JAJSL83D August 2020 – September 2022 BQ79612-Q1 , BQ79614-Q1 , BQ79616-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power Supplies
- 9.3.2 Measurement System
- 9.3.3 Cell Balancing
- 9.3.4 Integrated Hardware Protectors
- 9.3.5 GPIO Configuration
- 9.3.6
Communication, OTP, Diagnostic Control
- 9.3.6.1
Communication
- 9.3.6.1.1 Serial Interface
- 9.3.6.1.2 Daisy Chain Interface
- 9.3.6.1.3 Start Communication
- 9.3.6.1.4 Communication Timeout
- 9.3.6.1.5 Communication Debug Mode
- 9.3.6.1.6 Multidrop Configuration
- 9.3.6.1.7 SPI Master
- 9.3.6.1.8 SPI Loopback
- 9.3.6.2 Fault Handling
- 9.3.6.3 Nonvolatile Memory
- 9.3.6.4 Diagnostic Control/Status
- 9.3.6.1
Communication
- 9.3.7 Bus Bar Support
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Register Maps
- 9.5.1 OTP Shadow Register Summary
- 9.5.2 Read/Write Register Summary
- 9.5.3 Read-Only Register Summary
- 9.5.4
Register Field Descriptions
- 9.5.4.1 Device Addressing Setup
- 9.5.4.2 Device ID and Scratch Pad
- 9.5.4.3
General Configuration and Control
- 9.5.4.3.1 DEV_CONF
- 9.5.4.3.2 ACTIVE_CELL
- 9.5.4.3.3 BBVC_POSN1
- 9.5.4.3.4 BBVC_POSN2
- 9.5.4.3.5 PWR_TRANSIT_CONF
- 9.5.4.3.6 COMM_TIMEOUT_CONF
- 9.5.4.3.7 TX_HOLD_OFF
- 9.5.4.3.8 STACK_RESPONSE
- 9.5.4.3.9 BBP_LOC
- 9.5.4.3.10 COMM_CTRL
- 9.5.4.3.11 CONTROL1
- 9.5.4.3.12 CONTROL2
- 9.5.4.3.13 CUST_CRC_HI
- 9.5.4.3.14 CUST_CRC_LO
- 9.5.4.3.15 CUST_CRC_RSLT_HI
- 9.5.4.3.16 CUST_CRC_RSLT_LO
- 9.5.4.4 Operation Status
- 9.5.4.5 ADC Configuration and Control
- 9.5.4.6
ADC Measurement Results
- 9.5.4.6.1 VCELL16_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.2 VCELL15_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.3 VCELL14_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.4 VCELL13_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.5 VCELL12_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.6 VCELL11_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.7 VCELL10_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.8 VCELL9_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.9 VCELL8_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.10 VCELL7_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.11 VCELL6_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.12 VCELL5_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.13 VCELL4_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.14 VCELL3_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.15 VCELL2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.16 VCELL1_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.17 BUSBAR_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.18 TSREF_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.19 GPIO1_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.20 GPIO2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.21 GPIO3_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.22 GPIO4_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.23 GPIO5_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.24 GPIO6_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.25 GPIO7_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.26 GPIO8_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.27 DIETEMP1_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.28 DIETEMP2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.29 AUX_CELL_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.30 AUX_GPIO_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.31 AUX_BAT_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.32 AUX_REFL_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.33 AUX_VBG2_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.34 AUX_AVAO_REF_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.35 