JAJSM11 may 2021 BQ25720
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power-Up Sequence
- 9.3.2 Vmin Active Protection (VAP) with Battery only
- 9.3.3 Two-Level Battery Discharge Current Limit
- 9.3.4 Fast Role Swap Feature
- 9.3.5 CHRG_OK Indicator
- 9.3.6 Input and Charge Current Sensing
- 9.3.7 Input Voltage and Current Limit Setup
- 9.3.8 Battery Cell Configuration
- 9.3.9 Device HIZ State
- 9.3.10 USB On-The-Go (OTG)
- 9.3.11 Converter Operation
- 9.3.12 Inductance Detection Through IADPT Pin
- 9.3.13 Converter Compensation
- 9.3.14 Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
- 9.3.15 Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM)
- 9.3.16 Switching Frequency and Dithering Feature
- 9.3.17 Current and Power Monitor
- 9.3.18 Input Source Dynamic Power Management
- 9.3.19 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 9.3.20 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 9.3.21 Processor Hot Indication
- 9.3.22
Device Protection
- 9.3.22.1 Watchdog Timer
- 9.3.22.2 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 9.3.22.3 Input Overcurrent Protection (ACOC)
- 9.3.22.4 System Overvoltage Protection (SYSOVP)
- 9.3.22.5 Battery Overvoltage Protection (BATOVP)
- 9.3.22.6 Battery Discharge Overcurrent Protection (BATOC)
- 9.3.22.7 Battery Short Protection (BATSP)
- 9.3.22.8 System Undervoltage Lockout (VSYS_UVP) and Hiccup Mode
- 9.3.22.9 Thermal Shutdown (TSHUT)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1 ChargeOption0 Register (SMBus address = 12h) [reset = E70Eh]
- 9.6.2 ChargeCurrent Register (SMBus address = 14h) [reset = 0000h]
- 9.6.3 ChargeVoltage Register (SMBus address = 15h) [reset value based on CELL_BATPRESZ pin setting]
- 9.6.4 ChargerStatus Register (SMBus address = 20h) [reset = 0000h]
- 9.6.5 ProchotStatus Register (SMBus address = 21h) [reset = B800h]
- 9.6.6 IIN_DPM Register With 10-mΩ Sense Resistor (SMBus address = 22h) [reset = 4100h]
- 9.6.7 ADCVBUS/PSYS Register (SMBus address = 23h)
- 9.6.8 ADCIBAT Register (SMBus address = 24h)
- 9.6.9 ADCIINCMPIN Register (SMBus address = 25h)
- 9.6.10 ADCVSYSVBAT Register (SMBus address = 26h)
- 9.6.11 ChargeOption1 Register (SMBus address = 30h) [reset = 3300h]
- 9.6.12 ChargeOption2 Register (SMBus address = 31h) [reset = 00B7]
- 9.6.13 ChargeOption3 Register (SMBus address = 32h) [reset = 0434h]
- 9.6.14 ProchotOption0 Register (SMBus address = 33h) [reset = 4A81h(2S~) 4A09(1S)]
- 9.6.15 ProchotOption1 Register (SMBus address = 34h) [reset = 41A0h]
- 9.6.16 ADCOption Register (SMBus address = 35h) [reset = 2000h]
- 9.6.17 ChargeOption4 Register (SMBus address = 36h) [reset = 0048h]
- 9.6.18 Vmin Active Protection Register (SMBus address = 37h) [reset = 006Ch(2s~4s)/0004h(1s)]
- 9.6.19 OTGVoltage Register (SMBus address = 3Bh) [reset = 09C4h]
- 9.6.20 OTGCurrent Register (SMBus address = 3Ch) [reset = 3C00h]
- 9.6.21 InputVoltage (VINDPM) Register (SMBus address = 3Dh) [reset = VBUS-1.28V]
- 9.6.22 VSYS_MIN Register (SMBus address = 3Eh) [reset value based on CELL_BATPRESZ pin setting]
- 9.6.23 IIN_HOST Register (SMBus address = 3Fh) [reset = 4100h]
- 9.6.24 ID Registers
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.2.2.3 Input Capacitor
Input capacitor should have enough ripple current rating to absorb input switching ripple current. The worst case RMS ripple current is half of the charging current (plus system current there is any system load) when duty cycle is 0.5 in buck mode. If the converter does not operate at 50% duty cycle, then the worst case capacitor RMS current occurs where the duty cycle is closest to 50% and can be estimated by Equation 4:
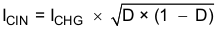
Low ESR ceramic capacitor such as X7R or X5R is preferred for input decoupling capacitor and should be placed in front of RAC current sensing and as close as possible to the power stage half bridge MOSFETs. Capacitance after RAC before power stage half bridge should be limited to 10 nF + 1 nF referring to Figure 10-2 diagram. Because too large capacitance after RAC could filter out RAC current sensing ripple information. Voltage rating of the capacitor must be higher than normal input voltage level, 25-V rating or higher capacitor is preferred for 19-V to 20-V input voltage. The minimum input effective capacitance recommendation based on refers to Table 10-2.
Ceramic capacitors (MLCC) show a dc-bias effect. This effect reduces the effective capacitance when a dc-bias voltage is applied across a ceramic capacitor, as on the input capacitor of a charger. The effect may lead to a significant capacitance drop, especially for high input voltages and small capacitor packages. See the manufacturer's data sheet about the derating performance with a dc bias voltage applied. It may be necessary to choose a higher voltage rating or nominal capacitance value in order to get the required effective capacitance value at the operating point. Considering the 25 V 0603 package MLCC capacitance derating under 19-V to 20-V input voltage, the recommended practical capacitors configuration can also be found in Table 10-2. Tantalum capacitors (POSCAP) can avoid dc-bias effect and temperature variation effect which is recommended for 90 W to 130 W higher power application.
| INPUT CAPACITORS vs TOTAL INPUT POWER | 65 W | 90 W | 130 W |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum effective input capacitance | 4 μF | 6 μF | 13 μF |
| Minimum practical input capacitors configuration | 4*10 μF (0603 25 V MLCC) | 6*10 μF (0603 25 V MLCC) | 3*10 μF (0603 25 V MLCC) 1* 10 μF (25 V to 35 V POSCAP) |