-
CC3200 SimpleLink Wi-Fi and Internet-of-Things Solution, a Single-Chip Wireless MCU
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 Handling Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On Hours
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Brown-Out and Black-Out
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics (3.3 V, 25°C)
- 4.7 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
- 4.8 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
- 4.9 Current Consumption
- 4.10 Thermal Characteristics for RGC Package
- 4.11 Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5Detailed Description
- 6Applications and Implementation
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGC|64
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGC|64
発注情報
CC3200 SimpleLink Wi-Fi and Internet-of-Things Solution, a Single-Chip Wireless MCU
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
- CC3200 SimpleLink Wi-Fi—Consists of Applications Microcontroller, Wi-Fi Network Processor, and Power-Management Subsystems
- Wi-Fi CERTIFIED™ Chip
- Applications Microcontroller Subsystem
- ARM®Cortex®-M4 Core at 80 MHz
- Embedded Memory
- RAM (Up to 256KB)
- External Serial Flash Bootloader, and Peripheral Drivers in ROM
- 32-Channel Direct Memory Access (μDMA)
- Hardware Crypto Engine for Advanced Fast Security, Including
- AES, DES, and 3DES
- SHA2 and MD5
- CRC and Checksum
- 8-Bit Parallel Camera Interface
- 1 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP) Interface with Support for Two I2S Channels
- 1 SD/MMC Interface
- 2 Universal Asynchronous Receivers and Transmitters (UARTs)
- 1 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 1 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 4 General-Purpose Timers with 16-Bit Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Mode
- 1 Watchdog Timer
- 4-Channel 12-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)
- Up to 27 Individually Programmable, Multiplexed GPIO Pins
- Dedicated External SPI Interface for Serial Flash
- Wi-Fi Network Processor Subsystem
- Featuring Wi-Fi Internet-On-a-Chip™
- Dedicated ARM MCU
- Wi-Fi and Internet Protocols in ROM
- 802.11 b/g/n Radio, Baseband, Medium Access Control (MAC), Wi-Fi Driver, and Supplicant
- TCP/IP Stack
- Industry-Standard BSD Socket Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
- 8 Simultaneous TCP or UDP Sockets
- 2 Simultaneous TLS and SSL Sockets
- Powerful Crypto Engine for Fast, Secure Wi-Fi and Internet Connections with 256-Bit AES Encryption for TLS and SSL Connections
- Station, AP, and Wi-Fi Direct® Modes
- WPA2 Personal and Enterprise Security
- SimpleLink Connection Manager for Autonomous and Fast Wi-Fi Connections
- SmartConfig™ Technology, AP Mode, and WPS2 for Easy and Flexible Wi-Fi Provisioning
- TX Power
- 18.0 dBm @ 1 DSSS
- 14.5 dBm @ 54 OFDM
- RX Sensitivity
- –95.7 dBm @ 1 DSSS
- –74.0 dBm @ 54 OFDM
- Application Throughput
- UDP: 16 Mbps
- TCP: 13 Mbps
Completely Offloads Wi-Fi and Internet Protocols from the Application Microcontroller
- Power-Management Subsystem
- Integrated DC-DC Supports a Wide Range of Supply Voltage:
- VBAT Wide-Voltage Mode: 2.1 to 3.6 V
- VIO is Always Tied with VBAT
- Preregulated 1.85-V Mode
- Advanced Low-Power Modes
- Integrated DC-DC Supports a Wide Range of Supply Voltage:
- Clock Source
- 40.0-MHz Crystal with Internal Oscillator
- 32.768-kHz Crystal or External RTC Clock
- Package and Operating Temperature
- 0.5-mm Pitch, 64-Pin, 9-mm × 9-mm QFN
- Ambient Temperature Range: –40°C to 85°C
1.2 Applications
- For Internet-of-Things applications, such as:
- Cloud Connectivity
- Home Automation
- Home Appliances
- Access Control
- Security Systems
- Smart Energy
- Internet Gateway
- Industrial Control
- Smart Plug and Metering
- Wireless Audio
- IP Network Sensor Nodes
1.3 Description
Start your design with the industry’s first Wi-Fi CERTIFIED single-chip microcontroller unit (MCU) with built-in Wi-Fi connectivity. Created for the Internet of Things (IoT), the SimpleLink CC3200 device is a wireless MCU that integrates a high-performance ARM Cortex-M4 MCU, allowing customers to develop an entire application with a single IC. With on-chip Wi-Fi, Internet, and robust security protocols, no prior Wi-Fi experience is required for faster development. The CC3200 device is a complete platform solution including software, sample applications, tools, user and programming guides, reference designs, and the TI E2E™ support community. The device is available in a QFN package that is easy to layout.
The applications MCU subsystem contains an industry-standard ARM Cortex-M4 core running at 80 MHz. The device includes a wide variety of peripherals, including a fast parallel camera interface, I2S, SD/MMC, UART, SPI, I2C, and four-channel ADC. The CC3200 family includes flexible embedded RAM for code and data and ROM with external serial flash bootloader and peripheral drivers.
The Wi-Fi network processor subsystem features a Wi-Fi Internet-on-a-Chip and contains an additional dedicated ARM MCU that completely offloads the applications MCU. This subsystem includes an 802.11 b/g/n radio, baseband, and MAC with a powerful crypto engine for fast, secure Internet connections with 256-bit encryption. The CC3200 device supports Station, Access Point, and Wi-Fi Direct modes. The device also supports WPA2 personal and enterprise security and WPS 2.0. The Wi-Fi Internet-on-a-chip includes embedded TCP/IP and TLS/SSL stacks, HTTP server, and multiple Internet protocols.
The power-management subsystem includes integrated DC-DC converters supporting a wide range of supply voltages. This subsystem enables low-power consumption modes, such as the hibernate with RTC mode requiring less than 4 μA of current.
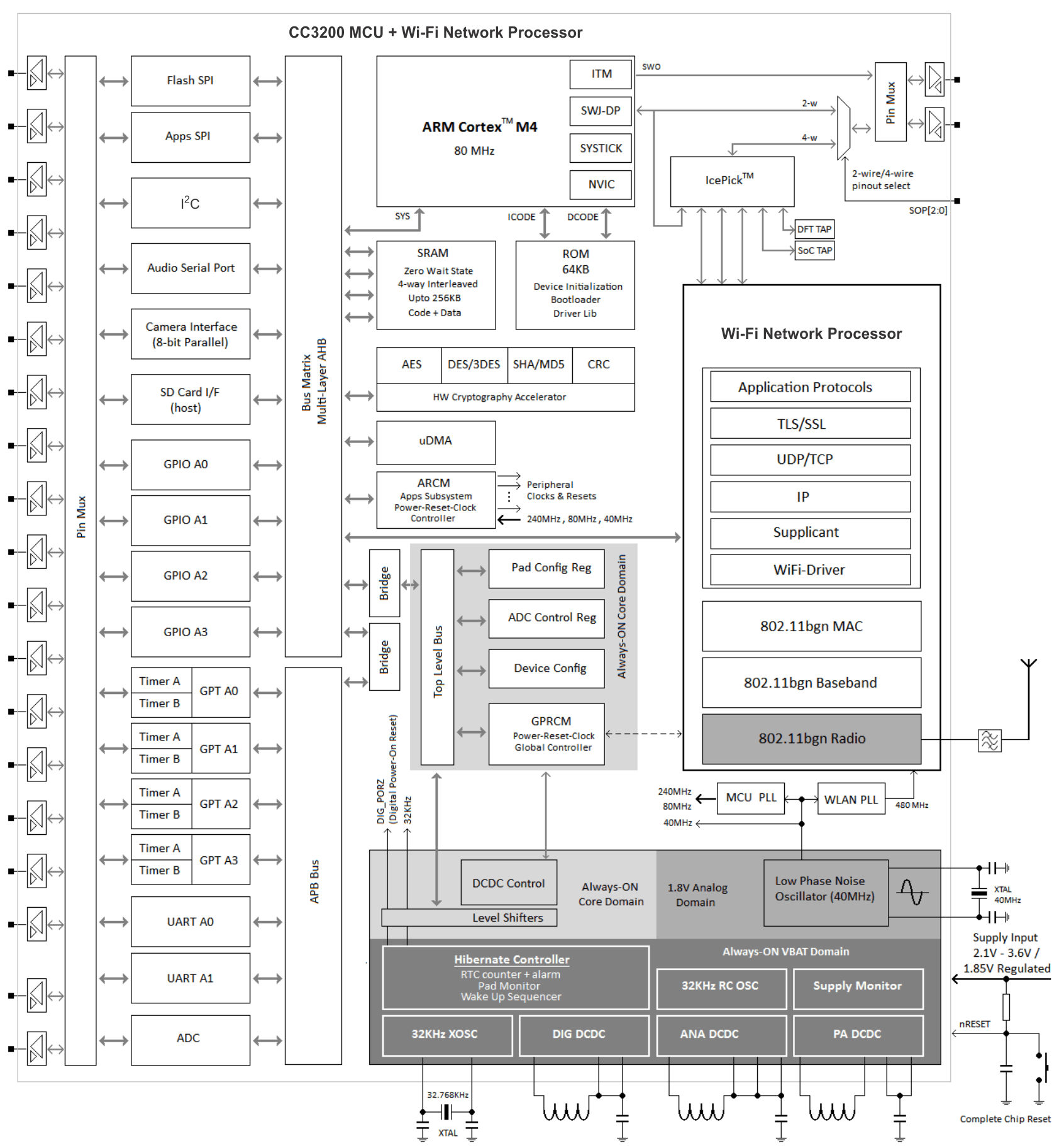
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows the CC3200 hardware overview.
