JAJSMZ5B September 2021 – February 2022 DRV8311
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Stage
- 8.3.2 Control Modes
- 8.3.3 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.4 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.5 Charge Pump
- 8.3.6 Slew Rate Control
- 8.3.7 Cross Conduction (Dead Time)
- 8.3.8 Propagation Delay
- 8.3.9 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.10 Current Sense Amplifiers
- 8.3.11 Protections
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 SPI Communication
- 9 DRV8311 Registers
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.6 Slew Rate Control
An adjustable gate-drive current control to the MOSFETs allows for easy slew rate control. The MOSFET VDS slew rates are a critical factor for optimizing radiated emissions, energy and duration of diode recovery spikes and switching voltage transients related to parasitic. These slew rates are predominantly determined by the rate of gate charge to internal MOSFETs as shown in Figure 8-18.
The slew rate of each half-bridge can be adjusted by SLEW pin in hardware device variant or by using SLEW register settings in SPI device variant. The slew rate is calculated by the rise-time and fall-time of the voltage on OUTx pin as shown in Figure 8-19.
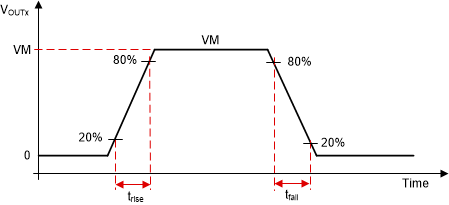 Figure 8-19 Slew Rate Timings
Figure 8-19 Slew Rate Timings