JAJSC41E September 2015 – February 2017 DRV3205-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PHP|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PHP|48
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| POS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | VS, VSH | DC voltage | –0.3 | 60 | V | |
| 2.1a | VS | DC voltage | Negative voltages with minimum serial resistor 5 Ω, TA = 25°C | –5 | V | |
| 2.1b | VSH | DC voltage | Negative voltages with minimum serial resistor 10 Ω, TA = 25°C | –5 | V | |
| 2.1c | VS | DC voltage | Negative voltages with minimum serial resistor 5 Ω, TA = 105°C | –2.5 | V | |
| 2.1d | VSH | DC voltage | Negative voltages with minimum serial resistor 10 Ω, TA = 105°C | –2.5 | V | |
| 2.2A | GHSx | Gate high-side voltage | –9 | 70 | V | |
| 2.2B | SHSx | Source high-side voltage | –9 | 70 | V | |
| 2.3 | GHSx-SHSx | Gate-source high-side voltage difference | Externally driven, internal limited, see position 5.4 in Electrical Characteristics | –0.3 | 15 | V |
| 2.4 | GLSx | Gate low-side voltage | –9 | 20 | V | |
| 2.5 | SLSx | Source low-side voltage | –9 | 7 | V | |
| 2.6 | GLSx-SLSx | Gate-source low-side voltage difference | Externally driven, internal limited, see position 5.5 in Electrical Characteristics | –0.3 | 15 | V |
| 2.7 | BOOST, SW | Boost converter | –0.3 | 70 | V | |
| 2.8 | INx, IPx | Current sense input voltage | –9 | 7 | V | |
| 2.8A | INx, IPx | Current sense input current | Clamping current | –5 | 5 | mA |
| 2.8C | Ox | Current sense output voltage | –0.3 | ADREF +0.3 | V | |
| 2.8D | Ox | Forced input current | –10 | 10 | mA | |
| 2.9 | VDDIO | Analog input voltage | –0.3 | 60 | V | |
| 2.9a | ADREF | Analog input voltage | –0.3 | 60 | V | |
| 2.10 | ILSx,IHSx, EN, DRVOFF, SCLK, NCS, SDI | Digital input voltage | –0.3 | 60 | V | |
| 2.11 | RVSET | Analog input voltage | –0.3 | 60 | V | |
| 2.13 | GNDA, GNDLS_B | Difference between GNDA and GNDLS_B | –0.3 | 0.3 | V | |
| 2.20 | Maximum slew rate of SHSx pins, SRSHS | –250 | 250 | V/µs | ||
| 2.21 | ERR, SDO, RO | Analog and digital output voltages | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| 2.21A | ERR, SDO, RO | Forced input/output current | –10 | 10 | mA | |
| 2.22 | TEST | Unused pins. Connect to GND. | –0.3 | 0.3 | V | |
| 2.24 | VCC5 | Internal supply voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| 2.24A | Short-to-ground current, IVCC5(3) | Internal current limit | 80 | mA | ||
| 2.25 | VCC3 | Internal supply voltage | –0.3 | 3.6 | V | |
| 2.26 | Short-to-ground current, IVCC3 | Limited by VCC5 | 80 | mA | ||
| 2.27 | Driver FET total gate charge (per FET), Qgmax | VS = 12 V, ƒPWM = 20 kHz, 6 FETs ON/OFF per PWM cycle | 200(4) | nC | ||
| 2.28 | VS = 24 V, ƒPWM = 20 kHz, 6 FETs ON/OFF per PWM cycle | 100(4) | nC | |||
| 2.14 | Operating virtual junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 150 | °C | ||
| 2.15 | Storage temperature, Tstg | –55 | 165 | °C | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to network ground terminal, unless specified otherwise.
(3) IVCC5 is not specifying VCC5 output current capability for external load. The allowed external load on VCC5 is specified at position 3.18 in Recommended Operating Conditions.