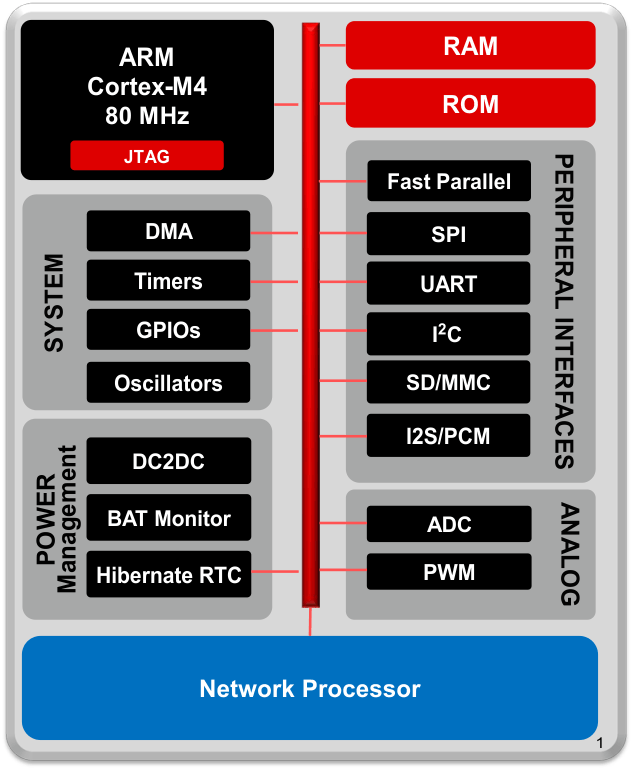 Figure 1-1 CC3200 Hardware Overview
Figure 1-1 CC3200 Hardware Overview
Figure 1-2 shows an overview of the CC3200 embedded software.
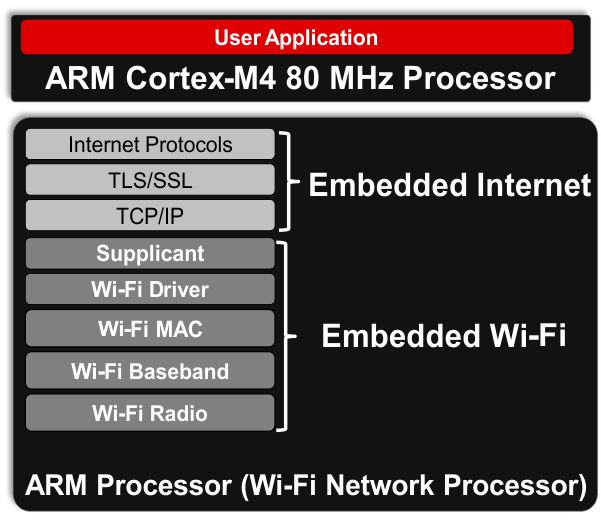 Figure 1-2 CC3200 Embedded Software Overview
Figure 1-2 CC3200 Embedded Software Overview
Figure 1-3 shows a block diagram of the CC3200 device.
2 Revision History
Changes from E Revision (August 2014) to F Revision
- Added Wi-Fi CERTIFIEDGo
- Added application throughput in Section 1.1, FeaturesGo
- Changed LPDS drain value from 120 µA in Section 1.1, FeaturesGo
- Changed idle connected from 695 µA in Section 1.1, FeaturesGo
- Added note defining X in part number in Device Information tableGo
- Changed part number in Device Information table from CC3200Go
- Changed SDCARD signal names for pins 6, 7, 8, and 64 in Table 3-1Go
- Changed use of pin 61 from no in Table 3-1Go
- Added note in Section 4.4, Recommended Operating Conditions, on avoiding the PA auto-protect featureGo
- Added Table 4-1Go
- Added note in Section 4.6, Electrical Characteristics (3.3 V, 25°C), on proper device resetGo
- Changed "current" to "active current" in note 7 of Section 4.9, Current ConsumptionGo
- Changed Figure 4-8 to reflect T2, T3, and T4 measurementsGo
- Changed Table 4-4 to reflect T2, T3, and T4 timing items Go
- Added note in Table 4-4 about extending wake-up time in Hibernate modeGo
- Changed frequency accuracy from ±20 ppm in Table 4-5Go
- Added Section 4.11.3.6, WLAN Filter RequirementsGo
- Deleted I3 (tLP) and I4 (tHP) from Table 4-10Go
- Deleted I3 (tLP) and I4 (tHP) from Table 4-11Go
- Changed TCP of throughput in Table 5-1 item 17 from 12 Mbps Go
- Changed part number of item 17 from CC3200R1-M2RTDR in Table 6-1Go
- Added note following Table 6-1Go
- Changed part number of item 16 from CC3200R1-M2RTDR in Table 6-2Go
- Added note following Table 6-2Go
3 Terminal Configuration and Functions
Figure 3-1 shows pin assignments for the 64-pin QFN package.
 Figure 3-1 QFN 64-Pin Assignments (Top View)
Figure 3-1 QFN 64-Pin Assignments (Top View)
3.1 Pin Attributes and Pin Multiplexing
The device makes extensive use of pin multiplexing to accommodate the large number of peripheral functions in the smallest possible package. To achieve this configuration, pin multiplexing is controlled using a combination of hardware configuration (at device reset) and register control.
NOTE
TI highly recommends using the CC3200 pin multiplexing utility to obtain the desired pinout.
The board and software designers are responsible for the proper pin multiplexing configuration. Hardware does not ensure that the proper pin multiplexing options are selected for the peripherals or interface mode used.
Table 3-1 describes the general pin attributes and presents an overview of pin multiplexing. All pin multiplexing options are configurable using the pin mux registers.
The following special considerations apply:
- All I/Os support drive strengths of 2, 4, and 6 mA. Drive strength is configurable individually for each pin.
- All I/Os support 10-µA pullups and pulldowns.
- These pulls are not active and all of the I/Os remain floating while the device is in Hibernate state.
- The VIO and VBAT supply must be tied together at all times.
- All digital I/Os are nonfail-safe.
NOTE
If an external device drives a positive voltage to the signal pads and the CC3200 device is not powered, DC current is drawn from the other device. If the drive strength of the external device is adequate, an unintentional wakeup and boot of the CC3200 device can occur. To prevent current draw, TI recommends any one of the following:
- All devices interfaced to the CC3200 device must be powered from the same power rail as the chip.
- Use level-shifters between the device and any external devices fed from other independent rails.
- The nRESET pin of the CC3200 device must be held low until the VBAT supply to the device is driven and stable.
Table 3-1 Pin Multiplexing
| General Pin Attributes | Function | Pad States | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pkg Pin | Pin Alias | Use | Select as Wakeup Source | Config Addl Analog Mux | Muxed with JTAG | Dig. Pin Mux Config Reg | Dig. Pin Mux Config Mode Value | Signal Name | Signal Description | Signal Direction | LPDS(1) | Hib(2) | nRESET = 0 |
| 1 | GPIO10 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_10 (0x4402 E0C8) |
0 | GPIO10 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 1 | I2C_SCL | I2C Clock | O (Open Drain) |
Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | GT_PWM06 | Pulse-Width Modulated O/P | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | UART1_TX | UART TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 6 | SDCARD_CLK | SD Card Clock | O | 0 | |||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP01 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 2 | GPIO11 | I/O | Yes | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_11 (0x4402 E0CC) |
0 | GPIO11 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 1 | I2C_SDA | I2C Data | I/O (Open Drain) |
Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | GT_PWM07 | Pulse-Width Modulated O/P | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | pXCLK (XVCLK) | Free Clock To Parallel Camera | O | 0 | |||||||||
| 6 | SDCARD_CMD | SD Card Command Line | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | UART1_RX | UART RX Data | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP02 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 13 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | GPIO12 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_12 (0x4402 E0D0) |
0 | GPIO12 | General Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 3 | McACLK | I2S Audio Port Clock O | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | pVS (VSYNC) | Parallel Camera Vertical Sync | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 5 | I2C_SCL | I2C Clock | I/O (Open Drain) |
Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | UART0_TX | UART0 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP03 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | GPIO13 | I/O | Yes | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_13 (0x4402 E0D4) |
0 | GPIO13 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 5 | I2C_SDA | I2C Data | I/O (Open Drain) |
||||||||||
| 4 | pHS (HSYNC) | Parallel Camera Horizontal Sync | I | ||||||||||
| 7 | UART0_RX | UART0 RX Data | I | ||||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP04 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 5 | GPIO14 | I/O | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_14 (0x4402 E0D8) |
0 | GPIO14 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 5 | I2C_SCL | I2C Clock | I/O (Open Drain) |
||||||||||
| 7 | GSPI_CLK | General SPI Clock | I/O | ||||||||||
| 4 | pDATA8 (CAM_D4) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 4 | I | ||||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP05 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 6 | GPIO15 | I/O | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_15 (0x4402 E0DC) |
0 | GPIO15 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 5 | I2C_SDA | I2C Data | I/O (Open Drain) |
||||||||||
| 7 | GSPI_MISO | General SPI MISO | I/O | ||||||||||
| 4 | pDATA9 (CAM_D5) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 5 | I | ||||||||||
| 13 | GT_CCP06 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 8 | SDCARD_ DATA0 |
SD Card Data | I/O | ||||||||||
| 7 | GPIO16 | I/O | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_16 (0x4402 E0E0) |
0 | GPIO16 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| Hi-Z | |||||||||||||
| Hi-Z | |||||||||||||
| 7 | GSPI_MOSI | General SPI MOSI | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | pDATA10 (CAM_D6) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 6 | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 5 | UART1_TX | UART1 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 13 | GT_CCP07 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 8 | SDCARD_CLK | SD Card Clock | O | O | |||||||||
| 8 | GPIO17 | I/O | Wake-Up Source | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_17 (0x4402 E0E4) |
0 | GPIO17 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 5 | UART1_RX | UART1 RX Data | I | ||||||||||
| 7 | GSPI_CS | General SPI Chip Select | I/O | ||||||||||
| 4 | pDATA11 (CAM_D7) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 7 | I | ||||||||||
| 8 | SDCARD_ CMD |
SD Card Command Line | I/O | ||||||||||
| 9 | VDD_DIG1 | Int pwr | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_DIG1 | Internal Digital Core Voltage | ||||
| 10 | VIN_IO1 | Sup. input | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VIN_IO1 | Chip Supply Voltage (VBAT) | ||||
| 11 | FLASH_SPI_ CLK |
O | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | FLASH_SPI_ CLK |
Clock To SPI Serial Flash (Fixed Default) | O | Hi-Z(3) | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 12 | FLASH_SPI_DOUT | O | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | FLASH_SPI_ DOUT |
Data To SPI Serial Flash (Fixed Default) | O | Hi-Z(3) | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 13 | FLASH_SPI_ DIN |
I | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | FLASH_SPI_ DIN |
Data From SPI Serial Flash (Fixed Default) | I | |||
| 14 | FLASH_SPI_ CS |
O | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | FLASH_SPI_ CS |
Chip Select To SPI Serial Flash (Fixed Default) | O | 1 | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 15 | GPIO22 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_22 (0x4402 E0F8) |
0 | GPIO22 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 7 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 5 | GT_CCP04 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 16 | TDI | I/O | No | No | MUXed with JTAG TDI | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_23 (0x4402 E0FC) |
1 | TDI | JTAG TDI. Reset Default Pinout. | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 0 | GPIO23 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | ||||||||||
| 2 | UART1_TX | UART1 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 9 | I2C_SCL | I2C Clock | I/O (Open Drain) |
Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 17 | TDO | I/O | Wake-Up Source | No | MUXed with JTAG TDO | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_ 24 (0x4402 E100) |
1 | TDO | JTAG TDO. Reset Default Pinout. | O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 0 | GPIO24 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | ||||||||||
| 5 | PWM0 | Pulse Width Modulated O/P | O | ||||||||||
| 2 | UART1_RX | UART1 RX Data | I | ||||||||||
| 9 | I2C_SDA | I2C Data | I/O (Open Drain) |
||||||||||
| 4 | GT_CCP06 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 6 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | ||||||||||
| 18 | GPIO28 | I/O | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_ 28 (0x4402 E110) |
0 | GPIO28 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | ||
| 19 | TCK | I/O | No | No | MUXed with JTAG/SWD-TCK | 1 | TCK | JTAG/SWD TCK Reset Default Pinout | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 8 | GT_PWM03 | Pulse Width Modulated O/P | O | ||||||||||
| 20 | TMS | I/O | No | No | MUXed with JTAG/SWD-TMSC | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_ 29 (0x4402 E114) |
1 | TMS | JATG/SWD TMS Reset Default Pinout | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 0 | GPIO29 | General-Purpose I/O | |||||||||||
| 21(4)(5) | SOP2 | O Only | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_ 25 (0x4402 E104) |
0 | GPIO25 | General-Purpose I/O | O | Hi-Z | Driven Low | Hi-Z |
| 9 | GT_PWM02 | Pulse Width Modulated O/P | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 2 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| See (6) | TCXO_EN | Enable to Optional External 40-MHz TCXO | O | O | |||||||||
| See (7) | SOP2 | Sense-On-Power 2 | I | ||||||||||
| 22 | WLAN_XTAL_N | WLAN Ana. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | See (6) | WLAN_XTAL_N | 40-MHz XTAL Pulldown if ext TCXO is used. |
||||
| 23 | WLAN_XTAL_P | WLAN Ana. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | WLAN_XTAL_P | 40-MHz XTAL or TCXO clock input | |||||
| 24 | VDD_PLL | Int. Pwr | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_PLL | Internal analog voltage | |||||
| 25 | LDO_IN2 | Int. Pwr | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | LDO_IN2 | Analog RF supply from ANA DC-DC output | |||||
| 26 | NC | WLAN Ana. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | NC | Reserved | |||||
| 27 | NC | WLAN Ana. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | NC | Reserved | |||||
| 28 | NC | WLAN Ana. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | NC | Reserved | |||||
| 29(8) | ANTSEL1 | O Only | No | User config not required (9) |
No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_26 (0x4402 E108) |
0 | ANTSEL1(3) | Antenna Selection Control | O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 30(8) | ANTSEL2 | O Only | No | User config not required (9) |
No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_27 (0x4402 E10C) |
0 | ANTSEL2(3) | Antenna Selection Control | O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 31 | RF_BG | WLAN Ana. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | RF_BG | RF BG band | |||||
| 32 | nRESET | Glob. Rst | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | nRESET | Master chip reset. Active low. | |||||
| 33 | VDD_PA_IN | Int. Pwr | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_PA_IN | PA supply voltage from PA DC-DC output. | |||||
| 34(5) | SOP1 | Config Sense | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | SOP1 | Sense On Power 1 | |||||
| 35(5) | SOP0 | Config Sense | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | SOP0 | Sense On Power 0 | |||||
| 36 | LDO_IN1 | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | LDO_IN1 | Analog RF supply from ana DC-DC output | |||||
| 37 | VIN_DCDC_ANA | Supply Input | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VIN_DCDC_ ANA |
Analog DC-DC input (connected to chip input supply [VBAT]) | |||||
| 38 | DCDC_ANA_SW | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | DCDC_ANA_ SW |
Analog DC-DC switching node. | |||||
| 39 | VIN_DCDC_PA | Supply Input | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VIN_DCDC_PA | PA DC-DC input (connected to chip input supply [VBAT]) | |||||
| 40 | DCDC_PA_SW_P | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | DCDC_PA_ SW_ P |
PA DCDC switching node | |||||
| 41 | DCDC_PA_SW_N | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | DCDC_PA_ SW_ N |
PA DCDC switching node | |||||
| 42 | DCDC_PA_OUT | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | DCDC_PA_ OUT |
PA buck converter output | |||||
| 43 | DCDC_DIG_SW | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | DCDC_DIG_ SW |
DIG DC-DC switching node | |||||
| 44 | VIN_DCDC_DIG | Supply Input | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VIN_DCDC_ DIG |
DIG DC-DC input (connected to chip input supply [VBAT]) | |||||
| 45(10) | DCDC_ANA2_SW_P | I/O | No | User config not required (9)(11) |
No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_31 (0x4402 E11C) |
0 | GPIO31 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 9 | UART0_RX | UART0 RX Data | I | ||||||||||
| 12 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | ||||||||||
| 2 | UART1_RX | UART1 RX Data | I | ||||||||||
| 6 | McAXR0 | I2S Audio Port Data 0 (RX/TX) | I/O | ||||||||||
| 7 | GSPI_CLK | General SPI Clock | I/O | ||||||||||
| See (6) | DCDC_ANA2_ SW_P |
ANA2 DCDC Converter +ve Switching Node. | |||||||||||
| 46 | DCDC_ANA2_SW_N | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | DCDC_ANA2_ SW_N |
ANA2 DCDC Converter -ve Switching Node. | ||||
| 47 | VDD_ANA2 | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_ANA2 | ANA2 DCDC O | ||||
| 48 | VDD_ANA1 | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_ANA1 | Analog supply fed by ANA2 DCDC output | ||||
| 49 | VDD_RAM | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_RAM | SRAM LDO output | ||||
| 50 | GPIO0 | I/O | No | User config not required (9) |
No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_0 (0x4402 E0A0) |
0 | GPIO0 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 12 | UART0_CTS | UART0 Clear To Send Input (Active Low) | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |||||||
| 6 | McAXR1 | I2S Audio Port Data 1 (RX/TX) | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | GT_CCP00 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 9 | GSPI_CS | General SPI Chip Select | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 10 | UART1_RTS | UART1 Request To Send O (Active Low) | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 3 | UART0_RTS | UART0 Request To Send O (Active Low) | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 4 | McAXR0 | I2S Audio Port Data 0 (RX/TX) | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 51 | RTC_XTAL_P | RTC Clock | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | RTC_XTAL_P | Connect 32.768-kHz XTAL or Froce external CMOS level clock | |||||
| 52(10) | RTC_XTAL_N | O Only | User config not required (9)(12) |
No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_32 (0x4402 E120) |
RTC_XTAL_N | Connect 32.768-kHz XTAL or connect a 100 kΩ to Vsupply. | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | ||||
| 0 | GPIO32 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 2 | McACLK | I2S Audio Port Clock O | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | McAXR0 | I2S Audio Port Data (Only O Mode Supported On Pin 52) | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | UART0_RTS | UART0 Request To Send O (Active Low) | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 8 | GSPI_MOSI | General SPI MOSI | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 53 | GPIO30 | I/O | No | User config not required (9) |
No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_30 (0x4402 E118) |