AUX_AVDD_REF_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.36 AUX_OV_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.37 AUX_UV_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.38 AUX_OT_OTCB_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.39 AUX_UT_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.40 AUX_VCBDONE_DAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.41 AUX_VCM_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.42 REFOVDAC_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.43 DIAG_MAIN_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.6.44 DIAG_AUX_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.7 Balancing Configuration, Control and Status
- 9.5.4.8 Protector Configuration and Control
- 9.5.4.9 GPIO Configuration
- 9.5.4.10 SPI Master
- 9.5.4.11 Diagnostic Control
- 9.5.4.12 Fault Configuration and Reset
- 9.5.4.13
Fault Status
- 9.5.4.13.1 FAULT_SUMMARY
- 9.5.4.13.2 FAULT_COMM1
- 9.5.4.13.3 FAULT_COMM2
- 9.5.4.13.4 FAULT_COMM3
- 9.5.4.13.5 FAULT_OTP
- 9.5.4.13.6 FAULT_SYS
- 9.5.4.13.7 FAULT_PROT1
- 9.5.4.13.8 FAULT_PROT2
- 9.5.4.13.9 FAULT_OV1
- 9.5.4.13.10 FAULT_OV2
- 9.5.4.13.11 FAULT_UV1
- 9.5.4.13.12 FAULT_UV2
- 9.5.4.13.13 FAULT_OT
- 9.5.4.13.14 FAULT_UT
- 9.5.4.13.15 FAULT_COMP_GPIO
- 9.5.4.13.16 FAULT_COMP_VCCB1
- 9.5.4.13.17 FAULT_COMP_VCCB2
- 9.5.4.13.18 FAULT_COMP_VCOW1
- 9.5.4.13.19 FAULT_COMP_VCOW2
- 9.5.4.13.20 FAULT_COMP_CBOW1
- 9.5.4.13.21 FAULT_COMP_CBOW2
- 9.5.4.13.22 FAULT_COMP_CBFET1
- 9.5.4.13.23 FAULT_COMP_CBFET2
- 9.5.4.13.24 FAULT_COMP_MISC
- 9.5.4.13.25 FAULT_PWR1
- 9.5.4.13.26 FAULT_PWR2
- 9.5.4.13.27 FAULT_PWR3
- 9.5.4.14
Debug Control and Status
- 9.5.4.14.1 DEBUG_CTRL_UNLOCK
- 9.5.4.14.2 DEBUG_COMM_CTRL1
- 9.5.4.14.3 DEBUG_COMM_CTRL2
- 9.5.4.14.4 DEBUG_COMM_STAT
- 9.5.4.14.5 DEBUG_UART_RC
- 9.5.4.14.6 DEBUG_UART_RR_TR
- 9.5.4.14.7 DEBUG_COMH_BIT
- 9.5.4.14.8 DEBUG_COMH_RC
- 9.5.4.14.9 DEBUG_COMH_RR_TR
- 9.5.4.14.10 DEBUG_COML_BIT
- 9.5.4.14.11 DEBUG_COML_RC
- 9.5.4.14.12 DEBUG_COML_RR_TR
- 9.5.4.14.13 DEBUG_UART_DISCARD
- 9.5.4.14.14 DEBUG_COMH_DISCARD
- 9.5.4.14.15 DEBUG_COML_DISCARD
- 9.5.4.14.16 DEBUG_UART_VALID_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.14.17 DEBUG_COMH_VALID_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.14.18 DEBUG_COML_VALID_HI/LO
- 9.5.4.14.19 DEBUG_OTP_SEC_BLK
- 9.5.4.14.20 DEBUG_OTP_DED_BLK
- 9.5.4.15
OTP Programming Control and Status
- 9.5.4.15.1 OTP_PROG_UNLOCK1A through OTP_PROG_UNLOCK1D
- 9.5.4.15.2 OTP_PROG_UNLOCK2A through OTP_PROG_UNLOCK2D
- 9.5.4.15.3 OTP_PROG_CTRL
- 9.5.4.15.4 OTP_ECC_TEST
- 9.5.4.15.5 OTP_ECC_DATAIN1 through OTP_ECC_DATAIN9
- 9.5.4.15.6 OTP_ECC_DATAOUT1 through OTP_ECC_DATAOUT9
- 9.5.4.15.7 OTP_PROG_STAT
- 9.5.4.15.8 OTP_CUST1_STAT
- 9.5.4.15.9 OTP_CUST2_STAT
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1
Base
Device Application Circuit
- 10.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.1.3 Application Curve
- 10.2.2 Daisy Device Application Circuit
- 10.2.1
Base
Device Application Circuit
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PAP|64
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PAP|64
発注情報
10.2.1.2.7.2 Devices Connected on Different PCBs
For devices that are daisy-chained to different PCBs through a pair of twisted cables, all three isolation types can be used for daisy chain isolation, however it is not possible to use one type of isolation on one side of the daisy chain (for example, transformer isolation on COMLP/N to the Battery Management Unit) while using a different type of isolation for the other side of the daisy chain (for example, capacitor isolation on COMH/N to the Cell Module Unit).