(4) The maximum value also depends on PCB thermal design, modulation scheme, and motor operation time.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| POS | VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.17 | V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | All pins | ±2000 | V |
| Pins 4, 6, and 14 | ±4000 | |||||
| 2.18 | Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±500 | |||
| 2.19 | Corner pins (1, 12, 13, 24, 25, 36, 37, and 48) | ±750 | ||||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates that HBM stressing shall be in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| POS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | VS | Supply voltage, normal voltage operation | Full device functionality. Operation at VS = 4.75 V only when coming from higher VS. Minimum VS for startup = 4.85 V | 4.75 | 40 | V | |
| 3.2 | VSLO | Supply voltage, logic operation | Logic functional (during battery cranking after coming from full device functionality) | 4 | 40 | V | |
| 3.3 | VDDIO | Supply voltage for digital I/Os | 2.97 | 5.5 | V | ||
| 3.4 | D | Duty cycle of bridge drivers | 0% | 100% | |||
| 3.5 | ƒPWM | PWM switching frequency | 0 | 22(1) | kHz | ||
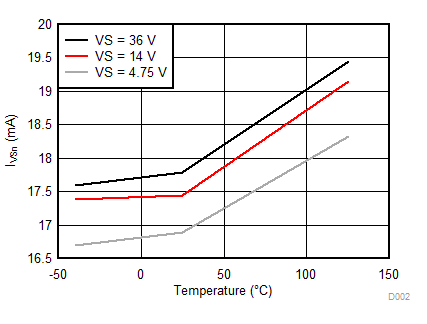
| 3.6A | IVSn | VS quiescent current normal operation (boost converter enabled, drivers not switching) | Boost converter enabled, see and for SHSx/SLSx connections. EN_GDBIAS = 1 | 22 | mA | ||
| 3.61A | IVSn | VS quiescent current normal operation (boost converter enabled, drivers not switching) | Boost converter enabled, see and for SHSx/SLSx connections. EN_GDBIAS = 0 | 22.3 | mA | ||
| 3.6B | IBOOSTn | BOOST pin quiescent current normal operation (drivers not switching) | 4.75 V < VS < 20 V, TA = 25°C to 125°C | 9 | mA | ||
| 3.62B | 4.75 V < VS < 20 V, TA = –40°C | 10 | mA | ||||
| 3.61B | IVSn | VS quiescent additional current normal operation because of RVSET thermal voltage output enabled (boost converter enabled, drivers not switching) | THERMAL_RVSET_EN = 1 | 0.6 | |||
| 3.6C | IBOOSTn | BOOST pin quiescent current normal operation (drivers not switching) | 20 < VS < 40 V, TA = 25°C to 125°C | 9.5 | mA | ||
| 3.61C | 20 < VS < 40 V, TA = –40°C | 10.5 | |||||
| 3.6D | IBOOST,sw | BOOST pin additional load current because of switching gate drivers | Excluding FET gate charge current. 20-kHz all gate drivers switching at the same time. EN_GDBIAS = 1 | 4 | mA | ||
| 3.61D | IBOOST,sw | BOOST pin additional load current because of switching gate drivers | Excluding FET gate charge current. 20-kHz all gate drivers switching at the same time. EN_GDBIAS = 0 | 5.4 | mA | ||
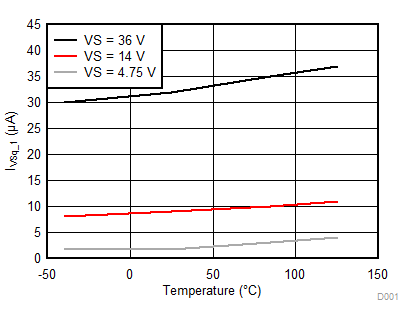
| 3.75 | IVSq_1 | VS quiescent current shutdown (sleep mode) 1 | VS = 14 V, no operation, TJ < 25°C, EN = Low, total leakage current on all supply connected pins | 20 | µA | ||
| 3.75a | IVSq_2 | VS quiescent current shutdown (sleep mode) 2 | VS = 14 V, no operation, TJ < 85°C, EN = Low, total leakage current on all supply connected pins | 30 | µA | ||
| 3.8 | TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | ||
| 3.9 | TA | Operating ambient free-air temperature | With proper thermal connection | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| 3.11 | VINx,VIPx | Current sense input voltage | VIPx – VInx, RO = 2.5 V GAIN = 12 | –0.15 | 0.15 | V | |
| 3.13 | ADREF | Clamping voltage for current sense amplifier outputs O1/2/3 | 2.97 | 5.5 | V | ||
| 3.13a | Reserved | V | |||||
| 3.13b | Reserved | V | |||||
| 3.14 | VCC3 | Internal supply voltage | VS > 4 V, external load current <100 µA, decoupling capacitor typical 0.1 µF | 3(1) | 3.3 | V | |
| 3.15 | IVCC3 | VCC3 output current | Intended for MCU ADC input | 0 | 100 | µA | |
| 3.16 | CVCC3 | VCC3 decoupling capacitance | 0.075 | 0.1 | 0.2 | µF | |
| 3.17 | VCC5 | Internal supply voltage | VS > 6 V, external load current < 100 µA, decoupling capacitor typical 1 µF | 5.15 | 5.45 | V | |
| 3.18 | IVCC5 | VCC5 output current | Intended for MCU ADC input | 0 | 100 | µA | |
| 3.19 | CVCC5 | VCC5 decoupling capacitance | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | µF | |
(1) Maximum PWM allowed also depends on maximum operating temperature, FET gate charge current, VS supply voltage, modulation scheme, and PCB thermal design.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DRV3205-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHP (HTQFP) | |||
| 48 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 25.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 10.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 5.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 0.3 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report (SPRA953).