0 | GPIO30 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 9 | UART0_TX | UART0 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 2 | McACLK | I2S Audio Port Clock O | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | GT_CCP05 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | GSPI_MISO | General SPI MISO | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 54 | VIN_IO2 | Supply Input | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VIN_IO2 | Chip Supply Voltage (VBAT) | |||||
| 55 | GPIO1 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_1 (0x4402 E0A4) |
0 | GPIO1 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 3 | UART0_TX | UART0 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 4 | pCLK (PIXCLK) | Pixel Clock From Parallel Camera Sensor | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | UART1_TX | UART1 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 7 | GT_CCP01 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 56 | VDD_DIG2 | Internal Power | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | VDD_DIG2 | Internal Digital Core Voltage | |||||
| 57(13) | GPIO2 | Analog Input (up to 1.8 V)/ Digital I/O | Wake-Up Source | See (10)(14) | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_2 (0x4402 E0A8) |
See (6) | ADC_CH0 | ADC Channel 0 Input (1.5V max) | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 0 | GPIO2 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | UART0_RX | UART0 RX Data | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | UART1_RX | UART1 RXt Data | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | GT_CCP02 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 58(13) | GPIO3 | Analog Input (up to 1.8 V)/ Digital I/O | No | See (10)(14) | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_3 (0x4402 E0AC) |
See (6) | ADC_CH1 | ADC Channel 1 Input (1.5V max) | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 0 | GPIO3 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | UART1_TX | UART1 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 4 | pDATA7 (CAM_D3) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 3 | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 59(13) | GPIO4 | Analog Input (up to 1.8 V)/ Digital I/O | Wake-up Source | See (10)(14) | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_4 (0x4402 E0B0) |
See (6) | ADC_CH2 | ADC Channel 2 Input (1.5V max) | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 0 | GPIO4 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | UART1_RX | UART1 RX Data | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | pDATA6 (CAM_D2) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 2 | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 60(13) | GPIO5 | Analog Input (up to 1.8 V)/ Digital I/O | No | See (10)(14) | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_5 (0x4402 E0B4) |
See (6) | ADC_CH3 | ADC Channel 3 Input (1.5V max) | I | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | |
| 0 | GPIO5 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 4 | pDATA5 (CAM_D1) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 1 | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | McAXR1 | I2S Audio Port Data 1 (RX/TX) | I/O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | GT_CCP05 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 61 | GPIO6 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_6 (0x4402 E0B8) |
0 | GPIO6 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 5 | UART0_RTS | UART0 Request To Send O (Active Low) | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 4 | pDATA4 (CAM_D0) | Parallel Camera Data Bit 0 | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | UART1_CTS | UART1 Clear To Send Input (Active Low) | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 6 | UART0_CTS | UART0 Clear To Send Input (Active Low) | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 7 | GT_CCP06 | Timer Capture Port | I | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 62 | GPIO7 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_7 (0x4402 E0BC) |
0 | GPIO7 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 13 | McACLKX | I2S Audio Port Clock O | O | Hi-Z | |||||||||
| 3 | UART1_RTS | UART1 Request To Send O (Active Low) | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 10 | UART0_RTS | UART0 Request To Send O (Active Low) | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 11 | UART0_TX | UART0 TX Data | O | 1 | |||||||||
| 63 | GPIO8 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_8 (0x4402 E0C0) |
0 | GPIO8 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 6 | SDCARD_IRQ | Interrupt from SD Card (Future support) | I | ||||||||||
| 7 | McAFSX | I2S Audio Port Frame Sync | O | ||||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP06 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 64 | GPIO9 | I/O | No | No | No | GPIO_PAD_CONFIG_9 (0x4402 E0C4) |
0 | GPIO9 | General-Purpose I/O | I/O | Hi-Z | Hi-Z | Hi-Z |
| 3 | GT_PWM05 | Pulse Width Modulated O/P | O | ||||||||||
| 6 | SDCARD_ DATA0 |
SD Cad Data | I/O | ||||||||||
| 7 | McAXR0 | I2S Audio Port Data (Rx/Tx) | I/O | ||||||||||
| 12 | GT_CCP00 | Timer Capture Port | I | ||||||||||
| 65 | GND_TAB | Thermal pad and electrical ground | |||||||||||
- LPDS mode: The state of unused GPIOs in LPDS is input with 500 kΩ pulldown. For all used GPIOs , the user can enable internal pulls, which would hold them in a valid state.
- Hibernate mode: The CC3200 device leaves the digital pins in a Hi-Z state without any internal pulls when the device enters hibernate state. This can cause glitches on output lines unless held at valid levels by external resistors.
- To minimize leakage in some serial flash vendors during LPDS, TI recommends the user application always enable internal weak pulldowns on FLASH_SPI_DATA and FLASH_SPI_CLK pins.
- This pin has dual functions: as a SOP[2] (device operation mode), and as an external TCXO enable. As a TXCO enable, the pin is an output on power up and driven logic high. During hibernate low-power mode, the pin is in a high impedance state but pulled down for SOP mode to disable TCXO. Because of SOP functionality, the pin must be used as output only.
- Higher leakage current from the onboard serial flash can occur due to floating inputs when the device enters Hibernate mode. See reference schematics for recommended pull-up and pull-down resistors.
- For details on proper use, see Section 3.2, Drive Strength and Reset States for Analog-Digital Multiplexed Pins.
- This pin is one of three that must have a passive pullup or pulldown resistor on board to configure the chip hardware power-up mode. For this reason, the pin must be output only when used for digital functions.
- This pin is reserved for WLAN antenna selection, controlling an external RF switch that multiplexes the RF pin of the CC3200 device between two antennas. These pins should not be used for other functionalities in general.
- Device firmware automatically enables the digital path during ROM boot.
- Pin 45 is used by an internal DC-DC (ANA2_DCDC) and pin 52 is used by the RTC XTAL oscillator. These modules use automatic configuration sensing. Therefore, some board-level configuration is required to use pin 45 and pin 52 as digital pads (see Figure 3-2). Because the CC3200R device does not require ANA2_DCDC, the pin can always be used for digital functions. However, pin 47 must be shorted to the supply input. Typically, pin 52 is used for RTC XTAL in most applications. However, in some applications a 32.768-kHz square-wave clock might always be available onboard. In such cases, the XTAL can be removed to free up pin 52 for digital functions. The external clock must then be applied at pin 51. For the chip to automatically detect this configuration, a 100K pull-up resistor must be connected between pin 52 and the supply line. To prevent false detection, TI recommends using pin 52 for output-only functions.
- VDD_FLASH must be shorted to Vsupply.
- To use the digital functions, RTC_XTAL_N must be pulled high to Vsupply using 100-KΩ resistor.
- This pin is shared by the ADC inputs and digital I/O pad cells. Important: The ADC inputs are tolerant up to 1.8 V. On the other hand, the digital pads can tolerate up to 3.6 V. Hence, care must be taken to prevent accidental damage to the ADC inputs. TI recommends that the output buffer(s) of the digital I/Os corresponding to the desired ADC channel be disabled first (that is, converted to high-impedance state), and thereafter the respective pass switches (S7, S8, S9, S10) should be enabled (see Section 3.2, Drive Strength and Reset States for Analog-Digital Multiplexed Pins).
- Requires user configuration to enable the ADC channel analog switch. (The switch is off by default.) The digital I/O is always connected and must be made Hi-Z before enabling the ADC switch.
 Figure 3-2 Board Configuration to Use Pins 45 and 52 as Digital Signals
Figure 3-2 Board Configuration to Use Pins 45 and 52 as Digital Signals
3.1.1 Connections for Unused Pins
All unused pins must be left as no connect (NC) pins. For a list of NC pins, see Table 3-2.
Table 3-2 Connections for Unused Pins
| FUNCTION | SIGNAL NAME | PIN NUMBER |
|---|---|---|
| WLAN Analog | NC | 26 |
| WLAN Analog | NC | 27 |
| WLAN Analog | NC | 28 |
3.1.2 Recommended Pin Multiplexing Configurations
Table 3-3 lists the recommended pin multiplexing configurations.
