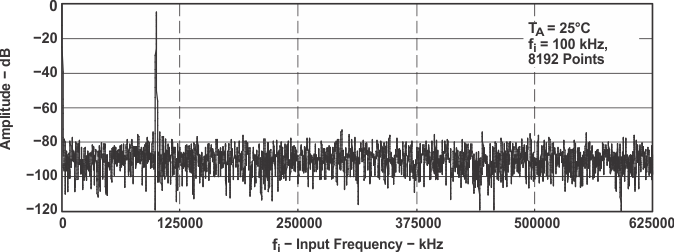 Figure 30. FFT
Figure 30. FFT
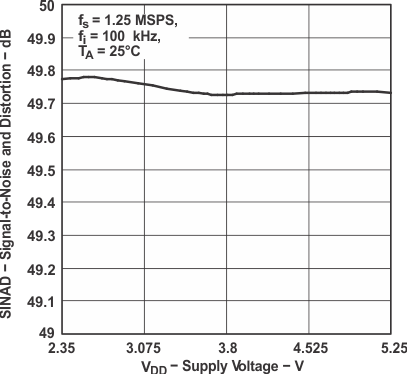 Figure 19. Signal-to-Noise and Distortion
Figure 19. Signal-to-Noise and Distortionvs Supply Voltage
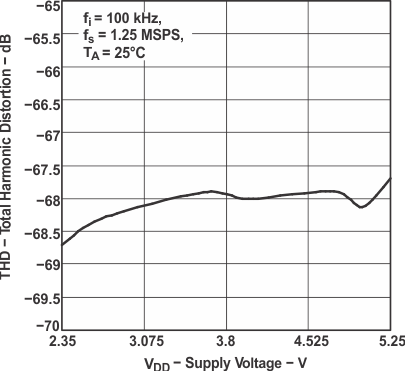 Figure 21. Total Harmonic Distortion
Figure 21. Total Harmonic Distortionvs Supply Voltage
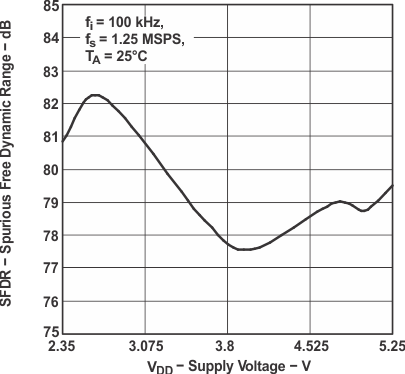 Figure 23. Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Figure 23. Spurious Free Dynamic Rangevs Supply Voltage
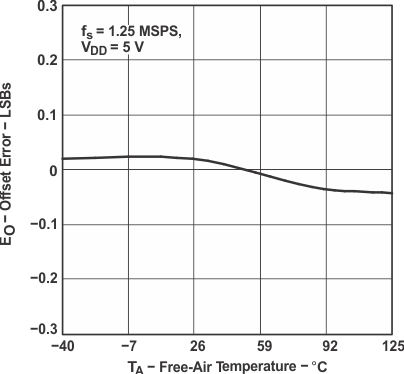 Figure 25. Offset Error vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 25. Offset Error vs Free-Air Temperature
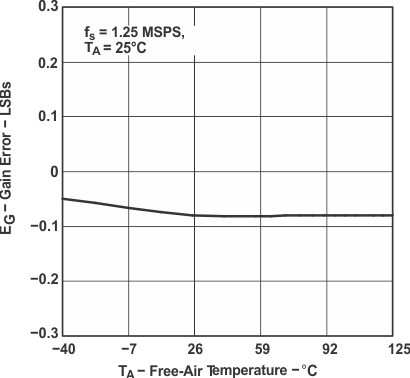 Figure 27. Gain Error vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 27. Gain Error vs Free-Air Temperature
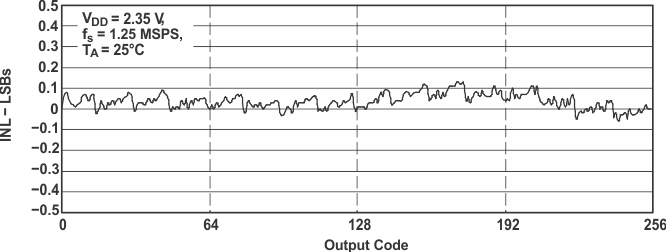 Figure 29. INL
Figure 29. INL