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating temperature TJ = –40°C to 150°C and recommended operating conditions, VS = 4.75 V to 40 V(4), ƒPWM < 20 kHz (unless otherwise noted)| POS | PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.1 | CURRENT SENSE AMPLIFIER | ||||||
| 4.2.1 | Voff1a | Initial input offset of amplifiers | TJ = 25°C, ADREF = 5 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50 |
±1 | mV | ||
| 4.2.1a | TJ = 25°C, ADREF = 3.3 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50 |
±1 | mV | ||||
| 4.2.2 | Voff1b | Temperature and aging offset(5) | ADREF = 5 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50 |
±1 | mV | ||
| 4.2.2a | ADREF = 3.3 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50 |
±1 | mV | ||||
| 4.2.3 | Vcom1(1) | Input common voltage range | –3 | 3 | V | ||
| 4.2.4 | VOa | Nominal output voltage level, positive ox swing | Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current |
ADREF – 0.5 + Voxm | V | ||
| 4.2.4a | VOa | Nominal output voltage level, negative ox swing | Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current |
0.5 | V | ||
| 4.2.4b | VOa | Nominal output voltage level 2, positive ox swing | Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 10-µA load current |
ADREF – 0.06 + Voxm | V | ||
| 4.2.4c | VOa | Nominal output voltage level 2, negative ox swing | Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 10-µA load current |
0.09 | V | ||
| 4.2.5 | VOb | Output voltage level during low voltage operation, positive ox swing | Low voltage operation, 4.75 V ≤ VS < 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current | VS – 1.25; ADREF – 0.5 + Voxm |
V | ||
| 4.2.5a | VOb | Output voltage level during low voltage operation, negative ox swing | Low voltage operation, 4.75 V ≤ VS < 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current | 0.5 | V | ||
| 4.2.5b | VOb | Output voltage level during low voltage operation 2, positive ox swing | Low voltage operation, 4.75 V ≤ VS < 5.75 V; 10-µA load current | VS – 0.75; ADREF – 0.06 + Voxm |
V | ||
| 4.2.5c | VOb | Output voltage level during low voltage operation 2, negative ox swing | Low voltage operation, 4.75 V ≤ VS < 5.75 V; 10-µA load current | 0.09 | V | ||
| 4.2.6 | GBP | Gain bandwidth product GBP | 0.5 V ≤ O1/2/3 ≤ 4.5 V, capacitor load = 25 pF, specified by design. |
5 | MHz | ||
| 4.2.8 | G1 | Gain 1 | SPI configurable, Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current | 7.896 | 8 | 8.096 | V/V |
| 4.2.9 | G2 | Gain 2 | SPI configurable, Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current | 11.856 | 12 | 12.144 | V/V |
| 4.2.10 | G3 | Gain 3 | SPI configurable, Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current | 15.808 | 16 | 16.192 | V/V |
| 4.2.11 | G4 | Gain 4 | SPI configurable, Normal voltage operation, VS ≥ 5.75 V; 0.5-mA load current | 31.616 | 32 | 32.384 | V/V |
| 4.2.12 | PSRRo123 | Power supply rejection ratio at DC | VS to O1/2/3 decoupling capacitor typical 1 µF on VCC5 / 0.1-µF VCC3 at DC Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 2.5 V, ADREF = 5 V, gain = 16, dVS / dOx dVCC5 / dOx |
60 | 80 | dB | |