Table 3-3 Recommended Pin Multiplexing Configurations
| CC3200 Recommended Pinout Grouping Use – Examples(2) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home Security High-end Toys | Wifi Audio ++ Industrial | Sensor-Tag | Home Security Toys | Wifi Audio ++ Industrial | WiFi Remote w/ 7x7 keypad and audio | Sensor Door-Lock Fire-Alarm Toys w/o Cam | Industrial Home Appliances | Industrial Home Appliances Smart-Plug | Industrial Home Appliances" | GPIOs | |
| External 32 kHz(1) | External 32 kHz (1) | External TCXO 40 MHZ (-40 to +85°C) | |||||||||
| Cam + I2S (Tx or Rx) + I2C + SPI + SWD + UART-Tx + (App Logger) 2 GPIO + 1PWM + *4 overlaid wakeup from Hib | I2S (Tx & Rx) + 1 Ch ADC + 1x 4wire UART + 1x 2wire UART + 1bit SD Card + SPI + I2C + SWD + 3 GPIO + 1 PWM + 1 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib | I2S (Tx & Rx) + 2 Ch ADC + 2wire UART + SPI + I2C + SWD + 2 PMW + 6 GPIO + 3 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib | Cam + I2S (Tx or Rx) + I2C + SWD + UART-Tx + (App Logger) 4 GPIO + 1PWM + *4 overlaid wakeup from HIB | I2S (Tx & Rx) + 1 Ch ADC + 2x 2wire UART + 1bit SD Card + SPI + I2C + SWD + 4 GPIO + 1 PWM + 1 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib | I2S (Tx & Rx) + 1 Ch ADC + UART (Tx Only) I2C + SWD + 15 GPIO + 1 PWM + 1 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib | I2S (Tx or Rx) + 2 Ch ADC + 2 wire UART + SPI + I2C + 3 PMW + 3 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib + 5 GPIO SWD + | 4 Ch ADC + 1x 4wire UART + 1x 2wire UART + SPI + I2C + SWD + 1 PWM + 6 GPIO + 1 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib Enable for Ext 40 MHz TCXO | 3 Ch ADC + 2wire UART + SPI + I2C + SWD + 3 PWM + 9 GPIO + 2 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib | 2 Ch ADC + 2wire UART + I2C + SWD + 3 PWM + 11 GPIO + 5 GPIO with Wake-From-Hib | ||
| Pin Number | Pinout #11 | Pinout #10 | Pinout #9 | Pinout #8 | Pinout #7 | Pinout #6 | Pinout #5 | Pinout #4 | Pinout #3 | Pinout #2 | Pinout #1 |
| 52 | GSPI-MOSI | McASP-D0 (Tx) | GPIO_32 output only | ||||||||
| 53 | GSPI-MISO | MCASP-ACLKX | MCASP-ACLKX | GPIO_30 | GPIO_30 | GPIO_30 | GPIO_30 | UART0-TX | GPIO_30 | UART0-TX | GPIO_30 |
| 45 | GSPI-CLK | McASP-AFSX | McASP-D0 | GPIO_31 | McASP-AFSX | McASP-AFSX | McASP-AFSX | UART0-RX | GPIO_31 | UART0-RX | GPIO_31 |
| 50 | GSPI-CS | McASP-D1 (Rx) | McASP-D1 | McASP-D1 | McASP-D1 | McASP-D1 | McASP-D1 | UART0-CTS | GPIO_0 | GPIO_0 | GPIO_0 |
| 55 | pCLK (PIXCLK) | UART0-TX | UART0-TX | PIXCLK | UART0-TX | UART0-TX | UART0-TX | GPIO-1 | UART0-TX | GPIO_1 | GPIO_1 |
| 57 | (wake) GPIO2 | UART0-RX | UART0-RX | (wake) GPIO2 | UART0-RX | GPIO_2 | UART0-RX | ADC-0 | UART0-RX | (wake) GPIO_2 | (wake) GPIO_2 |
| 58 | pDATA7 (D3) | UART1-TX | ADC-CH1 | pDATA7 (D3) | UART1-TX | GPIO_3 | ADC-1 | ADC-1 | ADC-1 | ADC-1 | GPIO_3 |
| 59 | pDATA6 (D2) | UART1-RX | (wake) GPIO_4 | pDATA6 (D2) | UART1-RX | GPIO_4 | (wake) GPIO_4 | ADC-2 | ADC-2 | (wake) GPIO_4 | (wake) GPIO_4 |
| 60 | pDATA5 (D1) | ADC-3 | ADC-3 | pDATA5 (D1) | ADC-3 | ADC-3 | ADC-3 | ADC-3 | ADC-3 | ADC-3 | GPIO_5 |
| 61 | pDATA4 (D0) | UART1-CTS | GPIO_6 | pDATA4 (D0) | GPIO_6 | GPIO_6 | GPIO_6 | UART0-RTS | GPIO_6 | GPIO_6 | GPIO_6 |
| 62 | McASP-ACLKX | UART1-RTS | GPIO_7 | McASP-ACLKX | McASP-ACLKX | McASP-ACLKX | McASP-ACLKX | GPIO_7 | GPIO_7 | GPIO_7 | GPIO_7 |
| 63 | McASP-AFSX | SDCARD-IRQ | McASP-AFSX | McASP-AFSX | SDCARD-IRQ | GPIO_8 | GPIO_8 | GPIO_8 | GPIO_8 | GPIO_8 | GPIO_8 |
| 64 | McASP-D0 | SDCARD-DATA | GT_PWM5 | McASP-D0 | SDCARD-DATA | GPIO_9 | GT_PWM5 | GT_PWM5 | GT_PWM5 | GT_PWM5 | GPIO_9 |
| 1 | UART1-TX | SDCARD-CLK | GPIO_10 | UART1-TX | SDCARD-CLK | GPIO_10 | GT_PWM6 | UART1-TX | GT_PWM6 | GPIO_10 | GPIO_10 |
| 2 | (wake) pXCLK (XVCLK) | SDCARD-CMD | (wake) GPIO_11 | (wake) pXCLK (XVCLK) | SDCARD-CMD | GPIO_11 | (wake) GPIO_11 | UART1-RX | (wake) GPIO_11 | (wake) GPIO_11 | (wake) GPIO_11 |
| 3 | pVS (VSYNC) | I2C-SCL | I2C-SCL | pVS (VSYNC) | I2C-SCL | GPIO_12 | I2C-SCL | I2C-SCL | I2C-SCL | GPIO_12 | GPIO_12 |
| 4 | (wake) pHS (HSYNC) | I2C-SDA | I2C-SDA | (wake) pHS (HSYNC) | I2C-SDA | GPIO_13 | I2C-SDA | I2C-SDA | I2C-SDA | (wake) GPIO_13 | (wake) GPIO_13 |
| 5 | pDATA8 (D4) | GSPI-CLK | GSPI-CLK | pDATA8 (D4) | GSPI-CLK | I2C-SCL | GSPI-CLK | GSPI-CLK | GSPI-CLK | I2C-SCL | GPIO_14 |
| 6 | pDATA9 (D5) | GSPI-MISO | GSPI-MISO | pDATA9 (D5) | GSPI-MISO | I2C-SDA | GSPI-MISO | GSPI-MISO | GSPI-MISO | I2C-SDA | GPIO_15 |
| 7 | pDATA10 (D6) | GSPI-MOSI | GSPI-MOSI | pDATA10 (D6) | GSPI-MOSI | GPIO_16 | GSPI-MOSI | GSPI-MOSI | GSPI-MOSI | GPIO_16 | GPIO_16 |
| 8 | (wake) pDATA11 (D7) | GSPI-CS | GSPI-CS | (wake) pDATA11 (D7) | GSPI-CS | GPIO_17 | GSPI-CS | GSPI-CS | GSPI-CS | (wake) GPIO_17 | (wake) GPIO_17 |
| 11 | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK | SPI-FLASH_CLK |
| 12 | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT | SPI-FLASH-DOUT |
| 13 | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN | SPI-FLASH-DIN |
| 14 | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS | SPI-FLASH-CS |
| 15 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 | GPIO_22 |
| 16 | I2C-SCL | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 | I2C-SCL | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 | GPIO_23 |
| 17 | I2C-SDA | (wake) GPIO_24 | (wake) GPIO_24 | I2C-SDA | (wake) GPIO_24 | (wake) GPIO_24 | (wake) GPIO_24 | (wake) GPIO_24 | (wake) GPIO_24 | GT-PWM0 | (wake) GPIO_24 |
| 19 | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK | SWD-TCK |
| 20 | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS | SWD-TMS |
| 18 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 | GPIO_28 |
| 21 | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | TCXO_EN | GT_PWM2 | GT_PWM2 | GPIO_25 out only |
3.2 Drive Strength and Reset States for Analog-Digital Multiplexed Pins
Table 3-4 describes the use, drive strength, and default state of these pins at first-time power up and reset (nRESET pulled low).
Table 3-4 Drive Strength and Reset States for Analog-Digital Multiplexed Pins
| Pin | Board Level Configuration and Use | Default State at First Power Up or Forced Reset | State after Configuration of Analog Switches (ACTIVE, LPDS, and HIB Power Modes) | Maximum Effective Drive Strength (mA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | Connected to the enable pin of the RF switch (ANTSEL1). Other use not recommended. | Analog is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 30 | Connected to the enable pin of the RF switch (ANTSEL2). Other use not recommended. | Analog is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 45 | VDD_ANA2 (pin 47) must be shorted to the input supply rail. Otherwise, the pin is driven by the ANA2 DC-DC. | Analog is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 50 | Generic I/O | Analog is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 52 | The pin must have an external pullup of 100 K to the supply rail and must be used in output signals only. | Analog is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 53 | Generic I/O | Analog is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 57 | Analog signal (1.8 V absolute, 1.46 V full scale) | ADC is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 58 | Analog signal (1.8 V absolute, 1.46 V full scale) | ADC is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 59 | Analog signal (1.8 V absolute, 1.46 V full scale) | ADC is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
| 60 | Analog signal (1.8 V absolute, 1.46 V full scale) | ADC is isolated. The digital I/O cell is also isolated. | Determined by the I/O state, as are other digital I/Os. | 4 |
3.3 Pad State After Application of Power To Chip But Prior To Reset Release
When a stable power is applied to the CC3200 chip for the first time or when supply voltage is restored to the proper value following a prior period with supply voltage below 1.5 V, the level of the digital pads are undefined in the period starting from the release of nRESET and until DIG_DCDC powers up. This period is less than approximately 10 ms. During this period, pads can be internally pulled weakly in either direction. If a certain set of pins are required to have a definite value during this pre-reset period, an appropriate pullup or pulldown must be used at the board level. The recommended value of this external pull is 2.7 KΩ.
4 Specifications
All measurements are referenced at the device pins, unless otherwise indicated. All specifications are over process and voltage, unless otherwise indicated.
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETERS | PINS | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBAT and VIO | 37, 39, 44 | –0.5 | 3.8 | V |
| VIO-VBAT (differential) | 10, 54 | 0.0 | V | |
| Digital inputs | –0.5 | VIO + 0.5 | V | |
| RF pins | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| Analog pins (XTAL) | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| Operating temperature range (TA ) | –40 | +85 | °C |
4.2 Handling Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –55 | +125 | °C | |
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | –2000 | +2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | –500 | +500 | V | ||
| CONDITIONS | POH | |
|---|---|---|
| TAmbient up to 85°C, assuming 20% active mode and 80% sleep mode | 17,500(1) | |
4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)(4)| PARAMETERS | PINS | CONDITIONS(2)(3) | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBAT, VIO (shorted to VBAT) | 10, 37, 39, 44, 54 | Direct battery connection | 2.1 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VBAT, VIO (shorted to VBAT) | 10, 37, 39, 44, 54 | Preregulated 1.85 V | 1.76 | 1.85 | 1.9 | V |
| Ambient thermal slew | –20 | 20 | °C/minute |
4.5 Brown-Out and Black-Out
The device enters a brown-out condition whenever the input voltage dips below VBROWN (see Figure 4-1 and Figure 4-2). This condition must be considered during design of the power supply routing, especially if operating from a battery. High-current operations (such as a TX packet) cause a dip in the supply voltage, potentially triggering a brown-out. The resistance includes the internal resistance of the battery, contact resistance of the battery holder (4 contacts for a 2 x AA battery) and the wiring and PCB routing resistance.
