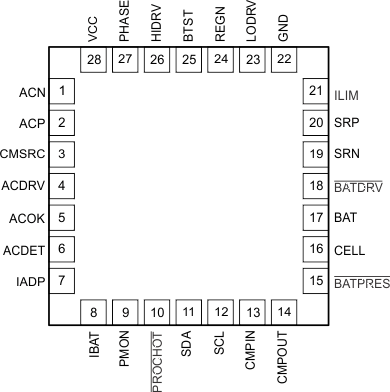
| 1 |
ACN |
Input current sense resistor negative input. Place an optional 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from ACN to GND for common-mode filtering. Place a 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from ACN to ACP to provide differential mode filtering. |
| 2 |
ACP |
Input current sense resistor positive input. Place a 1-µF and 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from ACP to GND for common-mode filtering. Place a 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from ACN to ACP to provide differential-mode filtering. |
| 3 |
CMSRC |
ACDRV charge pump source input. Place a 4 kΩ resistor from CMSRC to the common source of ACFET (Q1) and RBFET (Q2) limits the in-rush current on CMSRC pin.
When CMSRC is grounded, ACDRV pin becomes logic output internally puled up to REGN. ACDRV HIGH indicates to external driver that ACFET/RBFET can be turned on. It directly drives CMOS logic. |
| 4 |
ACDRV |
Charge pump output to drive both adapter input n-channel MOSFET (ACFET) and reverse blocking n-channel MOSFET (RBFET). ACDRV voltage is 6 V above CMSRC to turn on ACFET/RBFET when ACOK goes HIGH. Place a 4 kΩ resistor from ACDRV to the gate of ACFET and RBFET limits the in-rush current on ACDRV pin.
When CMSRC is grounded, ACDRV pin becomes logic output internally pulled up to REGN. ACDRV HIGH indicates that ACFET/RBFET can be turned on. It directly drives CMOS logic. |
| 5 |
ACOK |
Active HIGH AC adapter detection open drain output. It is pulled HIGH to external pull-up supply rail by external pull-up resistor when a valid adapter is present (ACDET above 2.4 V, VCC above UVLO but below ACOV and VCC above BAT). If any of the above conditions is not valid, ACOK is pulled LOW by internal MOSFET. Connect a 10-kΩ pull up resistor from ACOK to the pull-up supply rail. |
| 6 |
ACDET |
Adapter detection input. Program adapter valid input threshold by connecting a resistor divider from adapter input to ACDET pin to GND pin.
When ACDET pin is above 0.6 V and VCC is above UVLO, REGN LDO is present, ACOK comparator, and input current monitor buffer (IADP) are all active. Independent comparator, IBAT buffer, PMON buffer and PROCHOT can be enabled with SMBus/I2C.
When ACDET pin is above 2.4 V, and VCC is above BAT, but below ACOV, ACOK goes HIGH. ACFET/RBFET turns on. |
| 7 |
IADP |
Buffered adapter current output. V(IADP) = 40 or 80 × (V(ACP) – V(ACN))
The ratio of 40x and 80x is selectable with SMBus/I2C. Place 100pF or less ceramic decoupling capacitor from IADP pin to GND. This pin can be floating if it is not in use. IADP output voltage is clamped below 3.3 V. |
| 8 |
IBAT |
Buffered battery current selected by SMBus/I2C. V(IBAT) = 20 × (V(SRP) – V(SRN)) for charge current, or V(IBAT) = 8 or 16 × (V(SRN) – V(SRP)) for discharge current, with ratio selectable through SMBus/I2C. Place 100pF or less ceramic decoupling capacitor from IBAT pin to GND. This pin can be floating if not in use. Its output voltage is clamped below 3.3 V. |
| 9 |
PMON |
Current mode system power monitor. The output voltage is proportional to the total power from the adapter and battery. The gain is selectable through SMBus/I2C. This pin can be floating if not in use. Its output voltage is clamped below 3.3 V. The maximum cap on PMON is 100 pF. |
| 10 |
PROCHOT |
Active low open drain output of “processor hot” indicator. It monitors adapter input current, battery discharge current, and system voltage. After any event in the PROCHOT profile is triggered, a minimum 10-ms pulse is asserted. |
| 11 |
SDA |
SMBus/I2C open-drain data I/O. Connect to data line from the host controller or smart battery. Connect a 10-kΩ pull-up resistor according to SMBus/I2C specifications. |
| 12 |
SCL |
SMBus/I2C clock input. Connect to clock line from the host controller or smart battery. Connect a 10-kΩ pull-up resistor according to SMBus/I2C specifications. |
| 13 |
CMPIN |