| 4.2.12a | CMRRo123 | Common mode rejection ratio at DC | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 2.5 V, ADREF = 5 V, gain = 1, VS = 12 V |
70 | 80 | dB | |
| 4.2.12b | CMGo123 | Common mode gain at 500 kHz | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 2.5 V, ADREF = 5 V, gain = 16 |
–29 | dB | ||
| 4.2.12c | CMGo123 | Common mode gain peak | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 2.5 V, ADREF = 5 V, gain = 16 |
–15 | dB | ||
| 4.2.13 | Iinamp | Inx, IPx input bias current | VCM (input common mode voltage) = ±3 V, RSHUNT_MODE[1:0] = 11 | 50 | 90 | µA | |
| 4.2.13 | Iinamp2 | Inx, IPx input bias current | VCM (input common mode voltage) = ±3 V, RSHUNT_MODE[1:0] = 2’b000110 | 60 | 90 | µA | |
| 4.2.14 | TsettleO123 | Ox settling time to withing ±2% of final value | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF, RO = 2.5 V, ADREF = 5 V, gain = 16, 0.5 V ≤ O1/2/3 ≤ 4.5 V |
0.8 | µs | ||
| 4.2.15 | Iinampd | Inx, IPx Input bias differential current | VCM = ±3 V IIPx-INx, IPx-INx = 0 V, RSHUNT_MODE[1:0] = 11 | –1.2 | 1.2 | µA | |
| 4.2.16 | Rinam | Inx, IPx Input resistance | VCM = ±3 V | 9 | 12 | 15 | kΩ |
| 4.2.12d | PSRR3o123 | Power supply rejection ratio at DC | VS to O1/2/3 decoupling capacitor typical 1 µF on VCC5 / 0.1-µF VCC3 at DC specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 1.65 V ADREF = 3.3 V, gain = 16, dVS / dOx dVCC5 / dOx |
70 | 80 | dB | |
| 4.2.12e | CMRR3o123 | Common mode rejection ratio at DC | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 1.65 V ADREF = 3.3 V, gain = 16 VS = 12 V |
70 | 80 | dB | |
| 4.2.12f | CMG3o123 | Common mode gain at 500 kHz | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 1.65 V ADREF = 3.3 V, gain = 16 |
–29 | dB | ||
| 4.2.12g | CMG3o123 | Common mode gain peak | Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 1.65 V ADREF = 3.3 V, gain = 16 |
–15 | dB | ||
| 4.3 | SHIFT BUFFER | ||||||
| 4.3.2 | VRO | Shift output voltage range | ADREF = 5 V | 0.1 × ADREF | 0.5 × ADREF | V | |
| 4.3.3 | VRoffset | Shift voltage offset (with respect to RO) | ADREF = 5 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50, Iload = internal load |
±1.7 | mV | ||
| 4.3.3a | RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b00100: ADREF × 5 / 50-5’b10111: ADREF × 24 / 50 |
±4 | mV | ||||
| 4.3.3b | VRoffset | Shift voltage offset (with respect to ADREF (3.3 V) × 25 / 50 (RO_CFG [4:0] = 5'b11000)) | ADREF = 3.3 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50, Iload = internal load | ±1.7 | mV | ||
| 4.3.4 | CRO | RO output load capacitance range | 0 | 150 | pF | ||
| 4.3.5 | IRO | Shift output current capability | ADREF = 5 V, RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b11000: ADREF × 25 / 50 |
–5 | 5 | mA | |
| 4.3.6 | RO_CFG [4:0] = 5’b00100: ADREF × 5 / 50-5’b10111: ADREF × 24 / 50 |
–1 | 1 | mA | |||
| 4.3.7 | Tdgadref | ADREF UV/ OV detection deglitch time | 3 | 5 | 7 | µs | |
| 4.3.8 | PSRRRO | Power supply rejection ratio at DC | Decoupling capacitor typical 1 µF on VCC5 / 0.1 µF VCC3 at DC. Specified by design, capacitor load = 25 pF RO = 2.5 V ADREF = 5 V, Gain = 16, dVS / dRO dVCC5 / dRO |
70 | 80 | dB | |
| 4.4.9 | tdgadref | ADREF UV/OV detection deglitch time | 3 | 5 | 7 | µs | |
| 4.4 | ADREF / VDDIO | ||||||
