JAJS707E January 2001 – January 2018 DS92LV040A
PRODUCTION DATA.
11.1.1 Microstrip vs. Stripline Topologies
As per SLLD009, printed-circuit boards usually offer designers two transmission line options: Microstrip and stripline. Microstrips are traces on the outer layer of a PCB, as shown in Figure 12.
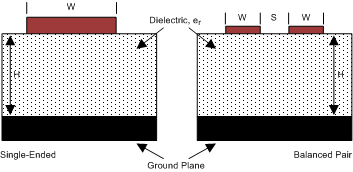 Figure 12. Microstrip Topology
Figure 12. Microstrip TopologyStriplines are traces between two ground planes. Striplines are less prone to emissions and susceptibility problems because the reference planes effectively shield the embedded traces. However, from the standpoint of high-speed transmission, juxtaposing two planes creates additional capacitance. TI recommends routing the signals on microstrip transmission lines if possible. The PCB traces allow designers to specify the necessary tolerances for ZO based on the overall noise budget and reflection allowances. Footnotes 1(1), 2(2), and 3(3) provide formulas for ZO and tPD for differential and single-ended traces. (1)(2)(3)
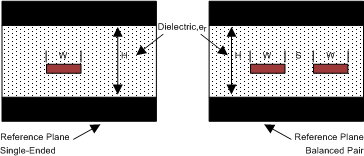 Figure 13. Stripline Topology
Figure 13. Stripline Topology