 Figure 4-1 Brown-Out and Black-Out Levels (1 of 2)
Figure 4-1 Brown-Out and Black-Out Levels (1 of 2)
 Figure 4-2 Brown-Out and Black-Out Levels (2 of 2)
Figure 4-2 Brown-Out and Black-Out Levels (2 of 2)
In the brown-out condition, all sections of the device shut down except for the Hibernate module (including the 32-kHz RTC clock), which remains on. The current in this state can reach approximately 400 µA.
The black-out condition is equivalent to a hardware reset event in which all states within the device are lost.
Table 4-1 lists the brown-out and black-out voltage levels.
Table 4-1 Brown-Out and Black-out Voltage Levels
| CONDITION | VOLTAGE LEVEL | UNIT |
|---|---|---|
| Vbrownout | 2.1 | V |
| Vblackout | 1.67 | V |
4.6 Electrical Characteristics (3.3 V, 25°C)
| GPIO Pins Except 29, 30, 45, 50, 52, and 53 (25°C)(1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
| CIN | Pin capacitance | 4 | pF | ||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDD | VDD + 0.5 V | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | –0.5 | 0.35 × VDD | V | |||
| IIH | High-level input current | 5 | nA | ||||
| IIL | Low-level input current | 5 | nA | ||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage (VDD = 3.0 V) | 2.4 | V | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage (VDD = 3.0 V) | 0.4 | V | ||||
| IOH | High-level source current, VOH = 2.4 |
2-mA Drive | 2 | mA | |||
| 4-mA Drive | 4 | mA | |||||
| 6-mA Drive | 6 | mA | |||||
| IOL | Low-level sink current, VOL = 0.4 |
2-mA Drive | 2 | mA | |||
| 4-mA Drive | 4 | mA | |||||
| 6-mA Drive | 6 | mA | |||||
| GPIO Pins 29, 30, 45, 50, 52, and 53 (25°C)(1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
| CIN | Pin capacitance | 7 | pF | ||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDD | VDD + 0.5V | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | –0.5 | 0.35 × VDD | V | |||
| IIH | High-level input current | 50 | nA | ||||
| IIL | Low-level input current | 50 | nA | ||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage (VDD= 3.0 V) |
2.4 | V | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage (VDD= 3.0 V) |
0.4 | V | ||||
| IOH | High-level source current, VOH = 2.4 | 2-mA Drive | 1.5 | mA | |||
| 4-mA Drive | 2.5 | mA | |||||
| 6-mA Drive | 3.5 | mA | |||||
| IOL | Low-level sink current, VOL = 0.4 | 2-mA Drive | 1.5 | mA | |||
| 4-mA Drive | 2.5 | mA | |||||
| 6-mA Drive | 3.5 | mA | |||||
| VIL | nRESET(2) | 0.6 | V | ||||
| Pin Internal Pullup and Pulldown (25°C)(1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
| IOH | Pull-Up current, VOH = 2.4 (VDD = 3.0 V) |
5 | 10 | µA | ||
| IOL | Pull-Down current, VOL = 0.4 (VDD = 3.0 V) |
5 | µA | |||
4.7 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
TA = +25°C, VBAT = 2.1 to 3.6 V. Parameters measured at SoC pin on channel 7 (2442 MHz)| Parameter | Condition (Mbps) | Min | Typ | Max | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (8% PER for 11b rates, 10% PER for 11g/11n rates)(10% PER)(2) |
1 DSSS | –95.7 | dBm | ||
| 2 DSSS | –93.6 | ||||
| 11 CCK | –88.0 | ||||
| 6 OFDM | –90.0 | ||||
| 9 OFDM | –89.0 | ||||
| 18 OFDM | –86.0 | ||||
| 36 OFDM | –80.5 | ||||
| 54 OFDM | –74.0 | ||||
| MCS0 (GF)(1) | –89.0 | ||||
| MCS7 (GF)(1) | –71.0 | ||||
| Maximum input level (10% PER) |
802.11b | –4.0 | |||
| 802.11g | –10.0 |
4.8 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
TA = +25°C, VBAT = 2.1 to 3.6 V. Parameters measured at SoC pin on channel 7 (2442 MHz).(1)| Parameter | Condition(2) | Min | Typ | Max | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum RMS output power measured at 1 dB from IEEE spectral mask or EVM | 1 DSSS | 18.0 | dBm | ||
| 2 DSSS | 18.0 | ||||
| 11 CCK | 18.3 | ||||
| 6 OFDM | 17.3 | ||||
| 9 OFDM | 17.3 | ||||
| 18 OFDM | 17.0 | ||||
| 36 OFDM | 16.0 | ||||
| 54 OFDM | 14.5 | ||||
| MCS7 (MM) | 13.0 | ||||
| Transmit center frequency accuracy | –25 | 25 | ppm |
4.9 Current Consumption
TA = +25°C, VBAT = 3.6 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS(1)(6) | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCU ACTIVE | NWP ACTIVE | TX | 1 DSSS | TX power level = 0 | 278 | mA | |||
| TX power level = 4 | 194 | ||||||||
| 6 OFDM | TX power level = 0 | 254 | |||||||
| TX power level = 4 | 185 | ||||||||
| 54 OFDM | TX power level = 0 | 229 | |||||||
| TX power level = 4 | 166 | ||||||||
| RX | 1 DSSS | 59 | |||||||
| 54 OFDM | 59 | ||||||||
| NWP idle connected(3) | 15.3 | ||||||||
| MCU SLEEP | NWP ACTIVE | TX | 1 DSSS | TX power level = 0 | 275 | mA | |||
| TX power level = 4 | 191 | ||||||||
| 6 OFDM | TX power level = 0 | 251 | |||||||
| TX power level = 4 | 182 | ||||||||
| 54 OFDM | TX power level = 0 | 226 | |||||||
| TX power level = 4 | 163 | ||||||||
| RX | 1 DSSS | 56 | |||||||
| 54 OFDM | 56 | ||||||||
| NWP idle connected(3) | 12.2 | ||||||||
| MCU LPDS | NWP active | TX | 1 DSSS | TX power level = 0 | 272 | mA | |||
| TX power level = 4 | 188 | ||||||||
| 6 OFDM | TX power level = 0 | 248 | |||||||
| TX power level = 4 | 179 | ||||||||
| 54 OFDM | TX power level = 0 | 223 | |||||||
| TX power level = 4 | 160 | ||||||||
| RX | 1 DSSS | 53 | |||||||
| 54 OFDM | 53 | ||||||||
| NWP LPDS(2) | 0.25 | ||||||||
| NWP idle connected(3) | 0.825 | ||||||||
| MCU hibernate(7) | NWP hibernate(4) | 4 | µA | ||||||
| Peak calibration current (5) | VBAT = 3.3 V | 450 | mA | ||||||
| VBAT = 2.1 V | 670 | ||||||||
| VBAT = 1.85 V | 700 | ||||||||

 Figure 4-4 TX Power and IBAT vs TX Power Level Settings (6 OFDM)
Figure 4-4 TX Power and IBAT vs TX Power Level Settings (6 OFDM)
 Figure 4-5 TX Power and IBAT vs TX Power Level Settings (54 OFDM)
Figure 4-5 TX Power and IBAT vs TX Power Level Settings (54 OFDM)
4.10 Thermal Characteristics for RGC Package
| AIR FLOW | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARAMETER | 0 lfm (C/W) | 150 lfm (C/W) | 250 lfm (C/W) | 500 lfm (C/W) |
| θja | 23 | 14.6 | 12.4 | 10.8 |
| Ψjt | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Ψjb | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.4 |
| θjc | 6.3 | |||
| θjb | 2.4 | |||
4.11 Timing and Switching Characteristics
4.11.1 Power Supply Sequencing
For proper operation of the CC3200 device, perform the recommended power-up sequencing as follows:
- Tie VBAT (pins 37, 39, 44) and VIO (pins 54 and 10) together on the board.
- Hold the RESET pin low while the supplies are ramping up. TI recommends using a simple RC circuit (100K || 0.1 µF, RC = 10 ms).
- For an external RTC clock, ensure that the clock is stable before RESET is deasserted (high).
For timing diagrams, see Section 4.11.2, Reset Timing.
4.11.2 Reset Timing
4.11.2.1 nRESET (32K XTAL)
Figure 4-6 shows the reset timing diagram for the 32K XTAL first-time power-up and reset removal.
 Figure 4-6 First-Time Power-Up and Reset Removal Timing Diagram (32K XTAL)
Figure 4-6 First-Time Power-Up and Reset Removal Timing Diagram (32K XTAL)
Table 4-2 describes the timing requirements for the 32K XTAL first-time power-up and reset removal.
Table 4-2 First-Time Power-Up and Reset Removal Timing Requirements (32K XTAL)
| Item | Name | Description | Min | Typ | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Supply settling time | Depends on application board power supply, decap, and so on | 3 ms | ||
| T2 | Hardware wakeup time | 25 ms | |||
| T3 | Time taken by ROM firmware to initialize hardware | Includes 32.768 -kHz XOSC settling time | 1.1 s | ||
| T4 | App code load time | Image size (KByte) x 0.75 ms |
4.11.2.2 nRESET (External 32K)
Figure 4-7 shows the reset timing diagram for the external 32K first-time power-up and reset removal.
