JAJSMU0 February 2023 DS90UB635-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 CSI-2 Receiver
- 7.3.2 FPD-Link III Forward Channel Transmitter
- 7.3.3 FPD-Link III Back Channel Receiver
- 7.3.4 Serializer Status and Monitoring
- 7.3.5 FrameSync Operation
- 7.3.6 GPIO Support
- 7.3.7 Unique ID
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Pattern Generation
- 7.7
Register Maps
- 7.7.1 I2C Device ID Register
- 7.7.2 Reset
- 7.7.3 General Configuration
- 7.7.4 Forward Channel Mode Selection
- 7.7.5 BC_MODE_SELECT
- 7.7.6 PLL Clock Control
- 7.7.7 Clock Output Control 0
- 7.7.8 Clock Output Control 1
- 7.7.9 Back Channel Watchdog Control
- 7.7.10 I2C Control 1
- 7.7.11 I2C Control 2
- 7.7.12 SCL High Time
- 7.7.13 SCL Low Time
- 7.7.14 Local GPIO DATA
- 7.7.15 GPIO Input Control
- 7.7.16 DVP_CFG
- 7.7.17 DVP_DT
- 7.7.18 Force BIST Error
- 7.7.19 Remote BIST Control
- 7.7.20 Sensor Voltage Gain
- 7.7.21 Sensor Temp Gain
- 7.7.22 Sensor Control 0
- 7.7.23 Sensor Control 1
- 7.7.24 Voltage Sensor 0 Thresholds
- 7.7.25 Voltage Sensor 1 Thresholds
- 7.7.26 Temperature Sensor Thresholds
- 7.7.27 CSI-2 Alarm Enable
- 7.7.28 Alarm Sense Enable
- 7.7.29 Back Channel Alarm Enable
- 7.7.30 CSI-2 Polarity Select
- 7.7.31 CSI-2 LP Mode Polarity
- 7.7.32 CSI-2 High-Speed RX Enable
- 7.7.33 CSI-2 Low Power Enable
- 7.7.34 CSI-2 Termination Enable
- 7.7.35 CSI-2 Packet Header Control
- 7.7.36 Back Channel Configuration
- 7.7.37 Datapath Control 1
- 7.7.38 Remote Partner Capabilities 1
- 7.7.39 Partner Deserializer ID
- 7.7.40 Target 0 ID
- 7.7.41 Target 1 ID
- 7.7.42 Target 2 ID
- 7.7.43 Target 3 ID
- 7.7.44 Target 4 ID
- 7.7.45 Target 5 ID
- 7.7.46 Target 6 ID
- 7.7.47 Target 7 ID
- 7.7.48 Target 0 Alias
- 7.7.49 Target 1 Alias
- 7.7.50 Target 2 Alias
- 7.7.51 Target 3 Alias
- 7.7.52 Target 4 Alias
- 7.7.53 Target 5 Alias
- 7.7.54 Target 6 Alias
- 7.7.55 Target 7 Alias
- 7.7.56 Back Channel Control
- 7.7.57 Revision ID
- 7.7.58 Device Status
- 7.7.59 General Status
- 7.7.60 GPIO Pin Status
- 7.7.61 BIST Error Count
- 7.7.62 CRC Error Count 1
- 7.7.63 CRC Error Count 2
- 7.7.64 Sensor Status
- 7.7.65 Sensor V0
- 7.7.66 Sensor V1
- 7.7.67 Sensor T
- 7.7.68 CSI-2 Error Count
- 7.7.69 CSI-2 Error Status
- 7.7.70 CSI-2 Errors Data Lanes 0 and 1
- 7.7.71 CSI-2 Errors Data Lanes 2 and 3
- 7.7.72 CSI-2 Errors Clock Lane
- 7.7.73 CSI-2 Packet Header Data
- 7.7.74 Packet Header Word Count 0
- 7.7.75 Packet Header Word Count 1
- 7.7.76 CSI-2 ECC
- 7.7.77 IND_ACC_CTL
- 7.7.78 IND_ACC_ADDR
- 7.7.79 IND_ACC_DATA
- 7.7.80 FPD3_TX_ID0
- 7.7.81 FPD3_TX_ID1
- 7.7.82 FPD3_TX_ID2
- 7.7.83 FPD3_TX_ID3
- 7.7.84 FPD3_TX_ID4
- 7.7.85 FPD3_TX_ID5
- 7.7.86
Indirect Access Registers
- 7.7.86.1 PGEN_CTL
- 7.7.86.2 PGEN_CFG
- 7.7.86.3 PGEN_CSI_DI
- 7.7.86.4 PGEN_LINE_SIZE1
- 7.7.86.5 PGEN_LINE_SIZE0
- 7.7.86.6 PGEN_BAR_SIZE1
- 7.7.86.7 PGEN_BAR_SIZE0
- 7.7.86.8 PGEN_ACT_LPF1
- 7.7.86.9 PGEN_ACT_LPF0
- 7.7.86.10 PGEN_TOT_LPF1
- 7.7.86.11 PGEN_TOT_LPF0
- 7.7.86.12 PGEN_LINE_PD1
- 7.7.86.13 PGEN_LINE_PD0
- 7.7.86.14 PGEN_VBP
- 7.7.86.15 PGEN_VFP
- 7.7.86.16 PGEN_COLOR0
- 7.7.86.17 PGEN_COLOR1
- 7.7.86.18 PGEN_COLOR2
