SLUSEK7 September 2024 BQ25773
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Power-Up Sequence
- 7.3.2 MODE Pin Detection
- 7.3.3 REGN Regulator (REGN LDO)
- 7.3.4 Independent Comparator Function
- 7.3.5 Battery Charging Management
- 7.3.6 Temperature Regulation (TREG)
- 7.3.7 Vmin Active Protection (VAP) When Battery Only Mode
- 7.3.8 Two Level Battery Discharge Current Limit
- 7.3.9 Fast Role Swap Feature
- 7.3.10 CHRG_OK Indicator
- 7.3.11 Input and Charge Current Sensing
- 7.3.12 Input Current and Voltage Limit Setup
- 7.3.13 Battery Cell Configuration
- 7.3.14 Device HIZ State
- 7.3.15 USB On-The-Go (OTG)
- 7.3.16 Quasi Dual Phase Converter Operation
- 7.3.17 Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
- 7.3.18 Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM)
- 7.3.19 Switching Frequency and Dithering Feature
- 7.3.20 Current and Power Monitor
- 7.3.21 Input Source Dynamic Power Management
- 7.3.22 Integrated 16-Bit ADC for Monitoring
- 7.3.23 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 7.3.24 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 7.3.25 Processor Hot Indication
- 7.3.26
Device Protection
- 7.3.26.1 Watchdog Timer (WD)
- 7.3.26.2 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 7.3.26.3 Input Overcurrent Protection (ACOC)
- 7.3.26.4 System Overvoltage Protection (SYSOVP)
- 7.3.26.5 Battery Overvoltage Protection (BATOVP)
- 7.3.26.6 Battery Charge Overcurrent Protection (BATCOC)
- 7.3.26.7 Battery Discharge Overcurrent Protection (BATDOC)
- 7.3.26.8 BATFET Charge Current Clamp Protection under LDO Regulation Mode
- 7.3.26.9 Sleep Comparator Protection Between VBUS and ACP_A (SC_VBUSACP)
- 7.3.26.10 High Duty Buck Exit Comparator Protection (HDBCP)
- 7.3.26.11 REGN Power Good Protection (REGN_PG)
- 7.3.26.12 System Under Voltage Lockout (VSYS_UVP) and Hiccup Mode
- 7.3.26.13 OTG Mode Over Voltage Protection (OTG_OVP)
- 7.3.26.14 OTG Mode Under Voltage Protection (OTG_UVP)
- 7.3.26.15 Thermal Shutdown (TSHUT)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 BQ25773 Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- REE|36
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8.2.2.6 Power MOSFETs Selection
Six external N-channel MOSFETs are used for a synchronous switching battery charger. The gate drivers are integrated into the IC with 5 V of gate drive voltage. MOSFET breakdown voltage (BVDSS) rating refers to Table 8-7 based on different input voltage and application position. 5mm*6mm package MOSFET is preferred for better thermal performance and 3.3mm*3.3mm package MOSFET is preferred for higher power density design.
| 20 V/100 W | 28 V/140 W | 36 V/180 W | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buck Half bridge (Q1_A,Q2_A,Q1_B,Q2_B) | BVDSS=30 V or higher | BVDSS=40 V or higher | BVDSS=60 V or higher |
| Boost Half bridge (Q3,Q4) and BATFET (Q5) | BVDSS=30 V or higher | BVDSS=30 V or higher | BVDSS=40 V or higher (for Buck HS short fault condition safety) |
Figure-of-merit (FOM) is usually used for selecting proper MOSFET based on a tradeoff between the conduction loss and switching loss. For the top side MOSFET, FOM is defined as the product of a MOSFET's on-resistance, RDS(ON), and the gate-to-drain charge, QGD. For the bottom side MOSFET, FOM is defined as the product of the MOSFET's on-resistance, RDS(ON), and the total gate charge, QG.
The lower the FOM value, the lower the total power loss. Usually lower RDS(ON) has higher cost with the same package size.
The top-side MOSFET loss includes conduction loss and switching loss. Taking buck mode operation as an example the power loss is a function of duty cycle (D=VOUT/VIN), charging current (ICHG), MOSFET's on-resistance (RDS(ON)_top), input voltage (VIN), switching frequency (fS), turn-on time (ton) and turn-off time (toff):
- IL_DC is the average inductor DC current under buck mode;
- Iripple is the inductor current ripple peak-to-peak value;
The first item Pcon_top represents the conduction loss which is straight forward. The second term Psw_top represents the multiple switching loss items in top MOSFET including voltage and current overlap losses (PIV_top), MOSFET parasitic output capacitance loss (PQoss_top) and gate drive loss (PGate_top). To calculate voltage and current overlap losses (PIV_top):
- ton is the MOSFET turn-on time that VDS falling time from VIN to almost zero (MOSFET turn on conduction voltage);
- toff is the MOSFET turn-off time that IDS falling time from Ipeak to zero;
The MOSFET turn-on and turn-off times are given by:
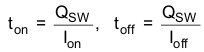
where Qsw is the switching charge, Ion is the turn-on gate driving current, and Ioff is the turn-off gate driving current. If the switching charge is not given in MOSFET datasheet, it can be estimated by gate-to-drain charge (QGD) and gate-to-source charge (QGS):
Gate driving current can be estimated by REGN voltage (VREGN), MOSFET plateau voltage (Vplt), total turn-on gate resistance (Ron), and turn-off gate resistance (Roff) of the gate driver:

To calculate top MOSFET parasitic output capacitance loss (PQoss_top):
- Qoss is the MOSFET parasitic output charge which can be found in MOSFET data sheet;
To calculate top MOSFET gate drive loss (PGate_top):
- QGate_top is the top MOSFET gate charge which can be found in MOSFET data sheet;
- Note here VIN is used instead of real gate drive voltage 6 V because, the gate drive 6 V is generated based on LDO from VIN under buck mode, the total gate drive related loss are all considered when VIN is used for gate drive loss calculation .
The bottom-side MOSFET loss also includes conduction loss and switching loss:
The first item Pcon_bottom represents the conduction loss which is straight forward. The second term Psw_bottom represents the multiple switching loss items in bottom MOSFET including reverse recovery losses (PRR_bottom), Dead time body diode conduction loss (PDead_bottom) and gate drive loss (PGate_bottom). The detail calculation can be found below:
- Qrr is the bottom MOSFET reverse recovery charge which can be found in MOSFET data sheet;
- VF is the body diode forward conduction voltage drop;
- tdead_rise is the SW rising edge deadtime between top and bottom MOSFETs which is around 20 ns;
- tdead_fall is the SW falling edge deadtime between top and bottom MOSFETs which is around 20 ns;
PGate_bottom can follow the same method as top MOSFET gate drive loss calculation approach refer to Equation 18.
N-channel MOSFETs is used for battery charging BATFET. The gate drivers are internally integrated into the IC with 5V of gate drive voltage. 30 V or higher voltage rating MOSFETs are preferred , the Ciss of N-channel MOSFET should be chosen less than 6 nF.