SLVSBA3C June 2012 – December 2015 DRV8806
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|16
発注情報
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The DRV8806 can be used to drive one unipolar stepper motor.
8.2 Typical Application
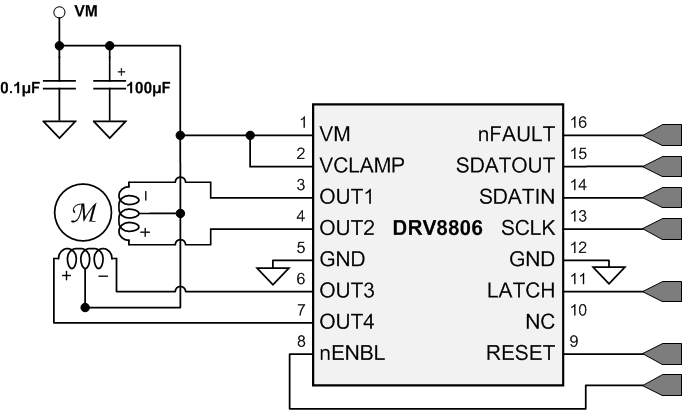 Figure 10. DRV8806 Typical Application
Figure 10. DRV8806 Typical Application
8.2.1 Design Requirements
For this design example, use the parameters listed in Table 1 as the input parameters.
Table 1. Design Parameters
| DESIGN PARAMETER | EXAMPLE VALUE |
|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VM | 24 V |
| Motor winding resistance, RL | 7.4 Ω/phase |