Option 1: Capacitor Isolation
| Components | Value | Description (Capacitor Isolation Between PCBs) |
|---|---|---|
| RTERM | 1 kΩ | Termination resistor |
| RSERIES | 49 Ω | Filter resistor and impedance matching resistor. The connection between devices must be ~120 Ω (~50 Ω on each end of the signal connection of the device plus 10-Ω internal resistance) |
| CBYPASS | 220 pF/50 V | Bypass capacitor |
| CISO | 2.2 nF | Isolation capacitor Voltage rating depends on application requirement. It is common to select 2x of module voltage rating to provide standoff margin in the event of a fault in the system. |
| ESD diode | TVS diode | The ESD protector should provide protection to the communication interface pins during hot-plug events and also for absorption of high-voltage transients during service disconnect or reconnect. Select the ESD diodes to limit the maximum voltage on the COM* bus to below the maximum rating. A voltage rating close to the maximum voltage to provide the highest possible common-mode voltage range is recommended for best EMC performance. The capacitance must be low compared to the coupling capacitance (if using capacitor coupling). |
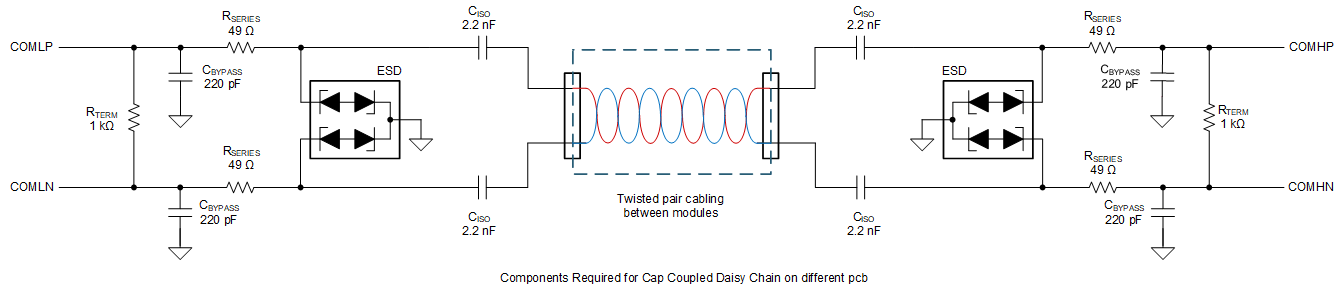 Figure 10-7 Capacitor Isolation on
Different PCB
Figure 10-7 Capacitor Isolation on
Different PCBFigure 10-7 shows the capacitor isolation circuit for devices connecting between PCBs. Similar to the capacitor isolation on the same PCB case, the capacitor must be rated with a high enough voltage to provide standoff margin in the event of a fault in the system that exposes the device to a local hazardous voltage. The voltage is determined by the application requirement but it is common to select 2x of the module voltage.
The capacitance on the daisy chain bus has a direct effect on performance. All parasitic capacitances from the support components and cabling must be taken into consideration when designing for communication robustness to EMC. Capacitance from the cables, ESD diodes, bypass capacitance, and chokes form a capacitive divider with the isolation capacitors that may affect performance. Additionally, the amount of capacitance on the bus has a direct impact to the operating current during communication (the capacitor charging or discharging).