| 4.4.1 | Voxm | Tolerance of ADREF voltage clamp | Relative to ADREF 5.75 V ≤ VS | –0.1 | 0.03 | 0.25 | V |
| 4.4.2 | Voxos | Overshoot of O1/2/3 over ADREF | Ox-ADREF; for <1 µs; specified by design | 1.2 | V | ||
| 4.4.3 | IADREF | Bias current for voltage clamping circuit | ADREF = 3.3 V, pin to ground | 300 | µA | ||
| 4.4.4 | Vovadref | Overvoltage threshold | ADREF: 3.3-V setting by RVSET resistor | 3.696 | 3.795 | 3.894 | V |
| 4.4.4a | ADREF: 5-V setting by RVSET resistor | 5.6 | 5.75 | 5.9 | V | ||
| 4.4.5 | Vuvadref | Undervoltage threshold | ADREF: 3.3-V setting by RVSET resistor | 2.706 | 2.805 | 2.904 | V |
| 4.4.5a | ADREF: 5-V setting by RVSET resistor | 4.1 | 4.25 | 4.4 | V | ||
| 4.4.7 | Vovvddio | Overvoltage threshold | VDDIO: 3.3-V setting by RVSET resistor | 3.696 | 3.795 | 3.894 | V |
| 4.4.7a | VDDIO: 5-V setting by RVSET resistor | 5.6 | 5.75 | 5.9 | V | ||
| 4.4.8 | Vuvvddio | Undervoltage threshold | VDDIO: 3.3-V setting by RVSET resistor | 2.706 | 2.805 | 2.904 | V |
| 4.4.8a | VDDIO: 5-V setting by RVSET resistor | 4.1 | 4.25 | 4.4 | V | ||
| 4.4.10 | Rvset33 | VDDIO = 3.3 V / ADREF = 3.3-V mode | STAT6 bit[3:0] = 4’b0001 | 135 | 150 | 165 | kΩ |
| 4.4.11 | Rvset53 | VDDIO = 5 V / ADREF = 3.3-V mode | STAT6 bit[3:0] = 4’b0100 | 46 | 51 | 56.5 | kΩ |
| 4.4.12 | Rvset35 | VDDIO = 3.3 V / ADREF = 5-V mode | STAT6 bit[3:0] = 4’b1000 | 13.5 | 15 | 16.5 | kΩ |
| 4.4.13 | Rvset55 | VDDIO = 5 V / ADREF = 5-V mode | STAT6 bit[3:0] = 4’b0010 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 5.65 | kΩ |
| 4.4.30 | Rvsetopen | RVSET resistor error detection | 650 | kΩ | |||
| 4.4.31 | Rvsetshort | RVSET resistor error detection | 1.4 | kΩ | |||
| 4.4.32 | Vrvsettjn40 | RVSET output voltage | –40°C TJ, THERMAL_RVSET_EN = 1 | 1.67 | 1.745 | 1.82 | V |
| 4.4.33 | Vrvsettj25 | 25°C TJ, THERMAL_RVSET_EN = 1 | 1.445 | 1.535 | 1.625 | ||
| 4.4.34 | Vrvsettj125 | 125°C TJ, THERMAL_RVSET_EN = 1 | 1.085 | 1.195 | 1.305 | ||
| VCC3 / VCC5 REGULATORS | |||||||
| 4.4.14 | VCC3 | VCC3 regulator output voltage | VS > 4 V | 3 | 3.15 | 3.3 | V |
| 4.4.15 | VCC3UV | VCC3 regulator undervoltage threshold | VS > 4 V | 2.7 | 2.85 | 3 | V |
| 4.4.16 | VCC3OV(1) | VCC3 regulator overvoltage threshold | VS > 4 V | 3.3 | 3.45 | 3.6 | V |
| 4.4.17 | VCC5_1 | VCC5 regulator output voltage 1 | VS > 6 V | 5.15 | 5.3 | 5.45 | V |
| 4.4.18 | VCC5_2 | VCC5 regulator output voltage 2 | 6 V > VS > 4.75 V | 4.6 | 5.45 | V | |
| 4.4.19 | VCC5UV | VCC5 regulator undervoltage threshold | VS > 4.75 V | 4.3 | 4.6 | V | |
| 4.4.20 | VCC5OV | VCC5 regulator overvoltage threshold | VS > 4.75 V | 5.45 | 5.6 | 5.75 | V |
| 5. | GATE DRIVER | ||||||
| 5.1 | VGS,low | Gate-source voltage low, high-side/low-side driver | Active pulldown, Iload = –2 mA | 0 | 0.2 | V | |
| 5.2 | RGSp | Passive gate-source resistance | Vgs ≤ 200 mV | 110 | 220 | 330 | kΩ |
| 5.3 | RGSsa | Semi-active gate-source resistance | In sleep mode, VGS > 2 V | 2 | 4 | kΩ | |
| 5.3b | IGSL01 | Low-side driver pullup/pulldown current | Gate driven low by gate driver, CURR1, 3 = 01, SPI configurable |
TYP × 0.65 | 0.65 | TYP × 1.35 | A |
| 5.3c | IGSL00 | Gate driven low by gate driver(1), CURR1, 3 = 00, SPI configurable |
