JAJSF16D march 2013 – september 2020 BQ51013B
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Details of a Qi Wireless Power System and BQ51013 Power Transfer Flow Diagrams
- 8.3.2 Dynamic Rectifier Control
- 8.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
- 8.3.4 RILIM Calculations
- 8.3.5 Input Overvoltage
- 8.3.6 Adapter Enable Functionality and EN1/EN2 Control
- 8.3.7 End Power Transfer Packet (WPC Header 0x02)
- 8.3.8 Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 WPC Communication Scheme
- 8.3.10 Communication Modulator
- 8.3.11 Adaptive Communication Limit
- 8.3.12 Synchronous Rectification
- 8.3.13 Temperature Sense Resistor Network (TS)
- 8.3.14 3-State Driver Recommendations for the TS/CTRL Pin
- 8.3.15 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.16 WPC v1.2 Compliance – Foreign Object Detection
- 8.3.17 Receiver Coil Load-Line Analysis
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RHL|20
発注情報
8.1 Overview
A wireless system consists of a charging pad (transmitter, TX or primary) and the secondary-side equipment (receiver, RX or secondary). There is a coil in the charging pad and in the secondary equipment which are magnetically coupled to each other when the secondary is placed on the primary. Power is then transferred from the transmitter to the receiver through coupled inductors (effectively an air-core transformer). Controlling the amount of power transferred is achieved by sending feedback (error signal) communication to the primary (to increase or decrease power).
The receiver communicates with the transmitter by changing the load seen by the transmitter. This load variation results in a change in the transmitter coil current, which is measured and interpreted by a processor in the charging pad. The communication is digital; packets are transferred from the receiver to the transmitter. Differential bi-phase encoding is used for the packets. The bit rate is 2-kbps.
Various types of communication packets have been defined. These include identification and authentication packets, error packets, control packets, end power packets, and power usage packets.
The transmitter coil stays powered off most of the time. It occasionally wakes up to see if a receiver is present. When a receiver authenticates itself to the transmitter, the transmitter will remain powered on. The receiver maintains full control over the power transfer using communication packets.
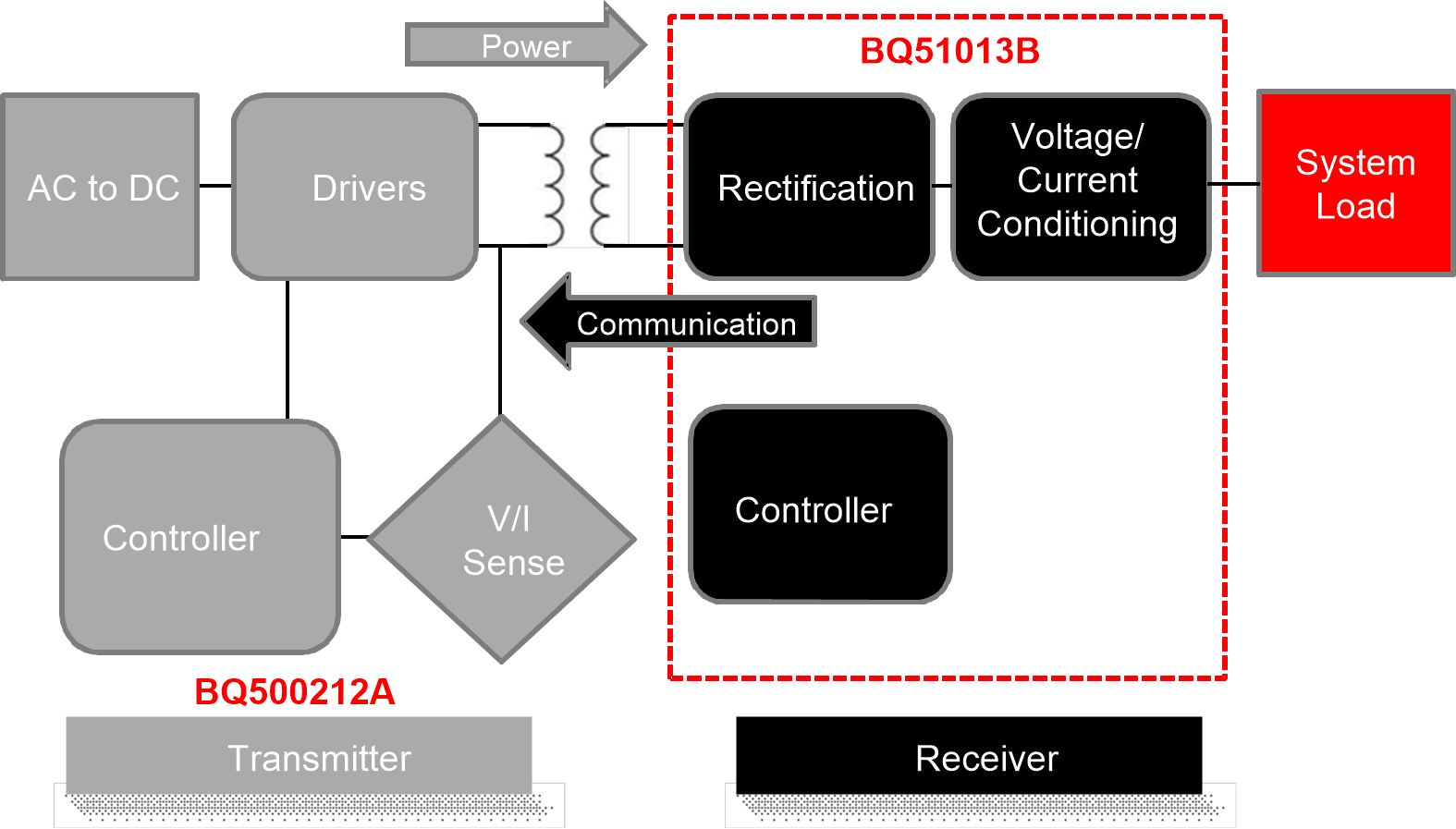 Figure 8-1 WPC Wireless Power System Indicating the Functional Integration of the BQ51013B
Figure 8-1 WPC Wireless Power System Indicating the Functional Integration of the BQ51013B