Option 2: Capacitor Plus Common-Mode Choke Isolation
| Components | Value | Description (Capacitor Plus Choke Isolation Between PCBs) |
|---|---|---|
| RTERM | 1 kΩ | Termination resistor |
| RSERIES | 49 Ω | Filter resistor and impedance matching resistor. The connection between devices must be ~120 Ω (~50 Ω on each end of the signal connection of the device plus 10-Ω internal resistance) |
| CBYPASS | 220 pF/50 V | Bypass capacitor |
| CISO | 2.2 nF | Isolation capacitor Voltage rating depends on application requirement. It is common to select 2x of module voltage rating to provide a standoff margin in the event of a fault in the system. |
| Common-mode choke | 100 μH to 500 μH | Common-mode choke (The inductance range 100 μH to 500 μH is a general guidance value, not a guaranteed range as there are many parameters affecting the performance of common-mode choke. When coming to specific recommended part, please refer to SLVAEP4 BQ79616-Q1 Daisy Chain Communications Application Report. User shall perform the through test in their environment.) |
| ESD diode (optional) | TVS diode | Optional ESD protection depends on pcb level ESD requirement (Adding this diode or not is subject to the user’s system level ESD requirement) |
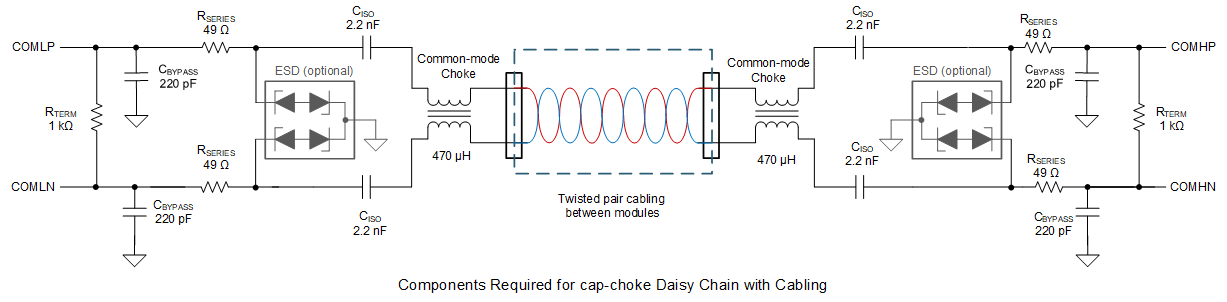 Figure 10-8 Capacitor Plus Choke
Isolation
Figure 10-8 Capacitor Plus Choke
IsolationLonger cable lengths, or abnormally noisy applications may require the use of a common-mode choke filter. Capacitor plus choke isolation has better noise immunity than capacitor only. For these applications, use an automotive grade from 100 μH to 500 μH common-mode filter minimum for proper operation. To achieve the best performance in noisy environments, use dual common-mode filters (470 μH). The recommended impedance of the choke is at least 1 kΩ from 1 MHz to 100 MHz and above 300 Ω for higher frequencies.
Option 3: Transformer Isolation
| Components | Value | Description (Capacitor Plus Choke Isolation Between PCBs) |
|---|---|---|
| RTERM | 1 kΩ | Termination resistor |
| RSERIES | 49 Ω | Filter resistor and impedance matching resistor. The connection between devices must be ~120 Ω (~50 Ω on each end of the signal connection of the device plus 10-Ω internal resistance) |
| CBYPASS | 220 pF/50 V | Bypass capacitor |
| Transformer | Inductance: 150 μH to 1400 μH | The inductance range 150 μH to 1400 μH is a general guidance value, not a guaranteed range as there are many parameters affecting the performance of transformer. When coming to specific recommended part, please refer to SLVAEP4 BQ79616-Q1 Daisy Chain Communications Application Report. User shall perform the through test in their environment. |
| ESD diode (optional) | TVS diode | Optional ESD protection depends on pcb level ESD requirement (Adding this diode or not is subject to the user’s system level ESD requirement) |
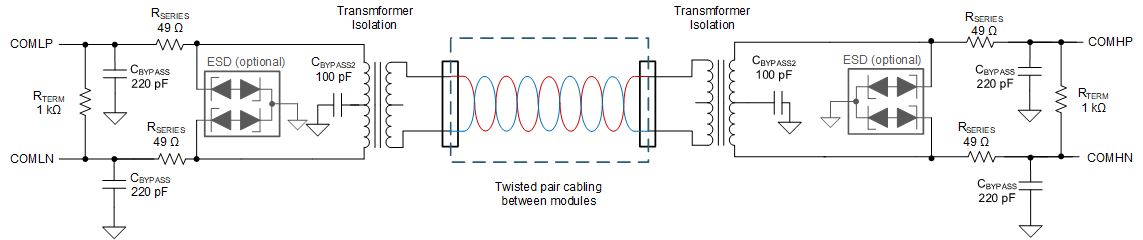 Figure 10-9 Transformer Isolation
Figure 10-9 Transformer IsolationTransformer isolation is supported and can be implemented as above. For example, transformer isolation can be used between the low-voltage and high-voltage boundary for galvanic isolation.