| Motor full step angle, θstep | 1.8°/step |
| Motor rated current, IRATED | 0.75 A |
| SCLK frequency, fSCLK | 1 MHz |
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
8.2.2.1 Motor Voltage
The motor voltage to use will depend on the ratings of the motor selected and the desired torque. A higher voltage shortens the current rise time in the coils of the stepper motor allowing the motor to produce a greater average torque. Using a higher voltage also allows the motor to operate at a faster speed than a lower voltage.
8.2.2.2 Drive Current
The current path is starts from the supply VM, moves through the inductive winding load, and low-side sinking NMOS power FET. Power dissipation losses in one sink NMOS power FET are shown in Equation 1.
The DRV8806 has been measured to be capable of 2-A Single Channel or 1-A Four Channels in a HTSSOP package at 25°C on standard FR-4 PCBs. The maximum RMS current varies based on PCB design and the ambient temperature.
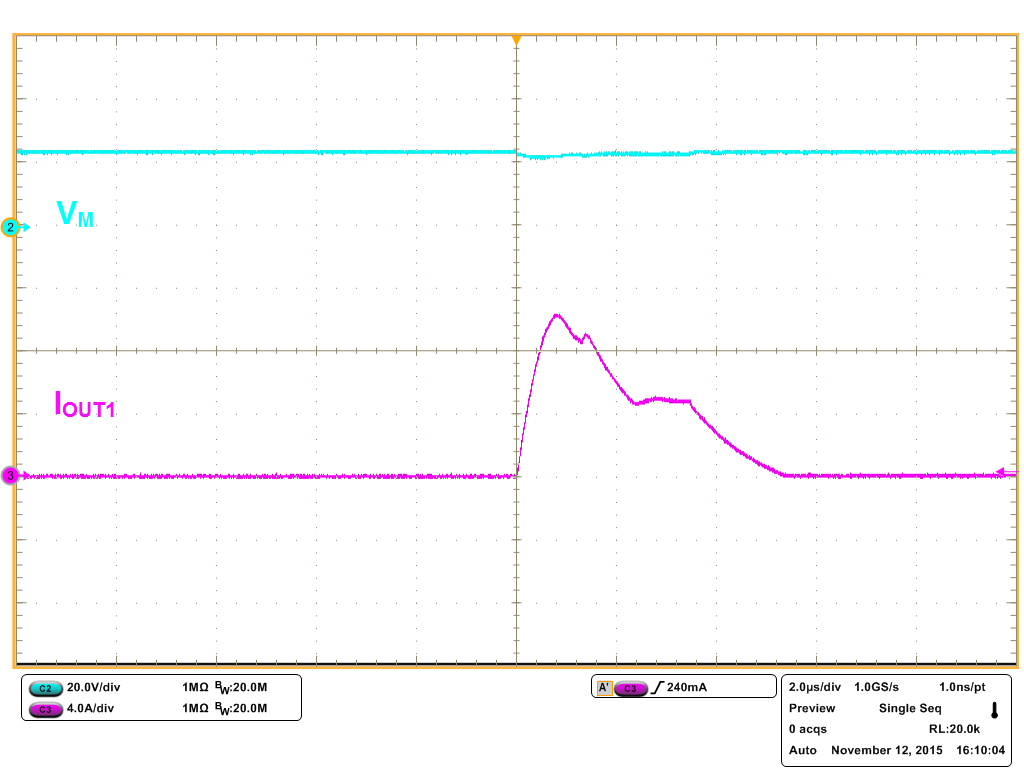
8.2.3 Application Curves
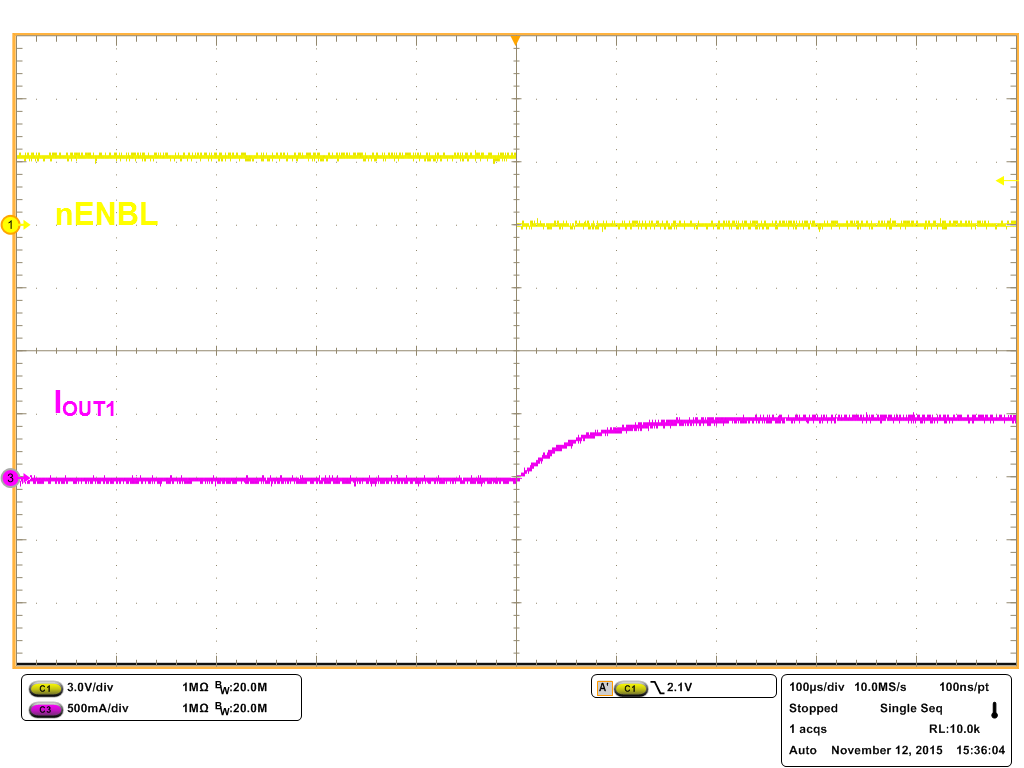
| 16-Ω, 1-mH, RL Load | ||
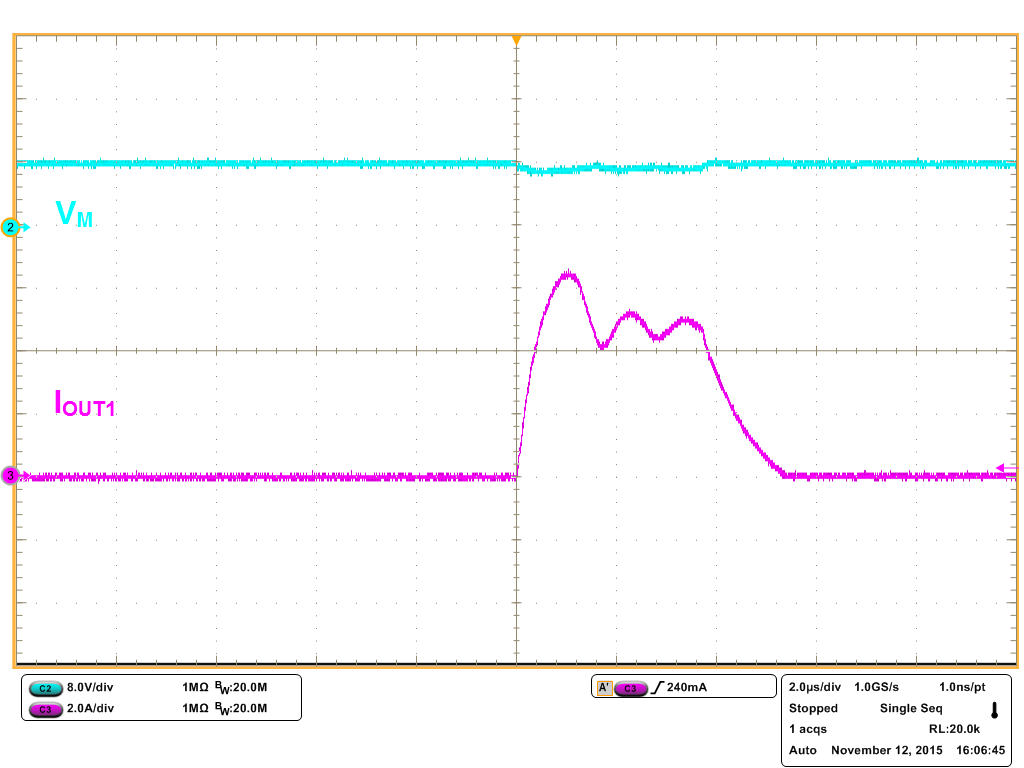
| Output shorted to VM | ||
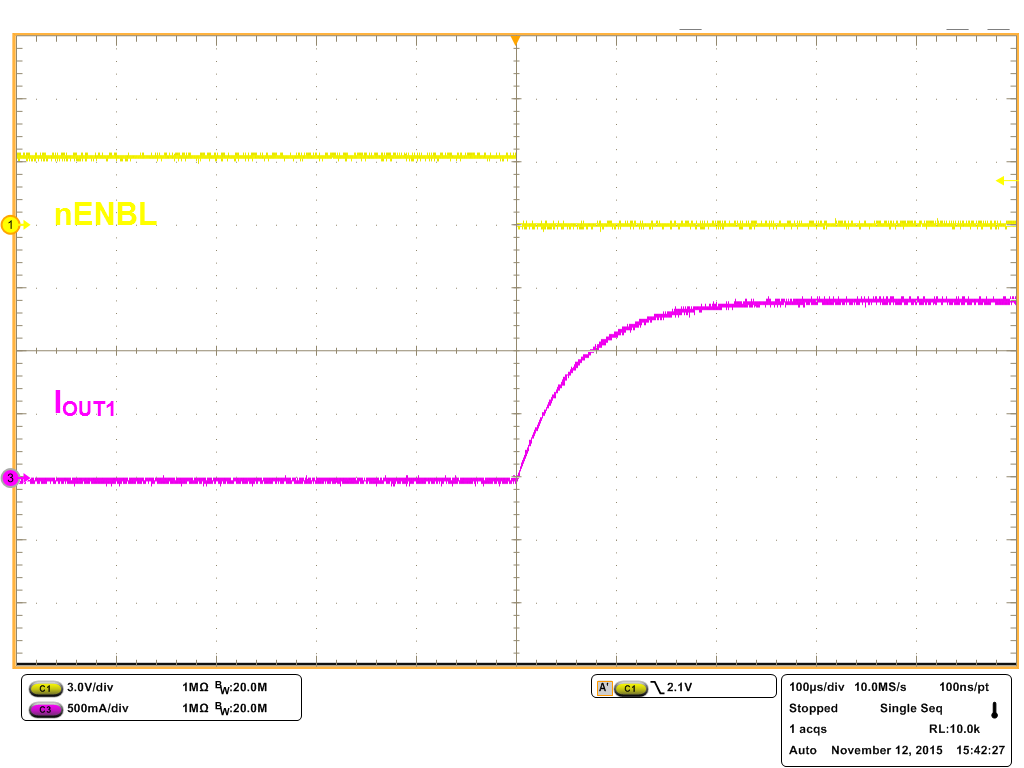
| 16-Ω, 1-mH RL Load | ||
| Output shorted to VM | ||