JAJSRJ2A September 2000 – January 2024 INA114
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Application and Implementation
- 7 Typical Applications
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- P|8
- DW|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6.1.5 Input Common-Mode Range
The linear common-mode range of the input op amps of the INA114 is approximately ±13.75V (or 1.25V from the power supplies). As the output voltage increases, however, the linear input range is limited by the output voltage swing of the input amplifiers, A1 and A2. The common-mode range is related to the output voltage of the complete amplifier—see typical characteristic curve Input Common-Mode Range vs Output Voltage.
A combination of common-mode and differential input signals can cause the output of A1 or A2 to saturate. Figure 6-4 shows the output voltage swing of A1 and A2 expressed in terms of a common-mode and differential input voltages. Output swing capability of these internal amplifiers is the same as the output amplifier, A3. For applications where input common-mode range must be maximized, limit the output voltage swing by connecting the INA114 in a lower gain (see performance curve Input Common-Mode Voltage Range vs Output Voltage). If necessary, add gain after the INA114 to increase the voltage swing.
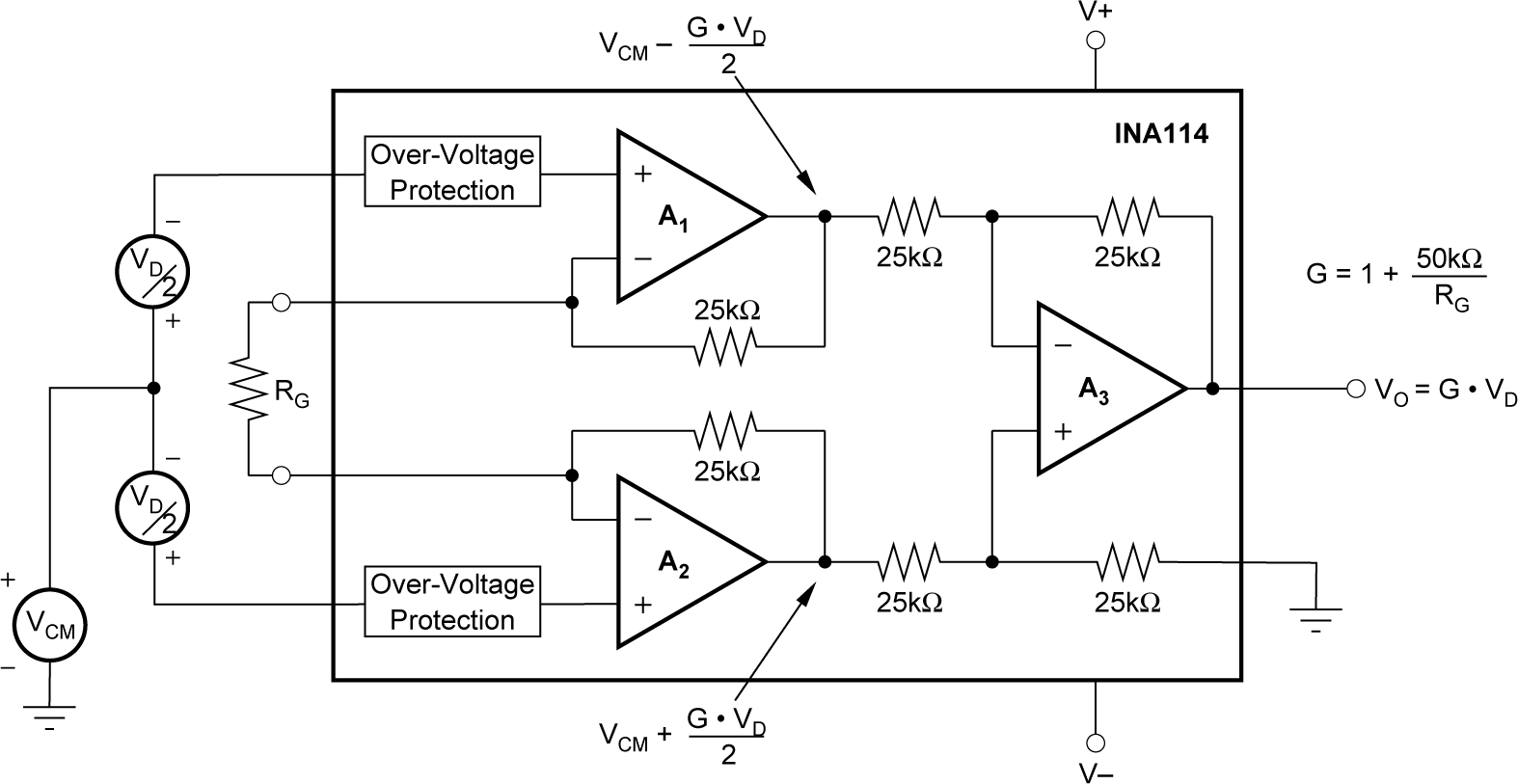 Figure 6-4 Voltage Swing of A1
and A2
Figure 6-4 Voltage Swing of A1
and A2Input overload often produces an output voltage that appears normal. For example, an input voltage of 20V on one input and 40V on the other input obviously exceeds the linear common-mode range of both input amplifiers. Both input amplifiers are saturated to nearly the same output voltage limit; therefore, the difference voltage measured by the output amplifier is near zero. The output of the INA114 is near 0V even though both inputs are overloaded.