 Figure 4-7 First-Time Power-Up and Reset Removal Timing Diagram (External 32K)
Figure 4-7 First-Time Power-Up and Reset Removal Timing Diagram (External 32K)
Table 4-3 describes the timing requirements for the external 32K first-time power-up and reset removal.
Table 4-3 First-Time Power-Up and Reset Removal Timing Requirements (External 32K)
| Item | Name | Description | Min | Typ | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Supply settling time | Depends on application board power supply, decap, and so on | 3 ms | ||
| T2 | Hardware wakeup time | 25 ms | |||
| T3 | Time taken by ROM firmware to initialize hardware | Time taken by ROM firmware | 3 ms | ||
| T4 | App code load time | Image size (KByte) x 0.75 ms |
4.11.2.3 Wakeup from Hibernate
Figure 4-8 shows the timing diagram for wakeup from the hibernate state.
NOTE
The 32.768-kHz XTAL is kept enabled by default when the chip goes to hibernate.
Table 4-4 describes the software hibernate timing requirements.
Table 4-4 Software Hibernate Timing Requirements
| Item | Name | Description | Min | Typ | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thib_min | Minimum hibernate time | The time for which the device has to be held in hibernate mode | 10 ms | ||
| T2 | Hardware wakeup time | Time taken by the hardware to initialize | 25 ms | ||
| T3 | Firmware initialization time | Time taken by the ROM firmware to initialize the hardware | 3 ms | ||
| T4 | Code download time | Time taken to download the code from the serial flash to on-chip RAM | Image size (KByte) x 0.75 ms | ||
4.11.3 Clock Specifications
The CC3200 device requires two separate clocks for its operation:
- A slow clock running at 32.768 kHz is used for the RTC.
- A fast clock running at 40 MHz is used by the device for the internal processor and the WLAN subsystem.
The device features internal oscillators that enable the use of cheaper crystals rather than dedicated TCXOs for these clocks. The RTC can also be fed externally to provide reuse of an existing clock on the system and reduce overall cost.
4.11.3.1 Slow Clock Using Internal Oscillator
The RTC crystal connected on the device supplies the free-running slow clock. The accuracy of the slow clock frequency must be 32.768 kHz ±150 ppm. In this mode of operation, the crystal is tied between RTC_XTAL_P (pin 51) and RTC_XTAL_N (pin 52) with a suitable load capacitance.
Figure 4-9 shows the crystal connections for the slow clock.
 Figure 4-9 RTC Crystal Connections
Figure 4-9 RTC Crystal Connections
4.11.3.2 Slow Clock Using an External Clock
When an RTC clock oscillator is present in the system, the CC3200 device can accept this clock directly as an input. The clock is fed on the RTC_XTAL_P line and the RTC_XTAL_N line is held to VIO. The clock must be a CMOS-level clock compatible with VIO fed to the device.
Figure 4-10 shows the external RTC clock input connection.
 Figure 4-10 External RTC Clock Input
Figure 4-10 External RTC Clock Input
4.11.3.3 Fast Clock (Fref) Using an External Crystal
The CC3200 device also incorporates an internal crystal oscillator to support a crystal-based fast clock. The XTAL is fed directly between WLAN_XTAL_P (pin 23) and WLAN_XTAL_N (pin 22) with suitable loading capacitors.
Figure 4-11 shows the crystal connections for the fast clock.
 Figure 4-11 Fast Clock Crystal Connections
Figure 4-11 Fast Clock Crystal Connections
4.11.3.4 Fast Clock (Fref) Using an External Oscillator
The CC3200 device can accept an external TCXO/XO for the 40-MHz clock. In this mode of operation, the clock is connected to WLAN_XTAL_P (pin 23). WLAN_XTAL_N (pin 22) is connected to GND. The external TCXO/XO can be enabled by TCXO_EN (pin 21) from the device to optimize the power consumption of the system.
If the TCXO does not have an enable input, an external LDO with an enable function can be used. Using the LDO improves noise on the TCXO power supply.
Figure 4-12 shows the connection.
 Figure 4-12 External TCXO Input
Figure 4-12 External TCXO Input
Table 4-5 lists the external Fref clock requirements.
Table 4-5 External Fref Clock Requirements (–40°C to +85°C)
| Characteristics | Condition | Sym | Min | Typ | Max | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 40.00 | MHz | |||||
| Frequency accuracy (Initial + temp + aging) | ±25 | ppm | |||||
| Frequency input duty cycle | 45 | 50 | 55 | % | |||
| Clock voltage limits | Sine or clipped sine wave, AC coupled | Vpp | 0.7 | 1.2 | Vpp | ||
| Phase noise @ 40 MHz | @ 1 kHz | –125 | dBc/Hz | ||||
| @ 10 kHz | –138.5 | dBc/Hz | |||||
| @ 100 kHz | –143 | dBc/Hz | |||||
| Input impedance | Resistance | 12 | KΩ | ||||
| Capacitance | 7 | pF | |||||
4.11.3.5 Input Clocks/Oscillators
Table 4-6 lists the RTC crystal requirements.
Table 4-6 RTC Crystal Requirements
| CHARACTERISTICS | CONDITION | SYM | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 32.768 | kHz | ||||
| Frequency accuracy | Initial + temp + aging | ±150 | ppm | |||
| Crystal ESR | 32.768 kHz, C1 = C2 = 10 pF | 70 | kΩ |
Table 4-7 lists the external RTC digital clock requirements.
Table 4-7 External RTC Digital Clock Requirements
| CHARACTERISTICS | CONDITION | SYM | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 32768 | Hz | ||||
| Frequency accuracy | ±150 | ppm | ||||
| (Initial + temp + aging) | ||||||
| Input transition time tr/tf (10% to 90%) | tr/tf | 100 | ns | |||
| Frequency input duty cycle | 20 | 50 | 80 | % | ||
| Slow clock input voltage limits | Square wave, DC coupled | Vih | 0.65 × VIO | VIO | V | |
| Vil | 0 | 0.35 × VIO | V peak | |||
| Input impedance | 1 | MΩ | ||||
| 5 | pF |
Table 4-8 lists the WLAN fast-clock crystal requirements.
Table 4-8 WLAN Fast-Clock Crystal Requirements
| CHARACTERISTICS | CONDITION | SYM | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 40 | MHz | ||||
| Frequency accuracy | Initial + temp + aging | ±25 | ppm | |||
| Crystal ESR | 40 MHz, C1 = C2 = 6.2 pF | 40 | 50 | 60 | Ohm |
4.11.3.6 WLAN Filter Requirements
The device requires an external bandpass filter to meet the various emission standards, including FCC. Table 4-9 presents the attenuation requirements for the bandpass filter. TI recommends using the same filter used in the reference design to ease the process of certification.
Table 4-9 WLAN Filter Requirements
| Parameter | Frequency (MHz) | Requirements | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Typ | Max | Units | ||
| Return loss | 2412 to 2484 | 10 | dB | ||
| Insertion loss(1) | 2412 to 2484 | 1 | 1.5 | dB | |
| Attenuation | 800 to 830 | 30 | 45 | dB | |
| 1600 to 1670 | 20 | 25 | |||
| 3200 to 3300 | 30 | 48 | |||
| 4000 to 4150 | 45 | 50 | |||
| 4800 to 5000 | 20 | 25 | |||
| 5600 to 5800 | 20 | 25 | |||
| 6400 to 6600 | 20 | 35 | |||
| 7200 to 7500 | 35 | 45 | |||
| 7500 to 10000 | 20 | 25 | |||
| Reference Impendence | 2412 to 2484 | 50 | Ω | ||
| Filter type | Bandpass | ||||
4.11.4 Peripherals
This section describes the peripherals that are supported by the CC3200 device:
- SPI
- McASP
- GPIO
- I2C
- IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- ADC
- Camera parallel port
- UART
4.11.4.1 SPI
4.11.4.1.1 SPI Master
The CC3200 microcontroller includes one SPI module, which can be configured as a master or slave device. The SPI includes a serial clock with programmable frequency, polarity, and phase, a programmable timing control between chip select and external clock generation, and a programmable delay before the first SPI word is transmitted. Slave mode does not include a dead cycle between two successive words.
Figure 4-13 shows the timing diagram for the SPI master.
 Figure 4-13 SPI Master Timing Diagram
Figure 4-13 SPI Master Timing Diagram
Table 4-10 lists the timing parameters for the SPI master.
Table 4-10 SPI Master Timing Parameters
| Parameter Number | Parameter(1) | Parameter Name | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | F | Clock frequency | 20 | MHz | |
| I2 | Tclk | Clock period | 50 | ns | |
| I5 | D | Duty cycle | 45 | 55 | % |
| I6 | tIS | RX data setup time | 1 | ns | |
| I7 | tIH | RX data hold time | 2 | ns | |
| I8 | tOD | TX data output delay | 8.5 | ns | |
| I9 | tOH | TX data hold time | 8 | ns |
4.11.4.1.2 SPI Slave
Figure 4-14 shows the timing diagram for the SPI slave.
 Figure 4-14 SPI Slave Timing Diagram
Figure 4-14 SPI Slave Timing Diagram
Table 4-11 lists the timing parameters for the SPI slave.
Table 4-11 SPI Slave Timing Parameters
| Parameter Number | Parameter(1) | Parameter Name | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | F | Clock frequency @ VBAT = 3.3 V | 20 | MHz | |
| Clock frequency @ VBAT ≤ 2.1 V | 12 | ||||
| I2 | Tclk | Clock period | 50 | ns | |
| I5 | D | Duty cycle | 45 | 55 | % |
| I6 | tIS | RX data setup time | 4 | ns | |
| I7 | tIH | RX data hold time | 4 | ns | |
| I8 | tOD | TX data output delay | 20 | ||
| I9 | tOH | TX data hold time | 24 | ns |
4.11.4.2 McASP
The McASP interface functions as a general-purpose audio serial port optimized for multichannel audio applications and supports transfer of two stereo channels over two data pins. The McASP consists of transmit and receive sections that operate synchronously and have programmable clock and frame-sync polarity. A fractional divider is available for bit-clock generation.