Input of independent comparator. Internal reference, output polarity and deglitch time is selectable by SMBus/I2C. With polarity HIGH (0x3B[6]=1), place a resistor between CMPIN and CMPOUT to program hysteresis. With polarity LOW (0x3B[6]=0), the internal hysteresis is 100 mV. If the independent comparator is not in use, tie CMPIN to ground. |
| 14 |
CMPOUT |
Open-drain output of independent comparator. Place 10kΩ pull-up resistor from CMPOUT to pull-up supply rail. Internal reference, output polarity and deglitch time are selectable by SMBus/I2C. |
| 15 |
BATPRES |
Active low battery present input signal. LOW indicates battery present, HIGH indicates battery absent. When BATPRES pin goes from LOW to HIGH, the device exits LEARN mode, and disable charge. REG 0x15() value goes back to default. Host can enable IDPM and charge through SMBus/I2C when BATPRES is HIGH. |
| 16 |
CELL |
Battery cell selection pin. GND for 1-cell, Float for 2-cell, and HIGH for 3- or 4-cell. CELL pin is biased from REGN. Before host writes to MaxChargeVoltage(), MaxChargeVotage() follows the CELL pin setting.
CELL pin also sets SYSOVP threshold. GND for 5 V, Float for 12 V and HIGH for 18.5 V. When REG 0x15() is above 15V, SYSOVP is disabled. |
| 17 |
BAT |
Battery-voltage remote sense. Directly connect a Kelvin sense trace from the battery-pack positive terminal to the BAT pin to accurately sense the battery pack voltage. Place a 0.1-μF capacitor from BAT to GND close to the IC to filter high-frequency noise. |
| 18 |
BATDRV |
P-channel battery FET (BATFET) gate driver output. It is shorted to SRN to turn off the BATFET. It goes below SRN to turn on BATFET. BATFET is in linear mode to regulate SYS at minimum system voltage when battery is depleted. BATFET is fully on during fast charge and supplement mode.
Connect the source of the BATFET to charge current sensing node SRN pin, and the drain of the BATFET to the battery pack positive node BAT pin. |
| 19 |
SRN |
Charge current sense resistor negative input. SRN pin is for battery voltage sensing as well. Connect SRN pin with a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor to GND for common-mode filtering. Connect a 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from SRP to SRN to provide differential mode filtering. |
| 20 |
SRP |
Charge current sense resistor positive input. Connect a 0.1-µF ceramic capacitor from SRP to SRN to provide differential mode filtering. |
| 21 |
ILIM |
Input current limit input. Program ILIM voltage by connecting a resistor divider from supply rail to ILIM pin to GND pin. The ILIM voltage is calculated as: V(ILIM) = 20 × IDPM × RAC, in which IDPM is the target regulation current.
The lower of ILIM voltage and DAC limit voltage sets input current regulation limit. Host can ignore the IDPM setting from ILIM pin by setting 0x38[7]=0. |
| 22 |
GND |
IC ground. On PCB layout, connect to analog ground plane, and only connect to power ground plane through the power pad underneath IC. |
| 23 |
LODRV |
Low side power MOSFET driver output. Connect to low side n-channel MOSFET gate. |
| 24 |
REGN |
5.4V linear regulator output supplied from VCC. The LDO is active when ACDET above 0.6V, VCC above UVLO. Connect a 1µF ceramic capacitor from REGN to power ground. |
| 25 |
BTST |
High side power MOSFET driver power supply. Connect a 0.047-µF capacitor from BTST to PHASE. The bootstrap diode between REGN and BTST is integrated. |
| 26 |
HIDRV |
High side power MOSFET driver output. Connect to the high side n-channel MOSFET gate. |
| 27 |
PHASE |
High side power MOSFET driver source. Connect to the source of the high side n-channel MOSFET. |
| 28 |
VCC |
Input supply from adapter or battery. Place Schottky diode-OR from adapter/battery. After the Schottky diode, place 10-Ω resistor and 1-µF capacitor to ground as low pass filter to limit inrush current. |
|
Thermal Pad |
Exposed pad beneath the IC. Analog ground and power ground star-connected only at the thermal pad plane. Always solder thermal pad to the board, and have vias on the thermal pad plane connecting to analog ground and power ground planes. It also serves as a thermal pad to dissipate the heat. |