- 7.7.86.19 PGEN_COLOR3
- 7.7.86.20 PGEN_COLOR4
- 7.7.86.21 PGEN_COLOR5
- 7.7.86.22 PGEN_COLOR6
- 7.7.86.23 PGEN_COLOR7
- 7.7.86.24 PGEN_COLOR8
- 7.7.86.25 PGEN_COLOR9
- 7.7.86.26 PGEN_COLOR10
- 7.7.86.27 PGEN_COLOR11
- 7.7.86.28 PGEN_COLOR12
- 7.7.86.29 PGEN_COLOR13
- 7.7.86.30 PGEN_COLOR14
- 7.7.86.31 PGEN_COLOR15
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.5.2 I2C Interface Operation
The serial control bus consists of two signals: SCL and SDA. SCL is a Serial Bus Clock Input / Output signal and the SDA is the Serial Bus Data Input / Output signal. Both SCL and SDA signals require an external pullup resistor to VI2C, chosen to be either 1.8 V or 3.3 V.
For the standard and fast I2C modes, a pullup resistor of RPU = 4.7 kΩ is recommended, while a pullup resistor of RPU = 470 Ω is recommended for the fast plus mode. However, the pullup resistor value may be additionally adjusted for capacitive loading and data rate requirements. The signals are either pulled High or driven Low. The IDX pin configures the control interface to one of two possible device addresses. A pullup resistor (RHIGH) and a pulldown resistor (RLOW) may be used to set the appropriate voltage on the IDX input pin.
The Serial Bus protocol is controlled by START, START-Repeated, and STOP phases. A START occurs when SDA transitions Low while SCL is High. A STOP occurs when SDA transitions High while SCL is also HIGH. See Figure 7-9.
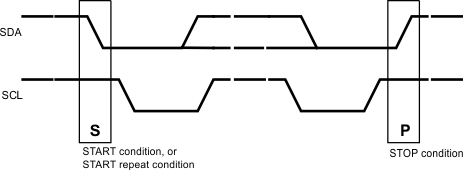 Figure 7-9 Start and Stop Conditions
Figure 7-9 Start and Stop ConditionsTo communicate with an I2C target, the host controller (controller) sends data to the target address and waits for a response. This response is referred to as an acknowledge bit (ACK). If a target on the bus is addressed correctly, the target Acknowledges (ACKs) the controller by driving the SDA bus low. If the address does not match a target address of the device, the target Not-acknowledges (NACKs) the controller by pulling the SDA High. ACKs also occur on the bus when data is being transmitted. When the controller is writing data, the target ACKs after every data byte is successfully received. When the controller is reading data, the controller ACKs after every data byte is received to let the target know that the controller wants to receive another data byte. When the controller wants to stop reading, the controller NACKs after the last data byte and creates a stop condition on the bus. All communication on the bus begins with either a start condition or a repeated start condition. All communication on the bus ends with a stop condition. A READ is shown in Figure 7-10 and a WRITE is shown in Figure 7-11.
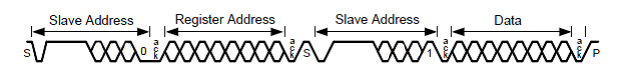 Figure 7-10 I2C Bus Read
Figure 7-10 I2C Bus Read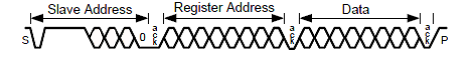 Figure 7-11 I2C Bus Write
Figure 7-11 I2C Bus WriteAny I2C controller located at the serializer must support I2C clock stretching. For more information on I2C interface requirements and throughput considerations, refer to the TI application note I2C communication over FPD-Link III with bidirectional control channel (SNLA131).