JAJSH82A April 2019 – September 2019 DLP3034-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.10 Physical Characteristics of the Micromirror Array
- 6.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.12 Window Characteristics
- 6.13 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
6.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
Table 1. Optical Parameters(3)
| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Micromirror Tilt Angle, landed (on-state or off-state) (see (1) and Figure 9) | 12 | ° | |||
| β | Micromirror Tilt Angle Variation, device to device (see (1) and Figure 9) | –1 | 1 | ° | ||
| DMD Efficiency, 400 nm – 680 nm (see (2)) | 66% | |||||
| Number of non-operational micromirrors(4) | Adjacent micromirrors | 0 | micromirrors | |||
| Non-adjacent micromirrors | 10 | |||||
(1) Mirror Tilt: Limits on variability of mirror tilt are critical in the design of the accompanying optical system. Variations in tilt angle within a device may result in apparent non-uniformities, such as line pairing and image mottling, across the projected image especially at higher system F/#. Variations in the average tilt angle between devices may result in colorimetry, brightness, and system contrast variations.
(2) DMD efficiency is measured photopically under the following conditions: 24° illumination angle, F/2.4 illumination and collection apertures, uniform source spectrum (halogen), uniform pupil illumination, the optical system is telecentric at the DMD, and the efficiency numbers are measured with 100% electronic mirror duty cycle and do not include system optical efficiency or overfill loss. Note that this number is measured under conditions described above and deviations from these specified conditions could result in a different efficiency value in a different optical sytem. The factors that can incluence the DMD efficiency related to system application include: light source spectral distribution and diffraction efficiency at those wavelengths (especially with discrete light sources such as LEDs or lasers), and illumination and collection apertures (F/#) and diffraction efficiency. The interaction of these system factors as well as the DMD efficiency factors that are not system dependent are described in detail in the DMD Optical Efficiency Application Note, which can be accessed by contacting TI Applications Engineering.
(3) Optical parameters are characterized at 25°C.
(4) A non-operational micromirror is defined as a micromirror that is unable to transition between the on-state and off-state positions.
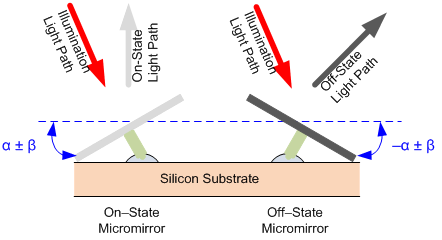 Figure 9. Micromirror Tilt Angle
Figure 9. Micromirror Tilt Angle