TYP × 0.1 | 0.15 | TYP × 1.9 | A | |
| 5.3d | IGSL10 | Gate driven low by gate driver, CURR1, 3 = 11, SPI configurable |
TYP × 0.65 | 1.1 | TYP × 1.35 | A | |
| 5.3f | IGSH01 | High-side driver pullup/pulldown current | Gate driven low by gate driver, CURR0, 2 = 01, SPI configurable |
TYP × 0.65 | 0.65 | TYP × 1.35 | A |
| 5.3g | IGSH00 | Gate driven low by gate driver(1), CURR0, 2 = 00, SPI configurable |
TYP × 0.1 | 0.15 | TYP × 1.9 | A | |
| 5.3h | IGSH11 | Gate driven low by gate driver, CURR0, 2 = 11, SPI configurable |
TYP × 0.65 | 1.1 | TYP × 1.35 | A | |
| 5.3i | IGSHsd | High-side/low-side driver shutdown current | 2 | 30 | 70 | mA | |
| 5.4 | VGS,HS,high | High-side output voltage | Iload = –2 mA; 4.75 V < VS < 40 V | 9 | 13.4 | V | |
| 5.5 | VGS,LS,high | Low-side output voltage | Iload = –2 mA | 9 | 13.4 | V | |
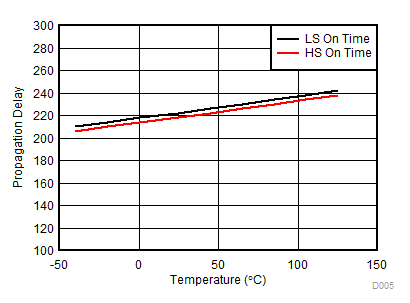
| 5.27 | tDon | Propagation on delay time(5) | After ILx/IHx rising edge, Cload = 10 nF, CURR1, 3 = 10, VGS = 1 V | 100 | 200 | 350 | ns |
| 5.31 | Adt | Accuracy of dead time | If not disabled in CFG1 | –15% | 15% | ||
| 5.32 | IHSxlk_1 | Source leak current, total leakage current of source pins | EN = L, SHSx = 1.5 V, TJ < 125°C | –5 | 5 | µA | |
| 5.32a | IHSxlk_2 | EN = L, SHSx = 1.5 V, 125°C < TJ < 150°C | –40 | 40 | µA | ||
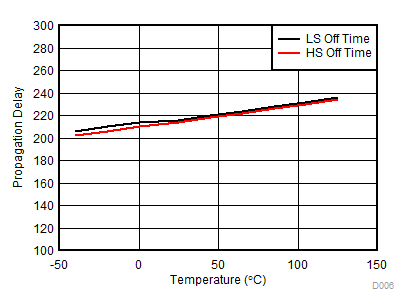
| 5.29 | tDoff | Propagation off delay time(5) | ILx/IHx falling edge to VGS,LS,high(VGS,HS,high) – 1 V Ciss = 10 nF, CURR1,3 = 10, | 100 | 200 | 350 | ns |
| 5.30 | tDoffdiff | Propagation off delay time difference(5) | LSx to LSy and HSx to HSy Cload = 10 nF, CURR1,3 = 10, VGS,LS,high(VGS,HS,high) – 1 V | 50 | ns | ||
| 5.30a | tDon_Doff_diff | Difference between propagation on delay time and propagation off delay time(5) | For each gate driver in each channel: Cload = 10 nF, CURR1, 3 = 10, VGS = 1 V (rising), VGS,LS,high(VGS,HS,high) – 1 V (falling) |
150 | ns | ||
| 5.30c | tENoff | Propagation off (EN) deglitching time(5) | After falling edge on EN | 2.5 | 6 | 12 | µs |
| 5.30d | tSD | Time until gate drivers initiate shutdown(5) | After falling edge on EN | 12 | 24 | µs | |
| 5.30e | tSDDRV | Time until gate drivers initiate shutdown(5) | After rising edge on DRVOFF | 10 | µs | ||
| 6. | BOOST CONVERTER | ||||||
| 6.1 | VBOOST | Boost output voltage excluding switching ripple and response delay. | BOOST-VS voltage | 14 | 15 | 16.5 | V |
| 6.1b | VBOOSTOV | Boost output voltage overvoltage with respect GND | 64 | 67.5 | 70 | V | |
| 6.2 | IBOOST | Output current capability | External load current including external MOSFET gate charge current BOOST – VS > VBOOSTUV |
40 | mA | ||
| 6.3 | ƒBOOST | Switching frequency | BOOST – VS > VBOOSTUV; ensured by characterization(3) | 1.8 | 2.5 | 3 | MHz |
| 6.31 | BOOST – VS > VBOOSTUV; VS < 6 V; ensured by characterization(3) | 1.1 | 3 | ||||
| 6.4 | VBOOSTUV | Undervoltage shutdown level | BOOST-VS voltage | 7 | 8 | V | |
| 6.4a | VBOOSTUV2 | Undervoltage condition that device may enter RESET state | BOOST-GND voltage | 10 | V | ||
| 6.5 | tBCSD | Filter time for undervoltage detection | 5 | 6 | µs | ||
| 6.7 | VGNDLS_B,off | Voltage at GNDLS_B pin at which boost FET switches off because of current limit | 110 | 150 | 200 | mV | |