4.11.4.2.1 I2S Transmit Mode
Figure 4-15 shows the timing diagram for the I2S transmit mode.
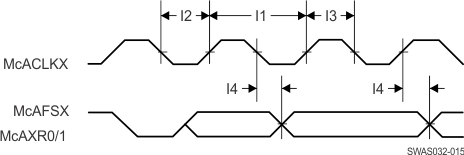 Figure 4-15 I2S Transmit Mode Timing Diagram
Figure 4-15 I2S Transmit Mode Timing Diagram
Table 4-12 lists the timing parameters for the I2S transmit mode.
Table 4-12 I2S Transmit Mode Timing Parameters
| Parameter Number | Parameter(1) | Parameter Name | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | fclk | Clock frequency | 9.216 | MHz | |
| I2 | tLP | Clock low period | 1/2 fclk | ns | |
| I3 | tHT | Clock high period | 1/2 fclk | ns | |
| I4 | tOH | TX data hold time | 22 | ns |
4.11.4.2.2 I2S Receive Mode
Figure 4-16 shows the timing diagram for the I2S receive mode.
 Figure 4-16 I2S Receive Mode Timing Diagram
Figure 4-16 I2S Receive Mode Timing Diagram
Table 4-13 lists the timing parameters for the I2S receive mode.
Table 4-13 I2S Receive Mode Timing Parameters
| Parameter Number | Parameter(1) | Parameter Name | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | fclk | Clock frequency | 9.216 | MHz | |
| I2 | tLP | Clock low period | 1/2 fclk | ns | |
| I3 | tHT | Clock high period | 1/2 fclk | ns | |
| I4 | tOH | RX data hold time | 0 | ns | |
| I5 | tOS | RX data setup time | 15 | ns |
4.11.4.3 GPIO
All digital pins of the device can be used as general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins.The GPIO module consists of four GPIO blocks, each of which provides eight GPIOs. The GPIO module supports 24 programmable GPIO pins, depending on the peripheral used. Each GPIO has configurable pullup and pulldown strength (weak 10 µA), configurable drive strength (2, 4, and 6 mA), and open-drain enable.
Figure 4-17 shows the GPIO timing diagram.
 Figure 4-17 GPIO Timing
Figure 4-17 GPIO Timing
4.11.4.3.1 GPIO Output Transition Time Parameters (Vsupply = 3.3 V)
Table 4-14 lists the GPIO output transition times for Vsupply = 3.3 V.
Table 4-14 GPIO Output Transition Times (Vsupply = 3.3 V)(1)(2)
| Drive Strength (mA) | Drive Strength Control Bits | Tr (ns) | Tf (ns) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Nom | Max | Min | Nom | Max | ||
| 2 | 2MA_EN=1 | 8.0 | 9.3 | 10.7 | 8.2 | 9.5 | 11.0 |
| 4MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 4 | 2MA_EN=0 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 5.8 |
| 4MA_EN=1 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 8 | 2MA_EN=0 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.9 |
| 4MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=1 | |||||||
| 14 | 2MA_EN=1 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| 4MA_EN=1 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=1 | |||||||
4.11.4.3.2 GPIO Output Transition Time Parameters (Vsupply = 1.8 V)
Table 4-15 lists the GPIO output transition times for Vsupply = 1.8 V.
Table 4-15 GPIO Output Transition Times (Vsupply = 1.8 V)(1)(2)
| Drive Strength (mA) | Drive Strength Control Bits | Tr (ns) | Tf (ns) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Nom | Max | Min | Nom | Max | ||
| 2 | 2MA_EN=1 | 11.7 | 13.9 | 16.3 | 11.5 | 13.9 | 16.7 |
| 4MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 4 | 2MA_EN=0 | 13.7 | 15.6 | 18.0 | 9.9 | 11.6 | 13.6 |
| 4MA_EN=1 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 8 | 2MA_EN=0 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 7.4 | 3.8 | 4.7 | 5.8 |
| 4MA_EN=0 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=1 | |||||||
| 14 | 2MA_EN=1 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 3.3 |
| 4MA_EN=1 | |||||||
| 8MA_EN=1 | |||||||
4.11.4.3.3 GPIO Input Transition Time Parameters
Table 4-16 lists the input transition time parameters.
Table 4-16 GPIO Input Transition Time Parameters
| Parameter | Condition | Symbol | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input transition time (tr,tf), 10% to 90% | tr | 1 | 3 | ns | |
| tf | 1 | 3 |
4.11.4.4 I2C
The CC3200 microcontroller includes one I2C module operating with standard (100 Kbps) or fast (400 Kbps) transmission speeds.
Figure 4-18 shows the I2C timing diagram.
 Figure 4-18 I2C Timing
Figure 4-18 I2C Timing
Table 4-17 lists the I2C timing parameters.
Table 4-17 I2C Timing Parameters(3)
| Parameter Number | Parameter | Parameter Name | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 | tLP | Clock low period | See (1). | - | System clock |
| I3 | tSRT | SCL/SDA rise time | – | See (2). | ns |
| I4 | tDH | Data hold time | NA | – | |
| I5 | tSFT | SCL/SDA fall time | – | 3 | ns |
| I6 | tHT | Clock high time | See (1). | – | System clock |
| I7 | tDS | Data setup time | tLP/2 | System clock | |
| I8 | tSCSR | Start condition setup time | 36 | – | System clock |
| I9 | tSCS | Stop condition setup time | 24 | – | System clock |
4.11.4.5 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
The Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) port is an IEEE standard that defines a test access port (TAP) and boundary scan architecture for digital integrated circuits and provides a standardized serial interface to control the associated test logic. For detailed information on the operation of the JTAG port and TAP controller, see the IEEE Standard 1149.1,Test Access Port and Boundary- Scan Architecture.
Figure 4-19 shows the JTAG timing diagram.
 Figure 4-19 JTAG Timing
Figure 4-19 JTAG Timing
Table 4-18 lists the JTAG timing parameters.
Table 4-18 JTAG Timing Parameters
4.11.4.6 ADC
Table 4-19 lists the ADC electrical specifications.
Table 4-19 ADC Electrical Specifications
| Parameter | Description | Condition and Assumptions | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nbits | Number of bits | 12 | Bits | |||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | Worst-case deviation from histogram method over full scale (not including first and last three LSB levels) | –2.5 | 2.5 | LSB | |
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | Worst-case deviation of any step from ideal | –1 | 4 | LSB | |
| Input range | 0 | 1.4 | V | |||
| Driving source impedance | 100 | Ω | ||||
| FCLK | Clock rate | Successive approximation input clock rate | 10 | MHz | ||
| Input capacitance | 3.2 | pF | ||||
| Number of channels | 4 | |||||
| Fsample | Sampling rate of each ADC | 62.5 | KSPS | |||
| F_input_max | Maximum input signal frequency | 31 | kHz | |||
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise and distortion | Input frequency dc to 300 Hz and 1.4 Vpp sine wave input | 55 | 60 | dB | |
| I_active | Active supply current | Average for analog-to-digital during conversion without reference current | 1.5 | mA | ||
| I_PD | Power-down supply current for core supply | Total for analog-to-digital when not active (this must be the SoC level test) | 1 | µA | ||
| Absolute offset error | FCLK = 10 MHz | ±2 | mV | |||
| Gain error | ±2 | % |
Figure 4-20 shows the ADC clock timing diagram.
 Figure 4-20 ADC Clock Timing
Figure 4-20 ADC Clock Timing
4.11.4.7 Camera Parallel Port
The fast camera parallel port interfaces with a variety of external image sensors, stores the image data in a FIFO, and generates DMA requests. The camera parallel port supports 8 bits.
Figure 4-21 shows the timing diagram for the camera parallel port.
 Figure 4-21 Camera Parallel Port Timing Diagram
Figure 4-21 Camera Parallel Port Timing Diagram
Table 4-20 lists the timing parameters for the camera parallel port.
Table 4-20 Camera Parallel Port Timing Parameters
| Parameter Number | Parameter | Parameter Name | Min | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pCLK | Clock frequency | 2 | MHz | ||
| I2 | Tclk | Clock period | 1/pCLK | ns | |
| I3 | tLP | Clock low period | Tclk/2 | ns | |
| I4 | tHT | Clock high period | Tclk/2 | ns | |
| I7 | D | Duty cycle | 45 to 55 | % | |
| I8 | tIS | RX data setup time | 2 | ns | |
| I9 | tIH | RX data hold time | 2 | ns |
4.11.4.8 UART
The CC3200 device includes two UARTs with the following features:
- Programmable baud-rate generator allowing speeds up to 3 Mbps
- Separate 16 x 8 TX and RX FIFOs to reduce CPU interrupt service loading
- Programmable FIFO length, including 1-byte deep operation providing conventional double-buffered interface
- FIFO trigger levels of 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8
- Standard asynchronous communication bits for start, stop, and parity
- Line-break generation and detection
- Fully programmable serial interface characteristics
- 5, 6, 7, or 8 data bits
- Even, odd, stick, or no-parity bit generation and detection
- 1 or 2 stop-bit generation
- RTS and CTS hardware flow support
- Standard FIFO-level and End-of-Transmission interrupts
- Efficient transfers using μDMA
- Separate channels for transmit and receive
- Receive single request asserted when data is in the FIFO; burst request asserted at programmed FIFO level
- Transmit single request asserted when there is space in the FIFO; burst request asserted at programmed FIFO level
- System clock is used to generate the baud clock.