| 6.7a | tSW,off | Delay of the GNDLS_B current limit comparator | Specified by design | 100 | ns | ||
| 6.8 | ISW,fail | Internal second-level current limit | GNDLS_B = 0 V | 840 | 1600 | mA | |
| 6.9 | Rdson_BSTfet | Rdson resistance boost FET | VS ≥ 6 ISW = VGNDLS_B,off / 0.33 Ω |
0.25 | 1.5 | Ω | |
| 6.9a | VS < 6 ISW= VGNDLS_B,off / 0.33 Ω |
2 | Ω | ||||
| 7. | DIGITAL INPUTS | ||||||
| 7.1 | INL | Input low threshold | All digital inputs NCS, DRVOFF, ILSx, IHSx, SDI | VDDIO × 0.3 | V | ||
| 7.1a | ENH | EN input high threshold | VS > 4 V | 2.7 | V | ||
| 7.1b | ENL | EN input low threshold | VS > 4 V | 0.7 | V | ||
| 7.2 | INH | Input high threshold | All digital inputs NCS, DRVOFF, ILSx, IHSx, SDI | VDDIO × 0.7 | V | ||
| 7.3 | Inhys | Input hysteresis | All digital inputs EN, NCS, DRVOFF, ILSx, IHSx, SDI, VDDIO = 5 V | 0.3 | 0.4 | V | |
| 7.3a | Inhys | Input hysteresis | All digital inputs EN, NCS, DRVOFF, ILSx, IHSx, SDI, VDDIO = 3.3 V | 0.2 | 0.3 | V | |
| 7.4 | Rpd,EN | Input pulldown resistor at EN pin | EN | 140 | 200 | 360 | kΩ |
| 7.4a | tdeg,ENon | Power-up time after EN pin high from sleep mode to active mode | ERR = L → H | 5 | ms | ||
| 7.5 | Rpullup | Input pullup resistance | NCS, DRVOFF | 200 | 280 | 400 | kΩ |
| 7.6 | Rpulldown | Input pulldown resistance | ILSx, IHSx, SDI , SCLK Input voltage = 0.1 V | 100 | 140 | 200 | kΩ |
| 7.6a | Rpulldown | Input pulldown current | ILSx, IHSx, SDI, SCLK Input voltage = VDDIO | 4 | 50 | µA | |
| 8. | DIGITAL OUTPUTS | ||||||
| 8.1 | OH1 | Output high voltage 1 | All digital outputs: SDO, I = ±2 mA; VDDIO in functional range(6) | VDDIO × 0.9 | V | ||
| 8.2 | OL1 | Output low voltage 1 | All digital outputs: SDO, I = ±2 mA; VDDIO in functional range | VDDIO × 0.1 | V | ||
| 8.3 | OH2 | Output high voltage 2 | ERR I = –0.2 mA; VDDIO in functional range | VDDIO × 0.9 | V | ||
| 8.4 | OL2 | Output low voltage 2 | ERR I = +0.2 mA; VDDIO in functional range | VDDIO × 0.1 | V | ||
| 9. | VDS / VGS / RSHUNT MONITORING | ||||||
| 9.1 | VSCTH | VDS short-circuit threshold range | If not disabled in CFG1 | 0.1 | 2 | V | |
| 9.2 | Avds | Accuracy of VDS monitoring | 0.1-V to 0.5-V threshold setting | –50 | 50 | mV | |
| 0.6-V to 2-V threshold setting | –10% | 10% | |||||
| 9.3 | tVDS | Detection filter time | Only rising edge of VDS comparators are filtered | 5 | µs | ||
| 9.4 | Vgserr+_1 | VGS error detection 1 | STAT7, IHSx (ILSx) = H | 7 | 8.5 | V | |
| 9.5 | Vgserr– | VGS error detection | STAT7, IHSx (ILSx) = L | 2 | V | ||
| 9.6 | tVGS | Detection filter time | CFG6[5:4] | 1.0 | µs | ||
| 9.6a | tVGSm | Detection mask time | CFG6[2:0] | 2.5 | µs | ||
| 9.7 | VSHUNT | RSHUNT shutdown threshold range | SPI configurable | 75 | 540 | mV | |
| 9.8 | AVSHUNT | Accuracy of RSHUNT shutdown | 75-mV to 165-mV setting | –18 | 18 | mV | |
| 180-mV to 540-mV setting | –10% | 10% | |||||
| 9.9 | tVSHUNT | Detection filter time | 5 | µs | |||
| 10. | THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
| 10.1 | Tmsd0 | Thermal recovery | Specified by characterization | 130 | 153 | 178 | °C |
| 10.2 | Tmsd1 | Thermal warning | Specified by characterization | 140 | 165 | 190 | °C |
| 10.3 | Tmsd2 | Thermal global reset | Specified by characterization | 170 | 195 | 220 | °C |
| 10.4 | Thmsd | Thermal shutdown×2 hysteresis | Specified by characterization | 40 | °C | ||
| 10.5 | tTSD1 | Thermal warning filter time | Specified by characterization | 40 | 45 | 50 | µs |
| 10.6 | tTSD2 | Thermal shutdown×2 filter time | Specified by characterization | 2.5 | 6 | 12 | µs |
| 12. | VS MONITORING | ||||||
| 12.1 | VVS,OVoff0 | Overvoltage shutdown level range(2) | Programmable CFG5 mode1, 12-V/24-V mode | 29 | 38 | V | |
| 12.1a | VVS,OVoff1 | Overvoltage shutdown level(2) | 29-V threshold setting | 27.5 | 29 | 30.5 | V |
| 12.1b | VVS, OVon1 | Recovery level form overvoltage shutdown(2) | 29-V threshold setting | 26.5 | 28 | 29.5 | V |
| 12.1c | VVS,OVoff2 | Overvoltage shutdown level(2) | 33-V threshold setting | 32 | 33.5 | 35 | V |
| 12.1d | VVS, OVon2 | Recovery level form overvoltage shutdown(2) | 33-V threshold setting | 31 | 32.5 | 34 | V |
| 12.1e | VVS,OVoff3 | Overvoltage shutdown level(2) | 38-V threshold setting | 36.5 | 38 | 39.5 | V |
| 12.1f | VVS, OVon3 | Recovery level form overvoltage shutdown(2) | 38-V threshold setting | 35.5 | 37 | 38.5 | V |
| 12.2 | VVS,UVoff | Undervoltage shutdown level(2) | VS is falling from higher voltage than 4.75 V | 4.5 | 4.75 | V | |
| 12.2a | VVS,UVon | Recovery level form undervoltage shutdown(2) | Minimum VS for device startup | 4.6 | 4.85 | V | |
| 12.3 | tVS,SHD | Filter time for overvoltage/undervoltage shutdown | 5 | 6 | µs | ||
(1) ADREF / VDDIO overvoltage and undervoltage is set by RVSET.
(2) Shutdown signifies predriver shutdown, not VCC3/VCC5 regulator shutdown.
(3) During startup when BOOST-VS < VBOOSTUV , ƒBOOST is typically 1.25 MHz.
(4) Product life time depends on VS voltage, PCB thermal design, modulation scheme, and motor operation time. The product is designed for 12-V and 24-V battery system.
(5) Ensured by characterization.
(6) All digital outputs have a push-pull output stage between VDDIO and ground.
6.6 Serial Peripheral Interface Timing Requirements
| POS 13 | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.1 | ƒSPI | SPI clock (SCLK) frequency | 4(1) | MHz | ||
| 13.2 | tSPI | SPI clock period(2) | 250 | ns | ||
| 13.3 | thigh | High time: SCLK logic high duration(2) | 90 | ns | ||
| 13.4 | tlow | Low time: SCLK logic low duration(2) | 90 | ns | ||
| 13.5 | tsucs | Setup time NCS: time between falling edge of NCS and rising edge of SCLK(2) | tSPI / 2 | ns | ||
| 13.6 | td1 | Delay time: time delay from falling edge of NCS to data valid at SDO(2) | 60 | ns | ||
| 13.7 | tsusi | Setup time at SDI: setup time of SDI before the rising edge of SCLK(2) | 30 | ns | ||
| 13.8 | td2 | Delay time: time delay from falling edge of SCLK to data valid at SDO(2) | 0 | 60 | ns | |
| 13.9 | thcs | Hold time: time between the falling edge of SCLK and rising edge of NCS(2) | 45 | ns | ||
| 13.10 | thlcs | SPI transfer inactive time (time between two transfers)(2) | 250 | ns | ||
| 13.11 | ttri | Tri-state delay time: time between rising edge of NCS and SDO in tri-state(2) | 30 | ns | ||
(1) The maximum SPI clock tolerance is ±10%.
(2) Ensured by characterization.
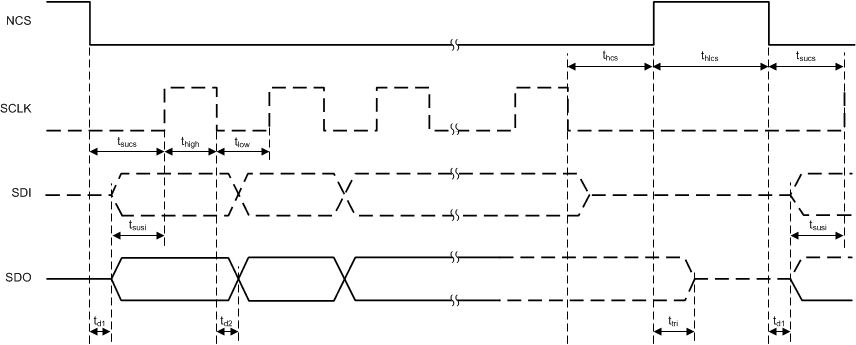 Figure 1. SPI Timing Parameters
Figure 1. SPI Timing Parameters